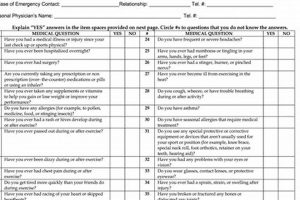
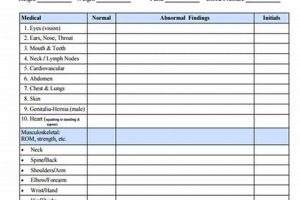
The medical evaluation required for student-athletes participating in college sports under the National Collegiate Athletic Association’s jurisdiction involves a comprehensive assessment of their health status. This typically includes a review of medical history, a physical examination, and may encompass additional screenings or tests as deemed necessary by medical professionals. For instance, cardiovascular screening and orthopedic evaluations are often incorporated. The documentation of this evaluation process serves as a record of the athlete’s health and fitness to participate in demanding athletic activities.
This process is crucial for safeguarding student-athlete well-being. It helps identify pre-existing conditions that might pose risks during intense physical activity and allows for appropriate medical interventions or modifications to training regimens. Early detection and management of health concerns can prevent serious complications and ensure a safer athletic experience. Furthermore, these evaluations facilitate compliance with NCAA regulations designed to protect student-athletes and maintain a level playing field. Historically, these protocols have evolved alongside advancements in sports medicine and a growing understanding of the unique health needs of competitive athletes.
This foundational understanding of the athlete evaluation process is essential for exploring related topics such as specific NCAA medical requirements, best practices for pre-participation screenings, and the role of sports medicine professionals in collegiate athletics. These interconnected aspects will be further examined in the following sections.
Successfully completing the required medical evaluation is a crucial step for any aspiring collegiate athlete. The following tips offer guidance for navigating this process efficiently and effectively.
Tip 1: Schedule the evaluation well in advance of the intended participation date. This allows ample time to address any potential health concerns that may arise during the examination.
Tip 2: Compile a comprehensive medical history, including any prior injuries, illnesses, or surgeries. Accurate and detailed information facilitates a thorough evaluation by medical professionals.
Tip 3: Be forthcoming with medical personnel about any current health concerns or symptoms. Open communication ensures appropriate assessment and management of potential health risks.
Tip 4: Ensure all required documentation, such as immunization records, is readily available. Organized documentation streamlines the evaluation process and avoids delays.
Tip 5: Follow all instructions provided by medical professionals regarding any necessary follow-up appointments or testing. Adherence to medical recommendations is vital for ensuring athlete health and safety.
Tip 6: Understand the specific requirements of the sport and institution in which participation is sought. Requirements can vary, so researching beforehand is essential.
Tip 7: Maintain open communication with coaches and athletic trainers regarding any health-related matters. A collaborative approach ensures appropriate support and management of any ongoing health concerns.
Adhering to these recommendations contributes significantly to a smooth and efficient evaluation process, allowing prospective athletes to focus on their athletic pursuits with the assurance that their health and well-being are prioritized.
By understanding the importance of these evaluations and following these practical tips, aspiring collegiate athletes can successfully navigate this crucial step towards participation in college sports. This preparation sets the stage for a safe and fulfilling athletic experience at the collegiate level.
1. Medical History
A comprehensive medical history forms a cornerstone of the NCAA athlete evaluation process. It provides crucial context for medical professionals, informing decisions regarding an athlete’s readiness for participation in collegiate sports. This detailed record of past health issues allows for identification of potential risk factors and facilitates appropriate medical management.
- Prior Injuries:
Documentation of previous injuries, including concussions, fractures, and sprains, is essential. For example, a history of multiple ankle sprains might indicate a need for preventative measures like ankle bracing or specific training exercises. Understanding prior injuries allows medical staff to assess potential vulnerabilities and tailor training programs accordingly, minimizing the risk of re-injury.
- Pre-existing Medical Conditions:
Conditions such as asthma, diabetes, or heart conditions require careful consideration. A student-athlete with asthma, for instance, might require an individualized asthma action plan and readily available medication during practices and competitions. Accurate reporting of pre-existing conditions ensures appropriate medical supervision and management, enabling safe participation in rigorous athletic activities.
