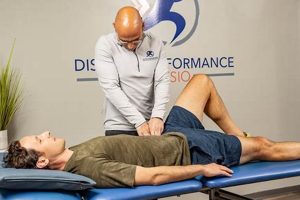
Collaborative rehabilitation employing evidence-based techniques to restore function, reduce pain, and improve mobility often involves a team of skilled professionals working together. This approach commonly addresses conditions resulting from injury, illness, or surgery, utilizing personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs and goals. For instance, a patient recovering from a knee replacement might receive targeted exercises, manual therapy, and modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation.
Restoring patients’ physical well-being contributes significantly to overall health and quality of life. This process empowers individuals to regain independence, participate in daily activities, and return to work or leisure pursuits. Historically, the field has evolved from rudimentary practices to a sophisticated science incorporating advanced technology and research-driven methodologies. This progress ensures patients receive optimal care based on the latest scientific understanding.
The following sections will delve deeper into specific treatment modalities, the role of various healthcare professionals in this collaborative approach, and the benefits patients can expect from comprehensive rehabilitation programs.
Tips for Effective Rehabilitation
Successful rehabilitation requires active patient participation and adherence to prescribed treatment plans. The following tips offer guidance for maximizing recovery potential.
Tip 1: Consistent Adherence to Exercise Programs: Consistent engagement with prescribed exercises is fundamental to restoring strength, flexibility, and function. Regular practice reinforces progress and facilitates a timely recovery.
Tip 2: Open Communication with Therapists: Maintaining open communication with healthcare providers is crucial. Reporting any pain, discomfort, or changes in condition allows therapists to adjust treatment plans accordingly, optimizing outcomes.
Tip 3: Proper Warm-up and Cool-down Routines: Preparing the body for activity with appropriate warm-up exercises and allowing for a gradual cool-down period minimizes the risk of injury and promotes muscle recovery.
Tip 4: Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle: Supporting the rehabilitation process requires embracing a healthy lifestyle that includes proper nutrition, adequate rest, and stress management techniques. These factors play a vital role in overall healing and well-being.
Tip 5: Setting Realistic Goals and Expectations: Establishing achievable goals provides motivation and a sense of accomplishment throughout the rehabilitation journey. Working collaboratively with therapists to set realistic expectations promotes a positive and productive experience.
Tip 6: Gradual Progression of Activities: Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of activities prevents setbacks and allows the body to adapt progressively to increasing demands. This approach minimizes the risk of re-injury and facilitates a safe return to normal function.
Tip 7: Long-Term Commitment to Wellness: Continuing to prioritize physical well-being even after formal therapy concludes is essential for maintaining long-term health and preventing recurrence. This might involve ongoing exercise, regular stretching, and continued attention to proper body mechanics.
By following these recommendations, patients can optimize their recovery potential and achieve lasting improvements in physical function, pain management, and overall quality of life.
The concluding section will summarize the key benefits of collaborative rehabilitation and emphasize the importance of a patient-centered approach.
1. Collaborative Care
Collaborative care forms the cornerstone of effective rehabilitation, optimizing patient outcomes through interdisciplinary teamwork. This approach leverages the expertise of multiple healthcare professionals, ensuring comprehensive and individualized treatment plans.
- Interprofessional Communication:
Effective communication among healthcare providers, including physicians, therapists, and other specialists, is essential for coordinated care. Regular communication ensures all team members are aligned on the patient’s progress, treatment goals, and any necessary adjustments to the plan. For instance, a therapist might consult with a physician regarding a patient’s medication management to optimize pain control during therapy sessions. This facilitates a unified approach, minimizing the risk of conflicting recommendations and maximizing the potential for positive outcomes.
- Shared Decision-Making:
Patients are actively involved in the decision-making process, contributing their preferences and goals to the development of the treatment plan. This patient-centered approach empowers individuals to take ownership of their recovery journey. For example, a patient might express a preference for certain types of exercises or modalities, which the team can then incorporate into the plan when appropriate. This shared decision-making fosters a sense of collaboration and improves adherence to the prescribed treatment.
- Coordinated Treatment Strategies:
Different healthcare professionals contribute their specialized skills to create a comprehensive treatment strategy. A physical therapist might focus on restoring mobility and function, while an occupational therapist addresses activities of daily living. A pain management specialist might contribute strategies for pain control, and a psychologist might provide support for emotional well-being. This integrated approach ensures all aspects of the patient’s condition are addressed, optimizing overall recovery.
- Continuity of Care:
Consistent communication and coordination across different healthcare settings ensure a seamless transition throughout the rehabilitation process. For example, clear communication between the hospital, rehabilitation facility, and outpatient clinic ensures continuity in the treatment plan and prevents disruptions in care. This streamlined approach promotes a smooth recovery and reduces the likelihood of setbacks.
