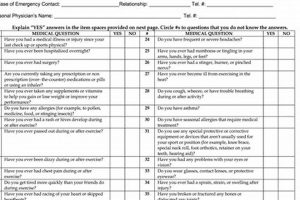
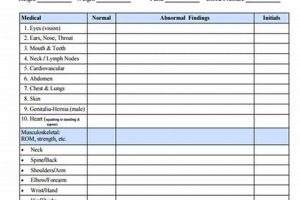
Student-athletes participating in collegiate athletics under the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) must meet specific medical requirements. These requirements are documented through standardized medical evaluations and paperwork, ensuring participants are physically prepared for the demands of their chosen sport. These evaluations typically encompass a comprehensive medical history, a physical examination, and may include additional assessments like cardiac screening or orthopedic evaluations depending on the sport and institutional requirements. For instance, a prospective basketball player may undergo a more stringent evaluation than a golfer.
These mandatory health assessments play a vital role in protecting student-athlete well-being. They allow medical professionals to identify potential health concerns that could pose a risk during competition or training. Early detection of underlying conditions can prevent serious injuries or health complications, contributing to a safer athletic environment. Furthermore, these standardized procedures ensure a level playing field by verifying that all participants meet minimum health standards. Over time, these evaluations have become increasingly sophisticated, reflecting advancements in sports medicine and a greater understanding of the unique physical demands of different sports.
The following sections will delve deeper into specific aspects of the medical clearance process, including required components of the evaluation, institutional variations, and resources available to student-athletes navigating these requirements. Additionally, the information provided will address common questions and concerns related to medical eligibility for NCAA participation.
Successfully completing the required medical evaluations is crucial for NCAA eligibility. These tips provide guidance for student-athletes preparing for this process.
Tip 1: Schedule Evaluations Early: Don’t wait until the last minute. Scheduling medical appointments well in advance of deadlines allows ample time to address any potential issues that may arise.
Tip 2: Gather Medical History: Compile a comprehensive medical history, including prior injuries, illnesses, and any ongoing medical conditions. This information streamlines the evaluation process and ensures accurate assessments.
Tip 3: Communicate with Medical Professionals: Open communication with physicians and athletic trainers is essential. Disclose all relevant medical information and ask questions to ensure a thorough understanding of the process and any specific requirements.
Tip 4: Maintain Current Immunization Records: Ensure all required immunizations are up-to-date and documented appropriately. Check with the specific institution for required vaccinations.
Tip 5: Follow Instructions Carefully: Adhere to all instructions provided by medical staff and the institution regarding required forms and procedures. This ensures compliance and avoids delays in the clearance process.
Tip 6: Understand Institutional Requirements: NCAA requirements provide a framework, but specific institutions may have additional policies. Consulting with the athletic department ensures compliance with all applicable rules and guidelines.
Tip 7: Be Proactive: Take ownership of the process by actively seeking information and addressing any potential concerns promptly. This proactive approach contributes to a smooth and efficient clearance experience.
By following these guidelines, prospective student-athletes can navigate the medical clearance process efficiently and ensure they meet all necessary requirements for NCAA participation.
The next section will provide further resources and contact information for additional assistance with NCAA medical eligibility.
1. Medical History
A comprehensive medical history forms the cornerstone of the NCAA’s pre-participation physical evaluation process. This detailed record of past and present health conditions provides crucial insights for medical professionals assessing an athlete’s readiness for collegiate-level competition. A thorough medical history allows for informed decisions regarding necessary additional screenings, individualized training plans, and potential modifications to participation. It plays a crucial role in mitigating risks and ensuring student-athlete well-being.
- Previous Injuries:
Documentation of prior injuries, including concussions, fractures, and sprains, is essential. For instance, a history of multiple ankle sprains might necessitate preventative measures like ankle bracing or specific strengthening exercises. This information informs athletic trainers and physicians about potential vulnerabilities and helps develop strategies to minimize re-injury risk.
- Pre-existing Medical Conditions:
Disclosure of conditions like asthma, diabetes, or heart conditions is vital. A student-athlete with asthma, for example, might require readily available inhalers and a modified training regimen. Accurate reporting of these conditions allows medical staff to develop appropriate management plans and ensure the athlete can participate safely and effectively.
