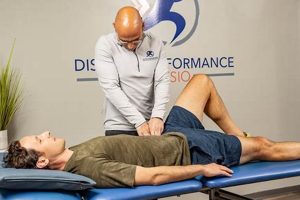
Restorative movement and rehabilitative care are essential for regaining function and improving quality of life after injury, illness, or surgery. Skilled practitioners employ evidence-based techniques to address pain, restore mobility, and enhance overall well-being. A customized treatment plan may include therapeutic exercises, manual therapy, modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation, and patient education. For example, a patient recovering from a knee replacement might receive a program incorporating range-of-motion exercises, strengthening activities, and gait training.
Such specialized care plays a vital role in helping individuals return to their daily activities and achieve their functional goals. It can reduce pain, improve strength and flexibility, prevent future injuries, and enhance overall physical function. The field has evolved significantly over time, incorporating advances in medical science and technology to provide more effective and personalized treatment options. This evolution has led to improved patient outcomes and a greater emphasis on preventative care.
This article will further explore various aspects of restorative movement and rehabilitation, including specific treatment approaches, the role of different healthcare professionals, and the benefits of incorporating these practices into overall healthcare strategies.
Tips for Optimizing Physical Well-being
Proactive strategies can significantly enhance physical health and prevent future discomfort. The following recommendations offer practical guidance for promoting mobility, strength, and overall wellness.
Tip 1: Maintain Proper Posture: Correct posture, whether sitting, standing, or lifting, distributes weight evenly, reducing strain on joints and muscles. Ergonomic assessments can help optimize workstation setup.
Tip 2: Incorporate Regular Exercise: A balanced exercise program encompassing cardiovascular activity, strength training, and flexibility exercises is crucial for maintaining physical function and overall health. Consult a healthcare professional for a personalized plan.
Tip 3: Prioritize Proper Lifting Techniques: Lifting heavy objects improperly can lead to injuries. Focus on bending at the knees, keeping the back straight, and using leg muscles to lift.
Tip 4: Listen to Your Body: Recognize pain signals and avoid pushing through discomfort. Rest and appropriate care are essential for recovery.
Tip 5: Warm Up Before Activity: Preparing muscles for activity through dynamic stretches and light movements can help prevent injuries. Cool-down routines after exercise promote flexibility and recovery.
Tip 6: Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration supports joint lubrication and overall bodily functions crucial for optimal physical performance.
Tip 7: Seek Professional Guidance: Consult qualified healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to individual needs and conditions.
By incorporating these strategies into daily routines, individuals can actively contribute to their physical well-being and minimize the risk of future complications. These proactive measures empower individuals to take control of their health and maintain an active lifestyle.
The following section will explore further resources and support available for individuals seeking to enhance their physical health and well-being.
1. Restorative Care
Restorative care forms a cornerstone of effective rehabilitation programs, aiming to return individuals to their highest level of function and independence. Within the context of rehabilitative therapies, restorative care emphasizes regaining lost skills and abilities following illness, injury, or surgery. This approach focuses on improving mobility, strength, balance, coordination, and overall physical function. The relationship between restorative care and rehabilitation is symbiotic; restorative care provides the foundational principles and goals, while rehabilitative therapies provide the practical tools and techniques to achieve them. For example, a patient recovering from a hip fracture would benefit from restorative care principles emphasizing weight-bearing exercises and gait training within their rehabilitation program. This combined approach facilitates a more comprehensive and successful recovery.
The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in the development of patient-centered treatment plans. By integrating restorative care principles, rehabilitation programs can better address individual needs and goals, promoting long-term functional independence and improved quality of life. This holistic approach acknowledges the interconnectedness of physical, emotional, and social well-being, recognizing that successful rehabilitation extends beyond addressing immediate physical impairments. For instance, a patient undergoing cardiac rehabilitation might benefit from restorative care principles that incorporate stress management techniques and lifestyle modifications alongside exercise and education, promoting overall cardiovascular health and long-term well-being.
In conclusion, restorative care serves as an essential framework for rehabilitative therapies, guiding the process of restoring function and improving overall well-being. Challenges may include varying individual responses to treatment and the need for ongoing adaptation of care plans. However, by prioritizing restorative care principles within rehabilitation programs, practitioners can effectively address the complex needs of individuals recovering from illness or injury, promoting meaningful improvements in their quality of life and fostering long-term independence.