These interconnected facets of collaborative care contribute significantly to the effectiveness of rehabilitation programs. By fostering a team-based approach, empowering patient participation, and ensuring seamless transitions, collaborative care maximizes the potential for positive patient outcomes and long-term well-being.
2. Personalized Treatment
Effective rehabilitation hinges on personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs and goals. This approach recognizes that each patient presents with a unique set of circumstances, requiring a customized strategy to optimize recovery. Within the context of collaborative rehabilitation, personalized treatment ensures that interventions are specifically designed to address the individual’s condition, functional limitations, and personal objectives.
- Individualized Assessment:
Thorough assessments form the foundation of personalized treatment. These evaluations encompass a comprehensive review of the patient’s medical history, current condition, functional limitations, and lifestyle factors. For instance, a patient recovering from a stroke might undergo assessments of motor function, balance, and cognitive abilities. This detailed information informs the development of a treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs and rehabilitation goals.
- Targeted Interventions:
Based on the individualized assessment, targeted interventions are selected and implemented. These interventions might include therapeutic exercises, manual therapy, modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation, and assistive devices. For example, a patient with lower back pain might receive manual therapy to address joint restrictions, combined with specific exercises to strengthen core muscles. This targeted approach ensures that the interventions are directly relevant to the patient’s condition and functional limitations.
- Goal-Oriented Approach:
Personalized treatment plans are inherently goal-oriented, focusing on achieving specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives. These goals are established collaboratively with the patient, ensuring they align with the individual’s priorities and desired outcomes. For example, a patient recovering from a knee injury might set a goal of returning to recreational sports within a specific timeframe. This collaborative approach fosters motivation and provides a clear roadmap for the rehabilitation process.
- Adaptive Progression:
Personalized treatment plans are not static; they are dynamically adjusted based on the patient’s progress and response to interventions. Regular monitoring and reassessment allow therapists to modify the plan as needed, ensuring it remains relevant and effective. For instance, if a patient experiences pain or plateaus in progress, the therapist can adjust the intensity, frequency, or type of interventions to optimize recovery. This adaptive approach ensures that the treatment plan remains tailored to the patient’s evolving needs throughout the rehabilitation journey.
These interconnected facets of personalized treatment contribute significantly to successful outcomes in collaborative rehabilitation. By tailoring interventions to individual needs, establishing meaningful goals, and adapting the plan based on progress, personalized treatment maximizes the potential for functional restoration, pain reduction, and improved quality of life.
3. Restoring Function
Restoring functional capacity is a central objective of collaborative, evidence-based rehabilitation. Functional limitations, arising from injury, illness, or surgery, can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities and participate in meaningful life roles. Collaborative rehabilitation aims to address these limitations through targeted interventions designed to improve mobility, strength, coordination, and overall physical performance. For instance, a patient recovering from a rotator cuff tear might experience difficulty reaching overhead. Targeted exercises and manual therapy can help restore shoulder range of motion and strength, enabling the individual to regain the ability to perform activities such as dressing and reaching for objects.
The process of restoring function requires a comprehensive understanding of the underlying impairment and its impact on the individual’s functional abilities. Assessment plays a crucial role in identifying specific areas of weakness and limitation. This information informs the development of a personalized treatment plan incorporating exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities aimed at improving the affected body part’s function. In the case of a neurological condition like multiple sclerosis, functional limitations might include difficulties with balance and gait. Rehabilitation may involve balance training, gait retraining, and strengthening exercises to improve mobility and reduce the risk of falls. The practical significance of restoring function extends beyond physical capacity; it directly impacts an individual’s independence, quality of life, and ability to participate in work, social activities, and leisure pursuits.
Successful restoration of function often necessitates a multidisciplinary approach, incorporating the expertise of various healthcare professionals. Physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech-language pathologists, and other specialists may collaborate to address the multifaceted nature of functional limitations. Addressing the underlying cause of impairment, mitigating its effects, and implementing strategies to improve functional capacity are key components of this collaborative process. Challenges may include comorbidities, patient motivation, and access to resources. However, by focusing on evidence-based practices and patient-centered care, collaborative rehabilitation strives to maximize functional outcomes and empower individuals to regain independence and improve overall well-being.
4. Reducing Pain
Pain reduction represents a cornerstone of collaborative, evidence-based rehabilitation. Chronic or acute pain stemming from injury, illness, or surgery can significantly diminish quality of life, impacting physical function, sleep, emotional well-being, and overall participation in daily activities. Collaborative rehabilitation aims to alleviate pain through a multifaceted approach incorporating various evidence-based techniques. For instance, a patient experiencing lower back pain might benefit from a combination of manual therapy to address joint restrictions, therapeutic exercises to strengthen supporting musculature, and modalities like heat or ultrasound to reduce inflammation and promote tissue healing.