- Surgeries and Hospitalizations:
Past surgeries or hospitalizations, even seemingly minor ones, offer valuable insights into an athlete’s health trajectory. A prior appendectomy, for example, might require specific considerations during physical examinations. This information contributes to a more complete understanding of an athlete’s overall health and resilience.
- Medications and Allergies:
Listing current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as well as any known allergies, is crucial. For instance, awareness of a medication allergy allows medical staff to avoid prescribing contraindicated substances. This detailed information is essential for preventing adverse reactions and ensuring the athlete’s safety.
These components of the medical history, when combined with the other elements of the athlete evaluation, provide a holistic view of the athlete’s health status. This comprehensive approach is integral to promoting safe and successful participation in collegiate athletics. By thoroughly evaluating an athlete’s medical background, potential risks can be mitigated, and appropriate medical support can be provided, ultimately contributing to a positive and healthy athletic experience.
2. Physical Examination
The physical examination constitutes a critical component of the NCAA athlete medical evaluation, directly informing the completion of the required documentation. This hands-on assessment provides real-time insights into an athlete’s current physical state, complementing the information gleaned from the medical history. It serves as a crucial bridge between past medical experiences and present health status, enabling medical professionals to identify potential risks and make informed decisions regarding participation eligibility. For example, an examination might reveal limited range of motion in a joint, suggesting a previous injury not fully disclosed in the medical history, prompting further investigation and potentially influencing training regimens.
Specific areas of focus during the physical examination often include cardiovascular health, pulmonary function, musculoskeletal integrity, and neurological assessment. Auscultation of the heart and lungs helps identify potential cardiac or respiratory issues. Evaluation of joint stability, flexibility, and strength provides insights into musculoskeletal health and potential vulnerabilities. Neurological assessments may include reflex testing and evaluation of balance and coordination. These comprehensive assessments contribute crucial data points to the overall evaluation, informing decisions related to sport-specific participation clearances. For instance, an athlete demonstrating instability in a knee joint might require further orthopedic evaluation before being cleared for high-impact sports.
In summary, the physical examination provides essential objective data that, in conjunction with the medical history, informs the completion of the necessary medical documentation. This process ensures a thorough evaluation of the athlete’s health and fitness for participation, contributing significantly to risk mitigation and the promotion of athlete well-being within the demanding context of collegiate sports. Understanding the integral role of the physical examination within the broader medical evaluation process reinforces the NCAA’s commitment to athlete safety and responsible participation in intercollegiate athletics.
3. Cardiovascular Screening
Cardiovascular screening represents a crucial component of the NCAA’s athlete medical evaluation process, directly contributing to the completion of the required documentation. This screening aims to identify potential underlying cardiac conditions that could pose risks to athletes participating in strenuous collegiate sports. Early detection of such conditions is paramount for implementing appropriate preventative measures and ensuring athlete safety. This proactive approach underscores the NCAA’s commitment to athlete well-being and responsible participation in competitive athletics.
- Family History:
A detailed family history of cardiac conditions, such as sudden cardiac death, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, or long QT syndrome, provides crucial information. For example, a family history of sudden cardiac death in young relatives might necessitate further specialized cardiac testing, such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) or echocardiogram. This information allows medical professionals to assess inherited risk factors and tailor screening protocols accordingly.
- Physical Examination Findings:
Specific findings during the physical examination, such as abnormal heart sounds (murmurs) or irregular heart rhythms, can raise red flags warranting further investigation. A newly detected heart murmur, for instance, might prompt a referral to a cardiologist for further evaluation and diagnostic testing. Integrating physical examination findings with other screening components allows for a more comprehensive assessment of cardiovascular health.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG):
An ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart, providing insights into its rhythm and function. This non-invasive test can detect a range of cardiac abnormalities, including arrhythmias and conduction defects. ECG findings might indicate the need for further specialized testing or lifestyle modifications to mitigate potential risks.
- Echocardiogram:
An echocardiogram uses ultrasound technology to create images of the heart, assessing its structure and function. This diagnostic test can detect structural abnormalities, such as valve defects or thickened heart muscle (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy). Echocardiography plays a pivotal role in identifying conditions that might predispose athletes to adverse cardiovascular events during intense physical activity.