- Surgeries and Hospitalizations:
Providing details of past surgeries or hospitalizations, including dates and reasons, offers valuable context for understanding current health status. A history of knee surgery, for instance, might warrant further orthopedic evaluation before clearance for participation. This information can also guide rehabilitation protocols and inform training decisions.
- Medications and Allergies:
Listing current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as well as any known allergies, is crucial. For instance, awareness of a student-athlete’s allergy to certain medications ensures appropriate alternatives are available in case of an emergency. This information is vital for preventing adverse reactions and maintaining athlete safety.
These facets of the medical history, when thoroughly documented and reviewed, provide a holistic view of a student-athlete’s health trajectory. This comprehensive understanding empowers medical professionals to make informed decisions regarding participation clearance, necessary accommodations, and appropriate medical care. Ultimately, the medical history contributes significantly to athlete safety and well-being within the demanding context of NCAA athletics.
2. Physical Examination
The physical examination constitutes a critical component of the NCAA’s pre-participation evaluation, directly informing decisions regarding medical eligibility for collegiate sports. This hands-on assessment, conducted by a qualified medical professional, provides objective data about a student-athlete’s current physical condition. It complements the medical history, offering a real-time snapshot of the individual’s health status. For instance, during a physical examination, a physician might identify limited range of motion in a joint, prompting further investigation and potentially influencing sport-specific training recommendations. The examination serves as a crucial link between documented medical history and the practical demands of athletic participation, facilitating informed decisions about safe engagement in collegiate sports.
Several key areas are typically assessed during the physical examination. Cardiovascular health is evaluated through measures like blood pressure and heart rate. Pulmonary function is assessed through auscultation of the lungs. Musculoskeletal integrity is examined, including range of motion, joint stability, and strength. Neurological function is also screened through assessments of reflexes, balance, and coordination. For example, an athlete demonstrating instability in a knee joint during the examination might require further orthopedic evaluation to determine the extent of the instability and potential implications for participation in a high-impact sport like basketball or soccer. These assessments provide crucial information to determine an athlete’s preparedness for the physical demands of their chosen sport.
Successful completion of the physical examination demonstrates an athlete’s current physical capacity to engage in collegiate-level competition. It provides crucial insights for medical professionals to identify potential risks and recommend appropriate interventions. The examination, in conjunction with the medical history, forms the basis for informed decision-making regarding participation clearance. Challenges can arise if underlying conditions are not detected during the examination. Therefore, thoroughness and accuracy during this process are paramount for safeguarding student-athlete health and well-being. This underscores the crucial role of the physical examination in upholding the NCAA’s commitment to athlete safety and fair play within collegiate sports.
3. Cardiac Screening
Cardiac screening plays a vital role within NCAA pre-participation physical evaluations, serving as a critical safeguard against potentially life-threatening heart conditions in student-athletes. The intense physical demands of collegiate athletics can exacerbate underlying cardiac issues, making early detection through comprehensive screening essential. This process aims to identify conditions such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes. HCM, often asymptomatic, can cause the heart to thicken, making it harder to pump blood efficiently. Strenuous exercise can trigger fatal arrhythmias in individuals with undiagnosed HCM. Incorporating cardiac screening into required physicals allows for early identification and appropriate medical management, significantly reducing the risk of tragic outcomes during athletic competition. For example, mandatory EKGs as part of the screening process can detect abnormalities suggestive of HCM or other heart conditions, prompting further evaluation and specialized care if necessary.
The practical significance of cardiac screening extends beyond identifying potentially fatal conditions. It also allows for the detection and management of less immediately life-threatening but still impactful cardiac issues. Conditions like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, which can cause rapid heart rates, or congenital heart defects may not pose an immediate threat but can significantly impact an athlete’s performance and long-term health. Early identification through screening enables appropriate medical intervention, including medication or lifestyle modifications, ensuring athletes can participate safely and optimize their athletic potential. This proactive approach benefits not only the individual athlete but also the integrity of collegiate sports, as it promotes a healthy and safe competitive environment. Moreover, the data collected through cardiac screening contributes to ongoing research in sports cardiology, furthering understanding and improving preventative strategies for future generations of athletes.
