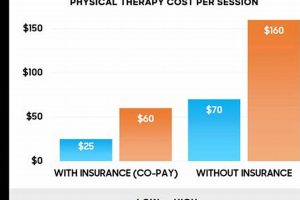
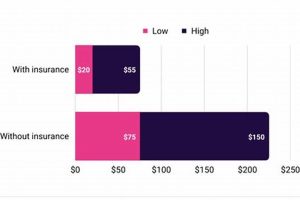
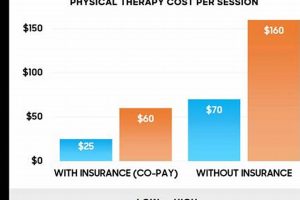
Restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment are employed to address impairments, restore function, and alleviate pain. A typical application involves customized exercise programs, manual therapies, and modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation to improve mobility and manage chronic conditions. For example, a patient recovering from a knee injury might undergo specific exercises to strengthen surrounding muscles and regain range of motion.
This approach plays a vital role in improving patients’ quality of life by reducing pain, increasing mobility, and promoting independence. Its roots trace back to ancient civilizations, but significant advancements during the 20th century, driven by the polio epidemics and world wars, led to its modern form. This evolution continues with the integration of new technologies and research findings.
This foundation provides a basis for understanding various aspects of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment, which will be further explored. Topics include specialized treatment areas, technological advancements, and the role of these practices in preventive care.
Tips for Optimizing Restorative Movement
Optimizing the benefits of restorative movement involves proactive measures and informed choices. The following tips offer guidance for maximizing recovery and overall well-being.
Tip 1: Consult a Qualified Professional: Seeking guidance from a licensed practitioner is crucial for accurate assessment and personalized treatment plans. A thorough evaluation helps identify specific needs and ensures appropriate interventions.
Tip 2: Adherence to Prescribed Programs: Consistent engagement with prescribed exercises and therapies is essential for optimal outcomes. Following instructions carefully and maintaining prescribed frequencies contribute significantly to progress.
Tip 3: Open Communication with Therapists: Maintaining open communication regarding pain levels, progress, and any concerns allows therapists to adjust treatment plans as needed and ensures optimal care.
Tip 4: Gradual Progression and Patience: Restorative processes often require time and patience. Progress should be gradual, avoiding overexertion and respecting the body’s natural healing pace.
Tip 5: Integration of Home Exercise Programs: Continuing exercises at home reinforces progress made during therapy sessions and promotes long-term benefits.
Tip 6: Focus on Proper Body Mechanics: Paying attention to posture and movement patterns in daily activities helps prevent re-injury and supports overall functional improvement.
Tip 7: Combining Modalities for Enhanced Recovery: Combining various treatment modalities, such as manual therapy and therapeutic exercises, can provide comprehensive benefits and address multiple aspects of recovery.
By following these guidelines, individuals can actively participate in their restorative journey and achieve optimal functional outcomes, promoting long-term health and well-being.
Understanding these practical tips provides a solid foundation for making informed decisions and maximizing the benefits of restorative movement. This information complements the earlier discussions and prepares the reader for the article’s concluding insights.
1. Restoring Function
Restoring functional capacity is a central objective of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment. It addresses limitations in performing daily activities and aims to maximize individual independence and overall quality of life. This involves a comprehensive approach encompassing various therapeutic interventions tailored to specific needs and conditions.
- Improving Range of Motion:
Limitations in joint movement can significantly impact daily tasks. Restorative therapies employ techniques like manual therapy and targeted exercises to improve flexibility and range of motion, facilitating activities such as dressing, reaching, and walking. For example, after a shoulder injury, restoring range of motion is crucial for regaining the ability to perform overhead activities.
- Enhancing Muscle Strength and Endurance:
Weakness and fatigue can hinder functional performance. Therapeutic exercises, including resistance training and functional activities, aim to strengthen muscles and improve endurance, enabling individuals to perform tasks requiring sustained effort, such as lifting groceries or climbing stairs. A patient recovering from surgery might engage in exercises to rebuild muscle strength and regain functional independence.
