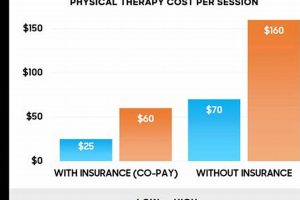
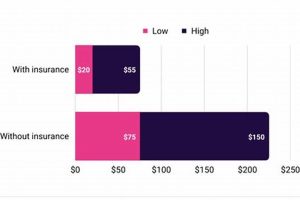
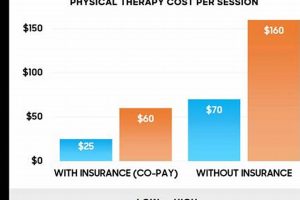
Proactive rehabilitation and prehabilitation services play a crucial role in optimizing physical function and overall well-being. These services empower individuals to prevent injuries, improve movement quality, and enhance performance in daily activities and athletic pursuits. For example, implementing a specialized exercise program before surgery can significantly reduce recovery time and improve postoperative outcomes.
Prioritizing proactive physical care contributes to long-term health and reduces the risk of future complications. It represents a shift towards preventative healthcare, empowering individuals to take control of their physical health. Historically, physical therapy has often been reactive, addressing injuries after they occur. The evolving understanding of the body’s capacity for adaptation and the effectiveness of early intervention has led to an increased emphasis on proactive strategies.
The following sections will explore specific applications of this proactive approach, discussing various techniques and their benefits in detail. Topics covered include injury prevention strategies, performance enhancement programs, and the role of these services in managing chronic conditions.
Proactive Strategies for Enhanced Physical Well-being
Implementing proactive strategies can significantly impact long-term physical health and overall quality of life. The following recommendations offer practical guidance for integrating these principles into daily routines.
Tip 1: Prioritize Regular Movement: Incorporating frequent movement throughout the day, such as short walks or stretching breaks, can improve circulation, reduce stiffness, and maintain joint mobility.
Tip 2: Integrate Strength Training: A well-structured strength training program builds muscle mass, supports joint stability, and enhances overall functional capacity.
Tip 3: Focus on Proper Posture: Maintaining correct posture during daily activities minimizes strain on the spine and surrounding muscles, reducing the risk of developing back pain and other musculoskeletal issues.
Tip 4: Warm-up Before Activity: Preparing the body for physical activity with dynamic stretches and light cardiovascular exercise reduces the risk of injury and improves performance.
Tip 5: Cool-Down After Exercise: Gentle stretching and low-intensity movement after exercise promotes recovery, reduces muscle soreness, and improves flexibility.
Tip 6: Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting a qualified physical therapist can provide personalized assessments, tailored exercise programs, and expert advice to address specific needs and prevent future issues.
Tip 7: Listen to Your Body: Paying attention to physical cues and respecting pain signals are essential for avoiding overexertion and preventing injuries. Rest and recovery are crucial components of any fitness program.
Adopting these strategies can lead to significant improvements in physical function, reduce the risk of injuries, and contribute to a healthier, more active lifestyle.
By embracing proactive physical care, individuals can invest in their long-term well-being and enjoy a higher quality of life.
1. Injury Prevention
Injury prevention forms a cornerstone of proactive physical therapy. Understanding the mechanics of injury allows for the development of targeted strategies to mitigate risk. This approach emphasizes identifying potential vulnerabilities based on individual movement patterns, activity levels, and pre-existing conditions. Cause-and-effect relationships are carefully considered. For example, a worker performing repetitive lifting motions might be susceptible to lower back injuries. Proactive physical therapy would address this by prescribing exercises to strengthen core muscles and improve lifting techniques, thereby reducing the likelihood of strain. Similarly, athletes engaging in high-impact sports can benefit from specialized training programs designed to enhance joint stability and neuromuscular control, minimizing the risk of common sports-related injuries like sprains and tears.
The practical significance of injury prevention within a proactive framework extends beyond minimizing immediate risks. It contributes to long-term musculoskeletal health and overall well-being. By addressing potential problems before they manifest, individuals can maintain higher levels of activity, avoid chronic pain, and improve their quality of life. For instance, incorporating regular balance exercises into a senior’s routine can prevent falls and subsequent fractures, preserving independence and mobility. In occupational settings, ergonomic assessments and tailored exercise programs can prevent repetitive strain injuries, reducing lost workdays and improving productivity.