These components of cardiovascular screening contribute significantly to the comprehensive medical evaluation required for NCAA athletes. By identifying potential cardiac risks early, appropriate medical interventions can be implemented, ranging from lifestyle modifications to specialized treatment plans. This proactive approach reinforces the NCAA’s commitment to athlete safety and responsible participation in intercollegiate sports. Thorough cardiovascular screening, in conjunction with other elements of the medical evaluation, ensures that athletes can pursue their athletic endeavors with minimized cardiovascular risks and optimized health outcomes.
4. Orthopedic Assessment
Orthopedic assessment constitutes a critical component of the NCAA physical form and evaluation process. This assessment focuses on the musculoskeletal system, evaluating joint stability, range of motion, strength, and overall functional capacity. Its purpose lies in identifying pre-existing or potential orthopedic conditions that could affect an athlete’s ability to safely participate in collegiate sports. This proactive approach helps mitigate the risk of injuries and ensures athlete well-being within the demanding context of intercollegiate athletics. Cause and effect relationships are central to this assessment, as prior injuries or underlying conditions can significantly influence current musculoskeletal health and future injury risk. For instance, a previous anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear might predispose an athlete to recurrent instability or other knee injuries, necessitating specific preventative measures or rehabilitation protocols.
The importance of orthopedic assessment as a component of the NCAA physical form lies in its ability to identify potential vulnerabilities and inform appropriate interventions. A thorough evaluation can reveal subtle biomechanical imbalances, joint laxity, or muscle weakness that might not be apparent during routine activities but could manifest as significant problems under the stresses of competitive sports. For example, limited shoulder range of motion in a baseball pitcher might indicate underlying rotator cuff dysfunction, increasing the risk of shoulder injuries if not addressed. Practical application of this understanding includes tailoring training programs, implementing preventative exercises, and recommending bracing or other supportive measures. These interventions aim to optimize musculoskeletal health and minimize injury risk, contributing significantly to an athlete’s long-term athletic performance and overall well-being. In cases of identified pre-existing conditions, the orthopedic assessment informs decisions regarding necessary treatment, rehabilitation, and return-to-play protocols.
In summary, the orthopedic assessment serves as a crucial element of the NCAA physical form, providing valuable insights into an athlete’s musculoskeletal health. By identifying potential vulnerabilities and informing appropriate interventions, this assessment plays a pivotal role in mitigating injury risk and promoting athlete well-being. Integrating orthopedic assessment within the broader medical evaluation process underscores the NCAA’s commitment to athlete safety and responsible participation in collegiate athletics. This proactive approach benefits both individual athletes and the overall integrity of intercollegiate sports by minimizing the impact of preventable injuries and fostering a culture of health and safety.
5. Clearance for Participation
Clearance for participation represents the culmination of the NCAA medical evaluation process, signifying an athlete’s medical eligibility to engage in collegiate sports. This designation, directly linked to the completion and review of the required medical documentation (often referred to as the “NCAA physical form”), hinges on a comprehensive assessment of an athlete’s health status. It serves as a critical safeguard, ensuring that participation in demanding athletic activities occurs within a framework of minimized health risks and prioritized athlete well-being.
- Comprehensive Review of Medical Information:
Clearance decisions rely on a thorough review of all compiled medical information, including the medical history, physical examination findings, and results of any specialized testing, such as cardiovascular screening or orthopedic assessments. For example, an athlete with a history of concussions might require additional neurological evaluation before clearance is granted. This comprehensive review ensures that all potential health concerns are identified and addressed before participation is permitted.
- Multidisciplinary Collaboration:
The clearance process often involves collaboration among various medical professionals, including physicians, athletic trainers, and specialists, such as cardiologists or orthopedists. This multidisciplinary approach ensures a holistic evaluation of the athlete’s health, considering diverse perspectives and expertise. For instance, an athlete with a complex medical history might require input from multiple specialists to determine appropriate clearance guidelines.