The relationship between pain and functional limitations is often cyclical. Pain can restrict movement and limit activity, leading to deconditioning and further exacerbating pain. Collaborative rehabilitation seeks to break this cycle by addressing both pain and functional limitations concurrently. Employing targeted interventions, clinicians aim to reduce pain, improve mobility, and restore function, facilitating a return to normal activities. Consider a patient recovering from a knee injury. Pain might limit weight-bearing and range of motion, hindering walking and other daily tasks. A comprehensive rehabilitation program incorporating pain management techniques alongside exercises to improve strength and flexibility can help restore knee function and alleviate pain, promoting a return to normal activity levels.
Effective pain management within collaborative rehabilitation requires a thorough understanding of the underlying cause of pain, individual patient factors, and available treatment options. Clinicians utilize a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches to address pain. Non-pharmacological strategies may include manual therapy, therapeutic exercise, modalities, and patient education on pain management techniques. Pharmacological interventions are used judiciously and in conjunction with other therapies to optimize pain relief and minimize reliance on medication. Addressing psychosocial factors contributing to pain, such as anxiety or depression, is also crucial for successful pain management. Integrated, patient-centered approaches incorporating these elements are essential for maximizing pain reduction, restoring function, and improving overall quality of life.
5. Improving Mobility
Enhanced mobility stands as a critical outcome within the framework of collaborative, evidence-based rehabilitation, often referred to as a key component of comprehensive physical therapy. Restrictions in mobility, arising from injury, illness, or surgery, can significantly impede an individual’s capacity to perform essential daily tasks, participate in valued activities, and maintain independence. Restoring and improving mobility represents a primary focus, employing targeted interventions to enhance joint range of motion, flexibility, strength, and overall physical function.
- Range of Motion Enhancement
Restoring optimal joint range of motion is fundamental to improving mobility. Limitations in joint movement can restrict activities such as reaching, bending, and walking. Therapeutic exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities are employed to address joint restrictions and improve flexibility. For instance, a patient with adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder) might undergo manual therapy to mobilize the shoulder joint, combined with specific exercises to improve range of motion and restore functional use of the arm.
- Gait and Balance Training
Gait and balance impairments can significantly impact mobility and increase the risk of falls. Interventions targeting gait and balance focus on improving stability, coordination, and walking efficiency. This might involve exercises to strengthen lower extremity muscles, balance training activities, and assistive devices such as canes or walkers. For example, a patient recovering from a stroke might undergo gait retraining using a treadmill and assistive devices to improve walking ability and reduce fall risk.
- Strength and Conditioning
Adequate muscle strength and endurance are essential for supporting movement and maintaining mobility. Targeted exercises are prescribed to strengthen key muscle groups, improving stability, power, and overall physical performance. A patient with osteoarthritis of the knee might benefit from strengthening exercises for the quadriceps and hamstring muscles to improve knee stability and reduce pain during movement.
- Activity Modification and Adaptation
In some cases, modifying activities or adapting the environment can significantly improve mobility and facilitate participation in daily tasks. Occupational therapists play a key role in assessing an individual’s functional abilities and recommending modifications to activities or the environment to enhance independence. This might involve using assistive devices, adapting workspaces, or modifying daily routines to minimize strain and maximize functional capacity. For example, an individual with arthritis might benefit from using adaptive equipment in the kitchen to facilitate meal preparation.
These interconnected components of mobility improvement contribute significantly to achieving positive outcomes in comprehensive physical therapy. By addressing range of motion limitations, enhancing gait and balance, improving strength and conditioning, and implementing activity modifications, therapists strive to maximize functional independence, reduce pain, and improve overall quality of life for individuals seeking enhanced mobility and overall well-being. These facets contribute directly to patient empowerment, fostering greater participation in daily life and valued activities.
6. Evidence-based techniques
Evidence-based techniques form the foundation of effective and responsible rehabilitation. These techniques represent a commitment to utilizing treatments supported by rigorous scientific research and clinical trials, ensuring interventions are both safe and effective. This dedication to evidence-based practice ensures treatment plans are grounded in the latest scientific understanding, maximizing the potential for positive patient outcomes. For example, the use of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for pain management is supported by numerous studies demonstrating its efficacy in reducing pain perception. Similarly, specific exercise protocols for conditions like low back pain are developed based on research demonstrating their effectiveness in strengthening core muscles and improving functional outcomes. This reliance on evidence-based techniques fosters trust and transparency, assuring patients that their treatment is based on the best available scientific knowledge.