Successfully integrating injury prevention requires a comprehensive approach that combines education, movement analysis, and personalized interventions. Challenges may include adherence to prescribed exercises, access to qualified professionals, and integrating preventative strategies into existing routines. However, the long-term benefits of reduced injury rates, improved physical function, and enhanced quality of life underscore the importance of prioritizing injury prevention as a core component of proactive physical therapy. This proactive approach offers a sustainable path towards maintaining optimal physical health and minimizing the impact of preventable injuries.
2. Performance Enhancement
Performance enhancement represents a crucial facet of proactive physical therapy, focusing on maximizing physical capabilities through targeted interventions. This approach moves beyond injury prevention to optimize movement quality, enhance strength and power, improve endurance, and refine skill execution. Cause-and-effect relationships are central to this process, with specific training modalities employed to elicit desired physiological adaptations. For example, plyometric exercises can enhance explosive power in athletes, while targeted flexibility training can improve range of motion and reduce the risk of injury in dancers. Understanding these relationships allows practitioners to develop individualized programs tailored to specific performance goals. The importance of performance enhancement as a component of proactive physical therapy lies in its ability to empower individuals to reach their full physical potential. Whether an athlete striving to improve competitive performance or an individual seeking to enhance functional capacity in daily life, this approach provides the tools and strategies necessary to achieve desired outcomes.
Real-world examples illustrate the practical significance of this understanding. A golfer might utilize proactive physical therapy to improve swing mechanics and increase driving distance. A musician might focus on exercises to enhance finger dexterity and prevent repetitive strain injuries. The applications extend beyond specialized fields; individuals seeking to improve overall fitness can benefit from tailored programs designed to enhance cardiovascular health, muscular strength, and flexibility. The focus on continuous improvement and adaptation allows individuals to progressively challenge their physical limitations and achieve higher levels of performance.
Performance enhancement, within a proactive framework, requires ongoing assessment, adaptation, and collaboration between the individual and the physical therapist. Challenges may include balancing training demands with recovery needs, addressing individual biomechanical limitations, and setting realistic performance goals. However, the potential benefits of improved physical capacity, reduced injury risk, and enhanced overall well-being underscore the importance of integrating performance enhancement strategies into proactive physical therapy. This empowers individuals to not only achieve specific performance goals but also to cultivate a lifelong commitment to physical excellence and sustained well-being.
3. Personalized Care
Personalized care forms the foundation of effective proactive physical therapy, recognizing that individual needs and goals vary significantly. This approach emphasizes a comprehensive assessment process to understand each person’s unique circumstances, including medical history, current physical condition, lifestyle factors, and personal objectives. Tailoring interventions to these specific needs optimizes outcomes and ensures that treatment plans align with individual aspirations. This personalized approach distinguishes proactive physical therapy from standardized protocols, allowing for a more nuanced and effective approach to care.
- Individualized Assessment:
Thorough assessments consider anatomical variations, movement patterns, strength and flexibility levels, and any pre-existing conditions. A runner with flat feet, for example, requires different interventions than a runner with high arches. This detailed analysis informs the development of a personalized exercise program addressing specific biomechanical needs and minimizing the risk of injury. The implications of this individualized approach are significant, as it allows practitioners to target the root causes of dysfunction rather than simply addressing symptoms.
- Goal-Oriented Treatment Plans:
Collaboratively establishing realistic and achievable goals ensures that the treatment plan aligns with the individual’s aspirations. A post-surgical patient focused on regaining functional independence will have a different treatment plan than an athlete aiming to improve competitive performance. These goal-oriented plans provide motivation and direction, fostering a sense of ownership and active participation in the rehabilitation process. This collaborative approach fosters a stronger therapeutic alliance and contributes to improved adherence to the prescribed plan.
- Adaptive Programming:
Continuously monitoring progress and adapting the treatment plan as needed ensures optimal outcomes. As an individual’s physical condition improves, the exercises and interventions are modified to maintain challenge and progress towards goals. This adaptive approach recognizes that the body is constantly adapting, and the treatment plan must evolve accordingly. This flexibility allows practitioners to address unforeseen challenges and maximize the effectiveness of interventions throughout the rehabilitation process.