- Improving Balance and Coordination:
Balance and coordination are essential for safe and efficient movement. Therapeutic interventions address these aspects through exercises targeting postural control and coordination, reducing fall risk and improving mobility. This is particularly important for older adults or individuals recovering from neurological conditions.
- Promoting Neuromuscular Control:
Restoring neuromuscular control is crucial for coordinated movement and efficient muscle activation. Therapeutic techniques focus on improving the communication between the nervous system and muscles, enhancing movement precision and functional performance. This can be beneficial for individuals recovering from stroke or other neurological impairments.
These interconnected facets of restoring function highlight the comprehensive nature of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment. By addressing these aspects, these therapies empower individuals to regain lost function, improve their quality of life, and achieve greater independence in daily activities. This focus on functional restoration reinforces the fundamental role of these therapies in promoting overall well-being and enabling individuals to participate fully in their lives.
2. Reducing Pain
Pain reduction is a primary objective of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment. Addressing pain not only improves comfort and quality of life but also facilitates engagement in therapeutic activities essential for functional recovery. A variety of techniques are employed to manage and alleviate pain, depending on its source and characteristics.
Manual therapy techniques, including soft tissue mobilization, joint mobilization, and manipulation, can directly address musculoskeletal pain. These hands-on approaches aim to restore joint mechanics, reduce muscle tension, and alleviate pain. For example, manual therapy can address restricted joint movement contributing to back pain. Therapeutic modalities such as heat, ice, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation offer additional pain relief options. Heat can relax muscles and increase blood flow, while ice reduces inflammation and numbs the area. Ultrasound uses sound waves to penetrate deep tissues and promote healing, while electrical stimulation can modulate pain signals and reduce muscle spasms. A patient experiencing chronic knee pain might benefit from a combination of manual therapy and ultrasound.
Therapeutic exercises play a crucial role in pain management by strengthening supporting muscles, improving joint stability, and restoring functional movement. For instance, targeted exercises can strengthen core muscles to alleviate back pain. Patient education empowers individuals to manage their pain effectively through self-management strategies, including proper body mechanics, pacing activities, and understanding pain triggers. By integrating these various approaches, restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment effectively address pain, enabling individuals to engage in activities necessary for functional recovery and improve their overall quality of life. This multifaceted approach underscores the importance of pain management as an integral component of restoring function and well-being.
3. Improving Mobility
Enhanced mobility is a cornerstone of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment. Restricted movement significantly impacts an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks and participate fully in life. Therapeutic interventions address mobility limitations through targeted exercises, manual therapies, and other modalities to restore functional independence and improve overall well-being. Cause-and-effect relationships between impairments and mobility restrictions are carefully considered. For instance, limited hip mobility can contribute to lower back pain, and decreased shoulder flexibility can restrict reaching and dressing abilities. Addressing the root cause of the mobility restriction, such as joint stiffness or muscle weakness, is crucial for effective treatment.
Restorative therapies prioritize improving mobility as an essential component of comprehensive rehabilitation. Specific exercises aim to increase joint range of motion, flexibility, and muscle strength, directly impacting functional mobility. For example, a patient recovering from a knee replacement will undergo exercises to regain knee flexion and extension, improving walking ability. Similarly, stretching exercises and manual therapy can address tight muscles and improve overall flexibility, enhancing mobility for activities like bending and reaching. Individuals with neurological conditions, such as stroke, may benefit from targeted exercises to improve balance, coordination, and gait, increasing their independence in mobility-related tasks.
Understanding the practical significance of improved mobility underscores the value of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment. Increased mobility reduces fall risk, promotes independence in daily activities, and enhances overall quality of life. Regaining mobility enables individuals to participate more fully in social activities, recreational pursuits, and vocational endeavors. Challenges in improving mobility can include pain, fear of movement, and pre-existing medical conditions. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating pain management strategies, patient education, and adaptive techniques to optimize mobility outcomes and support long-term functional independence. This emphasis on mobility reinforces the overarching goal of restorative therapies to maximize functional capacity and enhance overall well-being.