2. Personalized Treatment
Effective rehabilitation hinges on individualized care tailored to specific needs and goals. Personalized treatment plans within rehabilitative therapies are essential for maximizing functional recovery and improving overall well-being. This approach recognizes that each individual presents with unique circumstances, requiring customized interventions to address specific impairments and facilitate optimal outcomes.
- Individualized Assessment:
Comprehensive evaluations form the foundation of personalized treatment. These assessments consider factors such as medical history, current functional limitations, lifestyle, and personal goals. A thorough understanding of individual needs allows practitioners to develop targeted interventions. For example, two individuals with the same diagnosis, such as osteoarthritis of the knee, may require different treatment approaches based on their activity levels and pain severity.
- Tailored Interventions:
Personalized treatment plans incorporate specific exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities chosen to address individual impairments. These interventions are progressively adjusted based on ongoing assessments and patient responses. For instance, a patient recovering from a shoulder injury may begin with passive range-of-motion exercises and progress to strengthening exercises as their condition improves.
- Goal-Oriented Approach:
Personalized treatment plans are driven by patient-centered goals, ensuring that interventions align with individual aspirations and desired outcomes. This collaborative approach empowers patients and fosters motivation throughout the rehabilitation process. A patient recovering from a stroke might prioritize regaining independence in daily activities, guiding the focus of their treatment plan.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Adaptation:
Personalized treatment requires continuous monitoring of progress and adaptation of interventions as needed. Regular reassessments allow practitioners to adjust the treatment plan based on individual responses and ensure continued progress toward goals. For example, if a patient experiences a plateau in their recovery, the treatment plan may be modified to incorporate new exercises or modalities.
These interconnected facets of personalized treatment contribute significantly to the effectiveness of rehabilitative therapies. By tailoring interventions to individual needs and goals, practitioners can optimize functional recovery and improve overall well-being, promoting a return to meaningful activities and enhanced quality of life. This emphasis on individualization distinguishes effective rehabilitation and underscores the importance of patient-centered care.
3. Evidence-based techniques
Effective rehabilitative care relies heavily on evidence-based techniques. These practices, grounded in scientific research and clinical trials, ensure treatment approaches demonstrate effectiveness and safety. Integrating evidence-based techniques into restorative movement and rehabilitation is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes and providing high-quality care. For example, studies demonstrating the efficacy of specific manual therapy techniques for low back pain inform treatment choices, leading to more effective pain management and improved functional mobility.
The application of evidence-based techniques translates into tangible benefits for patients. Treatment plans based on scientific evidence offer a higher likelihood of successful outcomes, reduced recovery times, and minimized risks of adverse effects. Consider the use of therapeutic exercises for individuals recovering from ACL reconstruction. Evidence supports specific exercise protocols that enhance stability, strength, and functional return, leading to improved long-term outcomes compared to less structured approaches. Furthermore, adhering to evidence-based guidelines ensures practitioners remain up-to-date with the latest advancements in the field, continuously refining their practices to deliver optimal care.
Incorporating evidence-based techniques represents a commitment to best practices and patient-centered care within restorative movement and rehabilitation. Challenges include staying abreast of evolving research and integrating new findings into practice. However, prioritizing this approach ensures treatments are informed by scientific rigor, maximizing the potential for positive outcomes and promoting optimal physical well-being. This focus on evidence ultimately elevates the quality of care provided and reinforces the importance of scientific inquiry in advancing rehabilitative practices.
4. Skilled Practitioners
The effectiveness of restorative movement and rehabilitative therapies hinges significantly on the expertise of skilled practitioners. These professionals possess the knowledge, training, and experience necessary to assess, diagnose, and treat individuals requiring such care. Their role is central to ensuring positive patient outcomes and facilitating a return to optimal physical function. The following facets illustrate the crucial connection between skilled practitioners and successful rehabilitation.