Integrating evidence-based techniques within collaborative rehabilitation fosters a culture of continuous improvement and professional accountability. Clinicians stay abreast of the latest research findings, ensuring treatment approaches remain current and aligned with best practices. This commitment to ongoing learning and professional development benefits both patients and practitioners. By utilizing treatments supported by evidence, therapists can confidently recommend interventions with a proven track record of success. Moreover, evidence-based practice promotes critical thinking and clinical reasoning, enabling therapists to tailor interventions to individual patient needs while adhering to established best practices. For instance, a therapist might choose a specific manual therapy technique based on research demonstrating its effectiveness for a particular joint restriction. This integration of evidence-based techniques enhances the overall quality and effectiveness of rehabilitation services.
The practical significance of evidence-based techniques lies in their capacity to improve patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and promote efficient resource utilization. By utilizing treatments supported by evidence, therapists can optimize treatment effectiveness, minimize the risk of adverse effects, and achieve desired outcomes more efficiently. This commitment to evidence-based practice ultimately benefits patients by ensuring they receive the most appropriate and effective care. Furthermore, it contributes to the overall advancement of the field of rehabilitation by promoting a culture of scientific inquiry and innovation. Challenges may include staying current with rapidly evolving research, access to relevant information, and integrating new evidence into clinical practice. However, by prioritizing evidence-based techniques, rehabilitation strives to deliver high-quality, patient-centered care grounded in the best available scientific knowledge. This dedication to evidence-informed practice underscores a commitment to excellence and continuous improvement in patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding collaborative, evidence-based rehabilitation, providing concise and informative responses.
Question 1: What conditions benefit from collaborative rehabilitation?
Numerous conditions, including musculoskeletal injuries, neurological disorders, post-surgical recovery, and chronic pain syndromes, can benefit. Specific examples include back pain, arthritis, stroke, multiple sclerosis, and post-operative rehabilitation following joint replacement.
Question 2: How long does a typical rehabilitation program last?
Program duration varies based on individual needs and the nature of the condition. Some individuals may require a few weeks of treatment, while others may benefit from longer-term programs. Factors influencing duration include the severity of the condition, individual healing rates, and overall treatment goals.
Question 3: What is the role of a physical therapist in collaborative rehabilitation?
Physical therapists play a central role in assessing functional limitations, developing individualized treatment plans, and implementing interventions to improve mobility, strength, and pain management. They collaborate closely with other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive care.
Question 4: How does evidence-based practice inform treatment decisions?
Treatment decisions are guided by the best available scientific evidence derived from research studies and clinical trials. This ensures that interventions are both safe and effective, maximizing the potential for positive patient outcomes.
Question 5: What can patients expect during a rehabilitation session?
Sessions typically involve a combination of therapeutic exercises, manual therapy techniques, modalities (e.g., ultrasound, electrical stimulation), and patient education. Specific activities and interventions are tailored to individual patient needs and treatment goals.
Question 6: How can patients optimize their rehabilitation outcomes?
Active participation, consistent adherence to the prescribed treatment plan, open communication with healthcare providers, and a commitment to a healthy lifestyle are crucial for maximizing rehabilitation outcomes and achieving long-term well-being.
Understanding these common inquiries can empower individuals to actively participate in their rehabilitation journey and achieve optimal outcomes. Collaborative, evidence-based rehabilitation emphasizes patient-centered care, individualized treatment plans, and a commitment to maximizing functional recovery and overall well-being.
The next section will offer concluding remarks and summarize the key benefits of collaborative rehabilitation.
Conclusion
Collaborative, evidence-based rehabilitation, as exemplified by the principles of alliant physical therapy, represents a comprehensive approach to restoring function, reducing pain, and improving mobility. This approach emphasizes individualized treatment plans tailored to specific patient needs, incorporating a range of interventions such as therapeutic exercise, manual therapy, and modalities. The collaborative nature of this model ensures integrated care, leveraging the expertise of multiple healthcare professionals to optimize patient outcomes. Furthermore, the commitment to evidence-based techniques guarantees treatments are grounded in scientific research, maximizing effectiveness and patient safety.
Through its patient-centered focus and dedication to best practices, collaborative rehabilitation empowers individuals to regain independence, improve quality of life, and achieve optimal physical well-being. Continued advancements in research and clinical practice promise further refinements in treatment approaches, offering hope for even more effective and personalized rehabilitation strategies in the future. The emphasis on collaborative, evidence-based care underscores a commitment to delivering high-quality rehabilitation services that prioritize individual needs and promote long-term health and wellness.