4. Preventing Injury
Injury prevention is an integral aspect of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment, extending beyond treating existing conditions to proactively mitigating future risks. This proactive approach emphasizes identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities before they lead to injuries. Cause-and-effect relationships between movement patterns, biomechanics, and injury risk are central to preventive strategies. For example, poor posture during repetitive lifting can lead to back injuries, while inadequate warm-up before exercise increases the risk of muscle strains. Understanding these relationships allows for targeted interventions to correct faulty movement patterns and minimize risk factors. The importance of injury prevention as a component of restorative therapies is underscored by its long-term impact on health and well-being. By preventing injuries, individuals can maintain an active lifestyle, avoid pain and disability, and reduce healthcare costs associated with injury treatment. This proactive approach empowers individuals to take control of their musculoskeletal health and optimize their functional capacity.
Practical applications of injury prevention within restorative therapies include ergonomic assessments, movement analysis, and targeted exercise programs. Ergonomic assessments evaluate workplace setups and recommend modifications to minimize strain and promote proper body mechanics, reducing the risk of work-related injuries. Movement analysis identifies movement patterns that may predispose individuals to injury, allowing for corrective exercises and strategies to improve biomechanics and reduce risk. Targeted exercise programs focus on strengthening muscles, improving flexibility, and enhancing neuromuscular control, providing a foundation for safe and efficient movement. Real-life examples include prescribing exercises to strengthen core muscles and improve posture for individuals with a history of back pain, or designing a flexibility program for athletes to prevent hamstring strains. These practical applications demonstrate the tangible benefits of integrating injury prevention principles into restorative therapies.
In summary, preventing injury is a crucial element of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment, contributing significantly to long-term health and well-being. By understanding the cause-and-effect relationships between movement and injury risk, and applying practical prevention strategies, individuals can minimize their susceptibility to injuries, maintain an active lifestyle, and optimize their functional capacity. Challenges in implementing injury prevention strategies include patient adherence to exercise programs and making necessary lifestyle modifications. Addressing these challenges through patient education, motivation, and support is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of injury prevention efforts and achieving optimal long-term outcomes. This focus on injury prevention reinforces the holistic nature of restorative therapies and their commitment to promoting overall health and well-being.
5. Managing chronic conditions
Managing chronic conditions is a critical application of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment. These conditions, often characterized by persistent pain, inflammation, and functional limitations, significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Restorative therapies offer a non-pharmacological approach to managing these conditions, focusing on improving function, reducing pain, and enhancing overall well-being. Cause-and-effect relationships are carefully considered. For instance, osteoarthritis can lead to decreased joint mobility and pain, impacting daily activities. Restorative therapies address the effects of osteoarthritis by improving joint range of motion, strengthening supporting muscles, and managing pain, thereby improving functional capacity and quality of life. The importance of managing chronic conditions as a component of restorative therapies stems from its potential to empower individuals to take control of their health, reduce reliance on medication, and improve their overall well-being. Real-life examples include using therapeutic exercises to manage symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, improving cardiovascular health in individuals with heart disease, or enhancing balance and coordination in patients with multiple sclerosis. These examples illustrate the practical significance of this approach in diverse chronic conditions.
Practical applications involve tailored exercise programs, manual therapy techniques, and patient education. Exercise programs focus on improving strength, flexibility, cardiovascular fitness, and endurance, depending on the specific condition. Manual therapies address pain, joint restrictions, and soft tissue limitations. Patient education empowers individuals to manage their condition effectively through self-management strategies, including pacing activities, understanding symptom triggers, and adhering to prescribed exercise programs. For example, a patient with chronic low back pain might benefit from a combination of core strengthening exercises, manual therapy to address joint restrictions, and education on proper body mechanics and posture. Individuals with fibromyalgia might engage in low-impact aerobic exercises, gentle stretching, and learn strategies for managing pain flares. These practical applications demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of restorative therapies in managing diverse chronic conditions.