Integrating cardiac screening into NCAA physical forms represents a crucial investment in student-athlete well-being. While the process may present challenges, such as cost and access to specialized testing, its importance remains paramount. Early detection and management of cardiac conditions, from life-threatening to performance-limiting, are crucial for ensuring safe participation and promoting long-term cardiovascular health. The ongoing refinement of screening protocols, informed by research and clinical experience, strengthens the NCAA’s commitment to athlete safety and underscores the critical link between cardiac health and participation in collegiate sports.
4. Orthopedic Assessment
Orthopedic assessment within NCAA pre-participation physical evaluations plays a crucial role in identifying existing musculoskeletal conditions and mitigating potential risks associated with athletic participation. This assessment focuses on evaluating the structural and functional integrity of the musculoskeletal system, encompassing bones, joints, ligaments, muscles, and tendons. Its inclusion in NCAA requirements reflects a proactive approach to injury prevention and athlete well-being. By identifying pre-existing conditions or vulnerabilities, medical professionals can implement preventative strategies and guide appropriate medical care, ultimately promoting safe and successful participation in collegiate sports.
- Joint Stability:
Assessing joint stability is essential for identifying potential vulnerabilities to injury. Laxity in ligaments, for example, can increase the risk of sprains or dislocations, particularly in high-impact sports like basketball or soccer. Evaluating joint stability during the orthopedic assessment allows for targeted interventions, such as strengthening exercises or bracing, to minimize risk and promote joint integrity.
- Range of Motion:
Evaluating range of motion in various joints provides insights into flexibility and identifies potential limitations that may hinder athletic performance or predispose an athlete to injury. Restricted range of motion in the shoulder, for instance, could impact a baseball pitcher’s ability to throw effectively and increase the risk of shoulder injuries. Addressing limitations through targeted stretching or physical therapy can improve performance and reduce injury risk.
- Previous Injuries:
Inquiry about previous musculoskeletal injuries, such as fractures, sprains, or dislocations, is crucial during the orthopedic assessment. Understanding the nature and extent of past injuries, along with any residual effects, informs decisions regarding return-to-play protocols and necessary precautions. For example, a history of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear might necessitate specific strengthening and stability exercises before full participation in a sport like soccer or basketball can be permitted.
- Functional Movement:
Observing an athlete’s functional movement patterns provides insights into how they utilize their musculoskeletal system during sport-specific activities. Assessing movements like running, jumping, or throwing can reveal biomechanical deficiencies that may contribute to injury. For instance, an athlete demonstrating improper landing mechanics during a jump might be at increased risk for knee injuries. Addressing these deficiencies through targeted training and corrective exercises enhances performance and reduces injury risk.
These facets of the orthopedic assessment provide a comprehensive evaluation of the musculoskeletal system, informing decisions regarding an athlete’s readiness for collegiate-level competition. By identifying potential vulnerabilities and addressing them proactively, the orthopedic assessment plays a vital role in injury prevention and contributes significantly to athlete safety and well-being within the NCAA’s framework for collegiate sports participation.
5. Immunization Records
Immunization records constitute a crucial component of NCAA physical forms for sports, directly impacting student-athlete eligibility and overall team health. Maintaining updated immunization records demonstrates compliance with NCAA health and safety protocols, mitigating the risk of communicable diseases within the collegiate athletic environment. This requirement reflects the NCAA’s commitment to athlete well-being and acknowledges the potential for rapid disease transmission within close-contact sports settings. Failure to provide complete and up-to-date immunization records can result in ineligibility for participation, impacting both individual athletes and team dynamics. For example, outbreaks of measles or mumps within a team can disrupt training schedules, postpone games, and compromise athletic performance. Therefore, adherence to immunization requirements serves as a critical preventative measure, safeguarding individual and collective health within collegiate athletic programs.