- Individualized Approach:
Clearance decisions are made on an individual basis, recognizing the unique health profiles and needs of each athlete. Factors such as pre-existing medical conditions, prior injuries, and sport-specific demands are considered. This individualized approach ensures that clearance guidelines align with the athlete’s specific circumstances, optimizing safety and minimizing potential risks. An athlete with a history of asthma, for example, might receive clearance contingent on having an asthma action plan in place and readily available medication.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Re-evaluation:
Clearance for participation is not necessarily a static designation. Ongoing monitoring of an athlete’s health status and periodic re-evaluations might be necessary, especially in cases of pre-existing conditions or previous injuries. This dynamic approach ensures that clearance remains aligned with the athlete’s evolving health needs and minimizes the risk of complications arising during the course of athletic participation. An athlete recovering from a significant injury, for instance, might undergo periodic re-evaluations to track progress and determine readiness for full participation.
These facets of clearance for participation demonstrate the intricate connection between this crucial designation and the comprehensive information gathered through the NCAA medical evaluation process, culminating in what is often known as the “NCAA physical form”. This interconnectedness underscores the NCAA’s commitment to athlete safety and responsible participation in collegiate sports. By prioritizing thorough evaluation and individualized clearance decisions, the NCAA strives to create an environment where athletes can pursue their athletic endeavors within a framework of minimized health risks and optimized well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the medical evaluation process required for participation in NCAA athletics.
Question 1: What constitutes the NCAA medical evaluation, and what documents are involved?
The evaluation typically involves a medical history review, physical examination, and potentially additional screenings like cardiovascular and orthopedic assessments. The documentation of this process, often referred to as the medical eligibility form, serves as a record of the athlete’s health status.
Question 2: How often is a medical evaluation required for NCAA athletes?
Generally, a comprehensive evaluation is required upon entry into an NCAA athletics program. Subsequent evaluations or specific screenings might be necessary depending on the sport, institutional policies, or the athlete’s individual health circumstances.
Question 3: What are the implications for an athlete who fails to complete the required medical evaluation?
Failure to complete the required evaluation typically renders an athlete ineligible for participation in NCAA-sanctioned competition. Compliance with these requirements is mandatory to ensure athlete safety and maintain a level playing field.
Question 4: Can pre-existing medical conditions disqualify an athlete from NCAA participation?
Not necessarily. A pre-existing medical condition might necessitate specific management strategies or modifications to training regimens, but it does not automatically disqualify an athlete. The primary focus is on ensuring safe participation while managing any health concerns effectively.
Question 5: What role do athletic trainers play in the medical evaluation process?
Athletic trainers play a vital role in coordinating and facilitating the medical evaluation process. They often serve as a liaison between athletes, physicians, and other healthcare professionals, ensuring that all necessary steps are completed and information is communicated effectively. They also contribute to injury prevention and ongoing health management throughout the athlete’s collegiate career.
Question 6: Where can further information about NCAA medical eligibility requirements be found?
Specific requirements and further details can be found on the official NCAA website and through respective institutional athletic departments. Consulting these resources provides the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Understanding the medical evaluation process is essential for both prospective and current NCAA athletes. Ensuring compliance with these requirements promotes athlete health, safety, and eligibility for competition.
The next section delves further into specific NCAA medical requirements and best practices for pre-participation screenings.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of collegiate athletics requires a thorough understanding of the medical evaluation process. This article has explored the essential components of this process, encompassing the medical history, physical examination, cardiovascular screening, orthopedic assessment, and the ultimate clearance for participation. Each element contributes crucial information, informing decisions regarding an athlete’s readiness for the demands of collegiate-level competition. The significance of accurate documentation throughout this process cannot be overstated, as it serves as a cornerstone of athlete health management and risk mitigation.
Prioritizing athlete health and safety remains paramount within the demanding environment of collegiate sports. Adherence to established medical evaluation protocols, coupled with ongoing health monitoring, contributes significantly to a safer and more productive athletic experience. The rigorous demands placed upon collegiate athletes necessitate a proactive and comprehensive approach to health management, ensuring that participation occurs within a framework of minimized risks and optimized well-being. The future of collegiate athletics relies on continued advancements in sports medicine and a steadfast commitment to athlete health and safety.