In summary, managing chronic conditions represents a vital aspect of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment. By addressing the underlying causes and symptoms of these conditions, restorative therapies empower individuals to improve their functional capacity, reduce pain, and enhance their overall quality of life. Challenges in managing chronic conditions include disease progression, fluctuating symptoms, and comorbid conditions. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing assessment, individualized treatment plans, and a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare professionals. This long-term perspective highlights the ongoing role of restorative therapies in supporting individuals with chronic conditions and maximizing their well-being throughout their lives. This reinforces the crucial role of these therapies in not only restoring function but also managing the complexities of long-term health conditions.
6. Enhancing Performance
Enhancing performance represents a key application of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment, extending beyond injury recovery to optimizing physical capabilities in various domains. This approach focuses on improving strength, power, endurance, flexibility, and other performance-related parameters. Cause-and-effect relationships are central to this application. For example, targeted strength training can improve an athlete’s power output, while enhanced flexibility can improve a dancer’s range of motion. The importance of performance enhancement as a component of restorative therapies lies in its ability to maximize individual potential, whether in athletics, performing arts, or everyday activities. Real-life examples include helping athletes recover from injuries and return to competition at a higher level, improving musicians’ dexterity and stamina, or enhancing a dancer’s flexibility and control. The practical significance of this understanding lies in its ability to translate therapeutic principles into tangible performance gains, benefiting individuals across various disciplines and activities. It demonstrates that restorative therapies are not solely for injury recovery but also for optimizing human potential.
Practical applications involve individualized training programs, biomechanical analysis, and injury prevention strategies. Tailored training programs address specific performance goals, incorporating exercises designed to improve strength, power, speed, agility, and endurance. Biomechanical analysis identifies areas for improvement in movement efficiency, leading to adjustments in technique and training to optimize performance and minimize injury risk. Injury prevention plays a crucial role in maintaining peak performance by addressing potential vulnerabilities and implementing strategies to minimize risk factors. Examples include designing a strength and conditioning program for a marathon runner to improve endurance and prevent overuse injuries, or working with a golfer to improve swing mechanics and reduce back strain. These practical applications highlight the versatility of restorative therapies in enhancing performance across diverse activities.
In summary, enhancing performance represents a significant aspect of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment, demonstrating its potential to optimize human capabilities in various domains. By understanding the cause-and-effect relationships between training, biomechanics, and performance, and applying targeted interventions, individuals can achieve higher levels of performance, minimize injury risk, and maximize their potential. Challenges in enhancing performance include individual variability in training response, balancing training load with recovery, and managing psychological factors influencing performance. Addressing these challenges requires individualized approaches, ongoing monitoring, and a collaborative approach between practitioners, coaches, and individuals seeking to optimize their performance. This emphasizes the comprehensive and individualized nature of performance enhancement within restorative therapies.
7. Promoting Independence
Promoting independence is a fundamental objective of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment. Restoring the ability to perform essential daily tasks fosters self-sufficiency and significantly enhances an individual’s quality of life. Cause-and-effect relationships are central to this objective. For example, limited mobility due to a stroke can restrict an individual’s ability to dress, bathe, or prepare meals independently. Restorative therapies address these limitations through targeted interventions, aiming to restore functional independence and empower individuals to participate more fully in their lives. The importance of promoting independence as a component of these therapies stems from its profound impact on overall well-being, self-esteem, and social engagement. Real-life examples include regaining the ability to walk after a hip replacement, restoring upper extremity function following a shoulder injury, or improving balance and coordination to reduce fall risk in older adults. The practical significance of this understanding lies in its ability to translate therapeutic gains into tangible improvements in daily living, enabling individuals to regain control over their lives and participate meaningfully in their communities.