- Comprehensive Assessment and Diagnosis:
Skilled practitioners conduct thorough assessments to identify the root cause of functional limitations, considering medical history, physical examination findings, and diagnostic imaging. Accurate diagnosis forms the basis of effective treatment planning. For instance, a skilled practitioner differentiating between radicular pain and referred pain can significantly alter the course of treatment and improve patient outcomes. This diagnostic precision is fundamental to personalized and effective care.
- Development of Individualized Treatment Plans:
Skilled practitioners develop tailored treatment plans that address specific impairments and patient goals. These plans incorporate evidence-based techniques, incorporating exercises, manual therapy, and modalities as appropriate. For example, a practitioner might create a program incorporating balance training, gait retraining, and strengthening exercises for a patient recovering from a stroke, addressing the multifaceted nature of their condition. This individualized approach is crucial for maximizing functional recovery.
- Skilled Application of Therapeutic Interventions:
Expertise in applying therapeutic techniques, such as manual therapy and exercise prescription, distinguishes skilled practitioners. Precise execution and appropriate progression of interventions are essential for optimizing treatment effectiveness and minimizing risks. A practitioner skilled in joint mobilization techniques can effectively address joint restrictions, improving range of motion and reducing pain. This proficiency in practical application is critical for achieving desired outcomes.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Adaptation of Care:
Skilled practitioners continuously monitor patient progress and adapt treatment plans as needed. This dynamic approach ensures interventions remain aligned with individual needs and responses throughout the rehabilitation process. For example, a practitioner might adjust the intensity or type of exercises based on a patient’s pain levels and functional improvements, optimizing the recovery trajectory. This responsiveness is essential for personalized and effective care.
These interconnected facets demonstrate the essential role skilled practitioners play in delivering effective restorative movement and rehabilitative therapies. Their expertise, from accurate diagnosis to personalized treatment and ongoing monitoring, significantly impacts patient outcomes and facilitates a return to optimal physical function. The integration of these skills ensures high-quality care and reinforces the importance of qualified professionals in the field of rehabilitation.
5. Improved Mobility
Restorative movement and rehabilitative therapies prioritize improved mobility as a core outcome. Enhanced mobility is essential for functional independence, allowing individuals to perform daily activities, participate in meaningful occupations, and maintain an active lifestyle. This section explores the multifaceted connection between improved mobility and effective rehabilitation.
- Range of Motion:
Restoring optimal range of motion in affected joints is fundamental to improved mobility. Therapeutic exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities are employed to address limitations and enhance joint flexibility. For instance, a patient recovering from a frozen shoulder might undergo joint mobilizations and stretching exercises to improve shoulder range of motion, facilitating activities such as reaching overhead. Improved range of motion lays the groundwork for more complex functional movements.
- Strength and Muscle Function:
Adequate muscle strength and neuromuscular control are crucial for supporting movement and maintaining stability. Targeted strengthening exercises and neuromuscular re-education are incorporated into rehabilitation programs to address muscle weakness and improve functional capacity. For example, a patient recovering from a knee injury might engage in quadriceps strengthening exercises to improve stability and support walking. Enhanced strength and muscle function contribute directly to improved mobility and functional independence.
- Balance and Coordination:
Balance and coordination are integral components of safe and efficient movement. Rehabilitative therapies often include balance training exercises and activities to improve postural stability and coordination. A patient recovering from a stroke might participate in balance exercises to reduce fall risk and improve walking stability. Enhanced balance and coordination contribute to safer movement and reduce the risk of falls and injuries.
- Functional Mobility Skills:
Improved mobility extends beyond basic movement components to encompass functional skills essential for daily life. Rehabilitation programs focus on retraining functional activities such as walking, stair climbing, transferring, and reaching. For example, a patient recovering from a hip replacement might undergo gait training to improve walking mechanics and restore functional ambulation. Improving functional mobility skills enables individuals to regain independence in daily activities and participate more fully in life.
These interconnected facets of mobility demonstrate the comprehensive approach required for effective rehabilitation. By addressing range of motion, strength, balance, and functional skills, restorative movement and rehabilitative therapies facilitate meaningful improvements in mobility, ultimately enhancing individual independence and quality of life. This emphasis on mobility underscores the fundamental goal of rehabilitation: restoring functional capacity and empowering individuals to engage in meaningful activities.