The practical significance of immunization records extends beyond immediate disease prevention. These records provide valuable information for medical professionals managing athlete health, facilitating informed decision-making regarding potential exposure risks and necessary preventative measures. In the event of an outbreak, immunization records enable rapid identification of susceptible individuals, allowing for targeted interventions such as booster shots or prophylactic medications. This proactive approach minimizes the spread of infection and protects vulnerable individuals within the team. Furthermore, maintaining accurate immunization records contributes to a broader public health effort, reducing the incidence of preventable diseases within the larger community. This collaborative approach benefits not only collegiate athletes but also the general population, highlighting the interconnectedness of individual and public health within the context of NCAA athletics.
In summary, immunization records play a fundamental role in NCAA physical forms, serving as a critical safeguard against communicable diseases and promoting a healthy and safe environment for student-athletes. Maintaining updated records is not merely a procedural requirement but a practical necessity with far-reaching implications for individual and team health. Challenges related to maintaining accurate records, such as access to healthcare and varying immunization schedules, underscore the importance of clear communication and collaboration between athletes, medical professionals, and athletic departments. Addressing these challenges reinforces the NCAA’s commitment to athlete well-being and strengthens its role in promoting public health within the context of collegiate sports.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding medical eligibility requirements for NCAA participation. Understanding these aspects is crucial for prospective student-athletes navigating the process.
Question 1: What is the typical timeframe for completing the required medical evaluations?
Completion timelines vary based on individual circumstances and institutional requirements. Generally, initiating the process several months prior to the intended start of athletic participation is recommended. This allows ample time to address any potential medical concerns that may arise.
Question 2: Are there specific medical conditions that automatically disqualify an individual from NCAA participation?
While certain conditions may require additional evaluation and potential modifications to participation, automatic disqualification is rare. Medical professionals assess each case individually, considering the specific condition, its severity, and the demands of the chosen sport.
Question 3: Who is responsible for the cost of the required medical evaluations?
Responsibility for costs varies. Some institutions cover expenses associated with pre-participation physicals, while others require student-athletes to assume responsibility. Clarifying financial obligations with the institution’s athletic department is essential.
Question 4: What happens if a medical issue is discovered during the evaluation process?
If a medical issue is identified, appropriate medical follow-up is arranged. Depending on the nature of the issue, this may involve further specialist consultations, additional testing, or specific treatment plans. The athlete’s participation status is determined based on medical recommendations and institutional policies.
Question 5: Can a student-athlete seek a second medical opinion if they disagree with the initial evaluation?
Seeking a second medical opinion is generally permissible. However, it is essential to ensure the second opinion is obtained from a qualified medical professional specializing in relevant areas of sports medicine. Institutional policies regarding second opinions should be reviewed.
Question 6: Where can additional information regarding NCAA medical eligibility requirements be found?
The NCAA website provides comprehensive information regarding medical eligibility requirements. Consulting with the institution’s athletic department or compliance office can also provide valuable guidance specific to institutional policies and procedures.
Understanding these frequently asked questions provides a foundation for successfully navigating the NCAA medical eligibility process. Prospective student-athletes are encouraged to proactively seek information and address any individual concerns to ensure a smooth and efficient clearance experience.
For further assistance and specific inquiries, please consult the resources provided in the following section.
Conclusion
Navigating the requirements documented through NCAA-mandated medical evaluations is crucial for prospective student-athletes. This comprehensive process, encompassing medical history reviews, physical examinations, cardiac screenings, orthopedic assessments, and immunization verification, prioritizes athlete well-being and establishes a foundation for safe participation in collegiate sports. Understanding the components of these evaluations, along with institutional variations and available resources, empowers student-athletes to successfully navigate the eligibility process.
Stringent adherence to these medical standards underscores the NCAA’s commitment to fostering a safe and equitable competitive landscape. The evolving nature of sports medicine and ongoing research continually refine these protocols, ensuring alignment with best practices and promoting the long-term health and safety of all collegiate athletes. Continued emphasis on preventative measures, early detection of potential health concerns, and comprehensive medical care contributes to a more robust and sustainable future for collegiate athletics. Diligence in meeting these requirements not only safeguards individual athletes but also reinforces the integrity and longevity of college sports.