Practical applications involve functional assessments, adaptive techniques, and home modifications. Functional assessments evaluate an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks, identifying specific areas requiring intervention. Adaptive techniques and assistive devices can compensate for limitations and promote independence in activities such as dressing, eating, and mobility. Home modifications, such as installing grab bars or ramps, create a safer and more accessible environment, further supporting independent living. A patient recovering from a spinal cord injury might utilize adaptive equipment for dressing and bathing, while a therapist might recommend home modifications to improve accessibility and reduce fall risk. Occupational therapists play a crucial role in assessing and addressing the needs of individuals in their home and community environments, maximizing their independence in daily activities. These examples demonstrate the practical application of promoting independence within restorative therapies.
In summary, promoting independence represents a crucial aspect of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment. By focusing on restoring functional abilities and providing individuals with the tools and strategies to manage daily tasks, these therapies empower individuals to regain control over their lives and achieve greater independence. Challenges in promoting independence include the severity of the underlying condition, individual motivation, and access to resources and support. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach involving individualized treatment plans, patient education, and collaboration with family members and caregivers. This holistic approach underscores the commitment of restorative therapies to maximizing individual potential and promoting overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions about Restorative Movement and Rehabilitative Treatment
This section addresses common inquiries regarding restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment, providing clear and concise information to promote understanding and informed decision-making.
Question 1: What conditions benefit from restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment?
Numerous conditions can benefit, including musculoskeletal injuries (such as back pain, sprains, and fractures), neurological conditions (like stroke, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease), chronic pain syndromes (such as fibromyalgia and arthritis), and cardiopulmonary conditions. The versatility of these therapies allows for individualized treatment approaches tailored to specific needs.
Question 2: How long does a typical treatment program last?
Treatment duration varies depending on the individual’s condition, severity, and response to therapy. Some individuals may require a few weeks of treatment, while others may benefit from longer-term programs. A qualified practitioner will assess individual needs and develop a personalized treatment plan with appropriate timelines.
Question 3: Is restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment painful?
While some discomfort may be experienced during certain exercises or manual therapies, the goal is to minimize pain and improve function. Practitioners prioritize patient comfort and adjust treatment intensity as needed. Open communication between the patient and practitioner is essential for ensuring a comfortable and effective treatment experience.
Question 4: What is the difference between restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment and surgery?
Restorative therapies offer a non-invasive approach to managing various conditions, often serving as a first-line treatment option. Surgery may be necessary in some cases, and restorative therapies can play a vital role in pre- and post-surgical rehabilitation to optimize outcomes.
Question 5: How can one find a qualified practitioner?
Referrals from physicians, online directories of professional organizations, and recommendations from trusted sources can help locate qualified practitioners. Verifying credentials and licensure is essential to ensure quality care.
Question 6: What role does patient participation play in successful outcomes?
Active patient participation, including adherence to prescribed exercise programs, open communication with practitioners, and engagement in self-management strategies, plays a crucial role in successful outcomes. Commitment to the therapeutic process significantly contributes to achieving functional goals and maximizing benefits.
Understanding these frequently asked questions provides a foundation for informed decision-making regarding restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment. These therapies offer a valuable approach to managing various conditions, improving function, and enhancing overall quality of life.
This concludes the frequently asked questions section. The following section will explore further resources and information for continued learning and support related to restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment.
Conclusion
This exploration has highlighted the multifaceted nature of restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment, emphasizing its crucial role in addressing various health conditions and promoting overall well-being. From restoring function and reducing pain to preventing injuries and managing chronic conditions, these therapies offer a comprehensive approach to improving quality of life. The interconnectedness of these aspects underscores the holistic nature of this field, where enhancing mobility, promoting independence, and even enhancing performance are integral components of the restorative process. The discussion encompassed practical applications, underlying principles, and the significance of patient participation in achieving optimal outcomes.
The evolving landscape of healthcare increasingly recognizes the value of non-invasive and proactive approaches to health management. Restorative movement and rehabilitative treatment stand as cornerstones of this evolving paradigm, offering sustainable solutions for long-term health and well-being. Continued research and advancements in this field promise further refinement of therapeutic techniques and expansion of their applications, ultimately empowering individuals to achieve and maintain optimal physical function and overall quality of life.