- Lifestyle Integration:
Integrating therapeutic exercises and strategies into daily routines enhances long-term adherence and promotes sustainable lifestyle changes. Providing practical advice on incorporating healthy habits into daily life empowers individuals to take ownership of their physical well-being beyond the clinic setting. A desk worker, for example, might benefit from ergonomic adjustments and regular movement breaks to prevent back pain. This lifestyle integration approach fosters lasting changes and promotes overall health and wellness.
These interconnected facets of personalized care underscore the importance of a patient-centered approach within proactive physical therapy. By tailoring interventions to individual needs and goals, practitioners can maximize the effectiveness of treatment, promote long-term adherence, and empower individuals to achieve optimal physical function and overall well-being. This personalized approach not only addresses current challenges but also equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to maintain a healthy and active lifestyle for years to come.
4. Movement Optimization
Movement optimization represents a core principle within proactive physical therapy, emphasizing the enhancement of biomechanics and movement efficiency. This approach recognizes that inefficient movement patterns can lead to decreased performance, increased energy expenditure, and elevated risk of injury. By analyzing and correcting these patterns, individuals can improve physical function, enhance athletic performance, and reduce the likelihood of developing musculoskeletal problems. Movement optimization provides a pathway towards achieving optimal physical capacity and minimizing strain on the body.
- Biomechanical Analysis
Biomechanical analysis forms the foundation of movement optimization. Through observation, assessment tools, and motion capture technology, practitioners evaluate joint angles, muscle activation patterns, and overall movement strategies. This analysis identifies deviations from optimal movement patterns, providing insights into the underlying causes of dysfunction and informing targeted interventions. For example, analyzing a runner’s gait can reveal imbalances that contribute to knee pain, allowing for the implementation of corrective exercises and strategies.
- Corrective Exercise
Corrective exercise strategies address identified biomechanical deficiencies and promote efficient movement patterns. These exercises target specific muscle groups and movement patterns to improve strength, flexibility, stability, and coordination. A golfer, for example, might incorporate exercises to improve hip rotation and core stability, enhancing swing mechanics and power. These targeted interventions optimize neuromuscular control and enhance overall movement efficiency.
- Functional Integration
Functional integration bridges the gap between isolated corrective exercises and real-world movements. This approach emphasizes training movement patterns that mimic activities of daily living and sport-specific movements. A tennis player, for example, might perform exercises that replicate the serve motion, integrating improved biomechanics into the actual skill. This functional integration ensures that optimized movement patterns translate into improved performance and reduced injury risk in real-world scenarios.
- Neuromuscular Re-education
Neuromuscular re-education focuses on retraining the nervous system to control movement more effectively. This approach utilizes techniques such as proprioceptive training and balance exercises to enhance sensory feedback and improve motor control. A patient recovering from an ankle sprain, for example, might engage in balance exercises to regain stability and prevent recurrent injury. This neuromuscular re-education optimizes the interplay between the nervous system and musculoskeletal system, promoting efficient and coordinated movement.
These interconnected facets of movement optimization contribute significantly to proactive physical therapy. By addressing the root causes of inefficient movement, practitioners can empower individuals to move with greater ease, efficiency, and resilience. This proactive approach not only enhances performance and reduces injury risk but also fosters a deeper understanding of the body’s movement capabilities and promotes lifelong physical well-being. Movement optimization offers a pathway towards unlocking the body’s full potential and maximizing its capacity for movement and functional expression.
5. Functional Restoration
Functional restoration represents a critical component of proactive physical therapy, emphasizing the recovery of lost function and the improvement of overall quality of life. This approach addresses impairments resulting from injury, illness, or surgery, aiming to restore individuals to their prior level of function or to the highest level possible. A cause-and-effect relationship underpins this process: addressing underlying impairments directly impacts functional capacity. For instance, restoring strength and range of motion in a knee following surgery directly influences the ability to walk, climb stairs, and engage in other essential activities. The importance of functional restoration within proactive physical therapy lies in its focus on enabling individuals to regain independence, participate in meaningful activities, and experience a fulfilling life. Real-life examples underscore the practical significance of this understanding. A stroke survivor might undergo functional restoration to regain the ability to dress and perform daily hygiene tasks. An individual with a back injury might focus on regaining the ability to lift objects and return to work. The emphasis on restoring function translates to tangible improvements in quality of life.