6. Pain Management
Effective pain management is integral to restorative movement and rehabilitative therapies. Addressing pain not only improves patient comfort but also facilitates active participation in the rehabilitation process, promoting optimal functional recovery. This section explores the multifaceted connection between pain management and effective rehabilitation.
- Modalities for Pain Relief:
Therapeutic modalities, such as heat, ice, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation, play a crucial role in managing pain and inflammation. These modalities can provide immediate pain relief, allowing patients to engage more comfortably in therapeutic exercises and other interventions. For example, applying heat before exercise can increase tissue flexibility and reduce pain, while ice can be beneficial after exercise to minimize inflammation and muscle soreness. The strategic use of modalities optimizes patient comfort and promotes active participation in rehabilitation.
- Manual Therapy Techniques:
Skilled manual therapy techniques, including joint mobilization, soft tissue mobilization, and manipulation, can effectively address musculoskeletal pain. These techniques can restore joint mechanics, reduce muscle tension, and alleviate pain, facilitating improved movement and function. For instance, manual therapy applied to a restricted joint can improve range of motion and reduce pain, enabling the patient to engage in therapeutic exercises more effectively. Manual therapy plays a crucial role in addressing the underlying causes of pain and promoting functional recovery.
- Therapeutic Exercise:
Therapeutic exercise is fundamental to pain management and functional restoration. Specific exercises can improve muscle strength, flexibility, and joint stability, reducing pain and enhancing overall function. For example, strengthening exercises for the core muscles can improve stability and reduce low back pain. A progressive exercise program tailored to individual needs is essential for long-term pain management and improved functional capacity. Therapeutic exercise empowers patients to actively manage their pain and improve their physical well-being.
- Patient Education and Self-Management:
Empowering patients with knowledge and self-management strategies is crucial for long-term pain management. Education about pain mechanisms, activity modification, and coping strategies equips patients to actively participate in their recovery and manage their pain effectively. For instance, teaching a patient proper body mechanics and posture can reduce strain on injured tissues and minimize pain. Patient education fosters self-efficacy and promotes long-term pain management, reducing reliance on passive interventions and empowering individuals to take control of their health.
These interconnected facets of pain management demonstrate the comprehensive approach required for effective rehabilitation. By integrating modalities, manual therapy, therapeutic exercise, and patient education, practitioners can effectively address pain, promote functional recovery, and improve overall patient well-being. Effective pain management is not merely a component of rehabilitation but a crucial foundation for achieving optimal outcomes and empowering individuals to regain control of their lives.
7. Functional Restoration
Functional restoration represents the ultimate goal of rehabilitative therapies, emphasizing the return to optimal physical function and participation in meaningful activities. Within the context of restorative movement and rehabilitation, functional restoration focuses on regaining the ability to perform daily tasks, occupational duties, and recreational pursuits. This outcome-oriented approach emphasizes practical application and individualized care, tailoring interventions to meet specific patient needs and goals. Understanding the multifaceted nature of functional restoration is crucial for developing effective rehabilitation programs and maximizing patient outcomes.
- Activities of Daily Living (ADLs):
Restoring independence in ADLs, such as dressing, bathing, grooming, and eating, is a primary focus of functional restoration. Rehabilitative interventions address specific impairments limiting these activities, incorporating adaptive strategies and assistive devices as needed. For example, a patient recovering from a stroke might relearn dressing techniques using adaptive equipment and modified movements. Regaining independence in ADLs significantly impacts quality of life and reduces reliance on caregivers.
- Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADLs):
Functional restoration extends beyond basic ADLs to encompass IADLs, which include more complex tasks such as meal preparation, managing finances, shopping, and using transportation. Rehabilitation programs address the underlying physical and cognitive skills required for these activities, promoting independence and community reintegration. For instance, a patient recovering from a hip fracture might undergo therapy to improve balance and walking endurance, enabling them to navigate public transportation and access community resources. Restoring IADLs enhances independence and social participation.