Several key elements contribute to successful functional restoration within a proactive framework. Targeted therapeutic exercises address specific impairments, while functional training integrates these improvements into real-world activities. Adaptive equipment and assistive devices may be employed to facilitate independence and participation. Pain management strategies play a crucial role in optimizing function and promoting comfort. Moreover, patient education empowers individuals to actively participate in their recovery and manage their condition effectively. For instance, a patient recovering from a shoulder injury might utilize resistance exercises to improve strength, practice reaching and lifting tasks to simulate daily activities, and learn pain management techniques to control discomfort. These interconnected strategies contribute to a comprehensive and individualized approach to functional restoration.
Functional restoration, within proactive physical therapy, requires a comprehensive assessment, individualized treatment planning, and ongoing monitoring of progress. Challenges may include the severity of the initial impairment, the presence of co-existing medical conditions, and access to appropriate resources and support. However, the potential benefits of improved physical function, increased independence, and enhanced quality of life underscore the vital role of functional restoration in proactive physical therapy. This approach empowers individuals to regain lost abilities, participate more fully in life, and experience a greater sense of well-being. By addressing the underlying causes of functional limitations, proactive physical therapy promotes not only physical recovery but also overall health and wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding proactive rehabilitation and prehabilitation services.
Question 1: How does a proactive approach to physical therapy differ from traditional reactive care?
Proactive physical therapy emphasizes prevention and early intervention to optimize physical function and mitigate potential risks, while reactive care typically addresses injuries or impairments after they occur. This proactive approach prioritizes long-term musculoskeletal health and overall well-being.
Question 2: What types of conditions can benefit from proactive physical therapy services?
Individuals of all ages and activity levels can benefit. Applications range from preventing sports-related injuries in athletes to improving functional mobility in older adults, managing chronic conditions, and enhancing postoperative outcomes. The adaptability of this approach allows it to address a wide spectrum of needs.
Question 3: How can prehabilitation optimize surgical outcomes?
Prehabilitation, or pre-surgical training, enhances physical function prior to surgery, optimizing recovery time and postoperative outcomes. Improved strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular fitness contribute to a smoother recovery process and minimize potential complications. This proactive preparation equips individuals for the physical demands of surgery and rehabilitation.
Question 4: What role does movement analysis play in proactive physical therapy?
Movement analysis identifies biomechanical inefficiencies and movement patterns that may contribute to pain or injury. This detailed assessment informs the development of targeted exercise programs and corrective strategies to optimize movement quality, reduce strain, and enhance performance.
Question 5: How can individuals incorporate proactive strategies into their daily routines?
Integrating regular exercise, prioritizing proper posture, incorporating movement breaks throughout the day, and warming up before physical activity represent key strategies. Consulting with a qualified physical therapist can provide personalized guidance and recommendations tailored to individual needs and goals.
Question 6: What are the long-term benefits of prioritizing proactive physical care?
Long-term benefits include reduced risk of injury, improved physical function, enhanced athletic performance, better management of chronic conditions, and increased overall well-being. Proactive physical therapy empowers individuals to take control of their physical health and invest in a healthier future.
Proactive physical therapy empowers individuals to achieve optimal physical function, prevent injuries, and enhance overall well-being. By addressing potential issues before they arise, individuals can improve their quality of life and maintain an active lifestyle.
The next section delves further into the specific applications of proactive physical therapy, exploring its role in various contexts and demonstrating its versatility as a healthcare approach.
Step Ahead Physical Therapy
This exploration of step ahead physical therapy has highlighted the importance of proactive care in optimizing physical function and overall health. From injury prevention and performance enhancement to personalized care, movement optimization, and functional restoration, the proactive approach emphasizes empowering individuals to take control of their physical well-being. By addressing potential issues before they manifest, individuals can minimize risk, enhance performance, and improve their quality of life.
Step ahead physical therapy represents a paradigm shift in musculoskeletal health management, moving beyond reactive care to prioritize prevention and early intervention. Embracing this proactive approach offers a pathway towards a healthier, more active, and fulfilling future. The potential benefits extend beyond individual well-being, contributing to a more resilient and productive society.