- Occupational and Recreational Activities:
Returning to work or engaging in recreational pursuits is a significant aspect of functional restoration. Rehabilitative therapies address the specific physical demands of occupational and recreational activities, tailoring interventions to individual needs and goals. A patient recovering from a shoulder injury might undergo targeted strengthening and range-of-motion exercises to regain the ability to perform job-related tasks or participate in a favorite sport. Successful reintegration into occupational and recreational activities contributes to overall well-being and quality of life.
- Community Reintegration:
Functional restoration encompasses community reintegration, enabling individuals to participate fully in social and community life. Rehabilitative therapies address mobility limitations, social interaction skills, and access to community resources, fostering independence and social engagement. For example, a patient recovering from a spinal cord injury might participate in community-based rehabilitation programs to improve mobility, access transportation, and connect with support networks. Successful community reintegration enhances social participation and promotes overall well-being.
These interconnected facets of functional restoration demonstrate the comprehensive and individualized nature of effective rehabilitation. By addressing ADLs, IADLs, occupational/recreational activities, and community reintegration, restorative movement and rehabilitative therapies empower individuals to regain functional independence, participate meaningfully in life’s activities, and experience an enhanced quality of life. This emphasis on functional restoration underscores the ultimate goal of rehabilitation: restoring individuals to their fullest potential and promoting overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding restorative movement and rehabilitative therapies, providing concise and informative responses.
Question 1: What conditions benefit from restorative movement and rehabilitation?
A wide range of conditions, including musculoskeletal injuries, neurological disorders, chronic pain conditions, and post-surgical recovery, can benefit. Specific examples include back pain, arthritis, stroke, multiple sclerosis, and post-operative rehabilitation following joint replacement.
Question 2: How long does a typical rehabilitation program last?
Program duration varies depending on individual needs and the specific condition being addressed. Some programs may last a few weeks, while others may extend for several months. Factors influencing duration include the severity of the condition, individual progress, and overall rehabilitation goals.
Question 3: What is the difference between physical therapy and occupational therapy?
While both disciplines aim to improve function, physical therapy focuses primarily on restoring movement and physical abilities, while occupational therapy emphasizes improving independence in daily activities and adapting to functional limitations. Often, these therapies work in conjunction to provide comprehensive care.
Question 4: Are rehabilitative therapies painful?
While some discomfort may be experienced during certain exercises or manual therapy techniques, the goal of rehabilitation is to minimize pain and improve function. Skilled practitioners adjust treatment intensity based on individual tolerance and prioritize patient comfort throughout the rehabilitation process.
Question 5: What is the role of patient participation in rehabilitation?
Active patient participation is crucial for successful rehabilitation. Engaging in prescribed exercises, adhering to treatment plans, and actively communicating with healthcare providers contribute significantly to positive outcomes and functional restoration.
Question 6: How can one find a qualified rehabilitation practitioner?
Recommendations from healthcare providers, online directories of licensed professionals, and inquiries with local hospitals or clinics can assist in locating qualified practitioners. Verifying credentials and experience is essential for ensuring quality care.
Understanding these frequently asked questions can help individuals make informed decisions regarding restorative movement and rehabilitative therapies. Open communication with healthcare providers is always recommended to address individual concerns and develop appropriate care plans.
The following section will explore case studies demonstrating the positive impact of restorative movement and rehabilitation on individuals recovering from various conditions.
Conclusion
Restorative movement and rehabilitative care, exemplified by practices within Revere Physical Therapy, offer a crucial pathway toward regaining function and improving overall well-being. This exploration has highlighted the significance of personalized treatment plans, evidence-based techniques, and the expertise of skilled practitioners in achieving optimal outcomes. From managing pain and improving mobility to restoring functional independence and facilitating community reintegration, the multifaceted benefits of these therapies underscore their essential role in healthcare. The integration of restorative care principles, coupled with a patient-centered approach, empowers individuals to actively participate in their recovery and achieve meaningful improvements in their quality of life.
The ongoing evolution of restorative movement and rehabilitation promises continued advancements in patient care and improved outcomes. As research expands and clinical practices refine, the potential for restoring function and enhancing well-being continues to grow, offering hope and opportunity for individuals seeking to regain their fullest physical potential and live fulfilling lives. Embracing proactive approaches to physical health and seeking qualified care remain crucial steps toward maximizing individual well-being and promoting a healthier future.