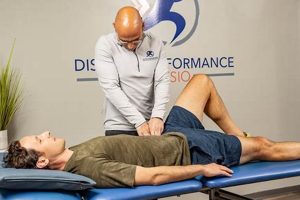
Effective rehabilitative care, delivered by skilled practitioners, addresses impairments and functional limitations through evidence-based interventions like therapeutic exercises, manual therapy, and modalities. A patient with limited mobility after knee surgery, for example, might receive a tailored program including exercises to strengthen supporting muscles, manual techniques to improve joint range of motion, and modalities like ultrasound to reduce pain and inflammation. This individualized approach fosters optimal recovery and improved physical function.
Expert, personalized treatment plans are crucial for restoring function, reducing pain, and improving overall well-being. Historically, rehabilitation involved generic approaches. Contemporary practice, however, emphasizes individualized programs tailored to specific patient needs and goals. This shift has led to more effective interventions and improved patient outcomes, contributing significantly to enhanced quality of life and a faster return to normal activities.
This understanding of effective rehabilitative care provides a foundation for exploring key aspects such as finding qualified practitioners, understanding different treatment approaches, and setting realistic expectations for the rehabilitation process.
Tips for Selecting Effective Rehabilitative Care
Choosing the right rehabilitation program is crucial for optimal recovery and improved functional outcomes. These tips offer guidance in navigating the selection process.
Tip 1: Seek referrals and recommendations. Consulting with physicians, other healthcare providers, and trusted individuals can provide valuable insights into reputable practitioners and facilities.
Tip 2: Verify practitioner credentials and experience. Confirming licensure, certifications, and specialization in relevant areas ensures qualified care.
Tip 3: Prioritize individualized treatment plans. Effective rehabilitation programs tailor interventions to specific patient needs and goals, rather than employing generic protocols.
Tip 4: Consider facility accessibility and amenities. Convenient location, accessible equipment, and a supportive environment contribute to a positive rehabilitation experience.
Tip 5: Inquire about communication and progress monitoring. Open communication between the patient, therapist, and other healthcare providers is essential for tracking progress and making necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Tip 6: Evaluate the emphasis on patient education and self-management. Empowering patients with knowledge and strategies for self-care promotes long-term health and well-being.
By considering these factors, individuals can make informed decisions to optimize their rehabilitation journey and achieve lasting functional improvements.
These tips provide a starting point for individuals seeking effective rehabilitation. The subsequent sections will delve deeper into specific aspects of the rehabilitation process.
1. Skilled Practitioners
The expertise of practitioners forms the cornerstone of effective rehabilitation. A practitioner’s skill level significantly influences the quality, efficacy, and overall success of therapeutic interventions. This section explores key facets that define skilled practitioners within the context of rehabilitative care.
- Comprehensive Assessment and Diagnosis:
Accurate assessment forms the foundation of effective treatment. Skilled practitioners conduct thorough evaluations, considering medical history, current symptoms, and functional limitations. This comprehensive approach ensures accurate diagnoses and informs the development of individualized treatment plans. For example, a skilled practitioner might utilize specific diagnostic tests to identify the root cause of a patient’s back pain, rather than simply addressing the presenting symptoms.
- Evidence-Based Treatment Approach:
Skilled practitioners prioritize interventions supported by scientific evidence and research. This commitment to best practices ensures that patients receive the most effective and up-to-date care. For instance, a practitioner might choose a specific exercise protocol based on research demonstrating its efficacy in treating a particular condition, rather than relying on outdated or unproven methods.
- Personalized Treatment Plans:
Recognizing that each patient’s needs are unique, skilled practitioners develop individualized treatment plans tailored to specific goals and circumstances. This personalized approach optimizes outcomes and promotes patient engagement in the rehabilitation process. A tailored plan might involve modifying exercises based on a patient’s progress and feedback, ensuring continuous optimization of the treatment approach.
- Effective Communication and Collaboration:
Skilled practitioners excel in communication and collaboration, fostering a strong therapeutic alliance with patients and other healthcare professionals. This collaborative approach ensures coordinated care and supports optimal patient outcomes. This could involve regular communication with a patient’s physician to coordinate care and ensure a unified approach to rehabilitation.
These interconnected facets of skilled practice underscore the crucial role practitioners play in delivering effective rehabilitative care. The integration of comprehensive assessment, evidence-based interventions, personalized treatment, and collaborative communication ultimately determines the overall quality and success of the rehabilitation process. This focus on practitioner expertise highlights the importance of seeking qualified professionals to optimize the potential for successful outcomes in rehabilitation.
2. Individualized Programs
Individualized programs represent a cornerstone of effective rehabilitative care, distinguishing it from generic approaches. Tailoring interventions to specific patient needs and goals optimizes outcomes and enhances the overall quality of the rehabilitation experience. This approach recognizes the inherent variability in patient presentations, ensuring that treatment plans address individual circumstances and maximize potential for functional restoration.
- Specific Condition Management:
Individualized programs address the unique demands of various conditions. For example, a rehabilitation program for a patient recovering from a stroke will differ significantly from a program designed for a patient managing osteoarthritis. Tailoring interventions to the specific condition ensures appropriate and effective treatment.
- Patient-Centered Goal Setting:
Individualized programs incorporate patient-centered goals, empowering individuals to actively participate in their rehabilitation journey. These goals might include returning to a specific activity, such as playing sports, or improving functional independence in daily tasks. Aligning treatment with personal goals enhances motivation and promotes adherence to the program.
- Adaptive Progression and Modification:
Individualized programs allow for adaptive progression and modification based on patient response and progress. As a patient improves, the program can be adjusted to increase challenge and promote continued advancement. Conversely, if a patient experiences setbacks, the program can be modified to ensure safety and address any emerging challenges. This flexibility is essential for optimizing outcomes and preventing plateaus in progress.
- Multidisciplinary Collaboration:
Individualized programs often involve collaboration among multiple healthcare professionals, such as physicians, therapists, and other specialists. This integrated approach ensures comprehensive care and addresses all aspects of a patient’s health and well-being. For instance, a rehabilitation program might involve coordination between a physical therapist and an occupational therapist to address both physical and functional limitations.
These facets of individualized programs highlight their crucial role in delivering high-quality rehabilitation. By tailoring interventions to specific patient needs, goals, and responses, individualized programs maximize the potential for successful outcomes and contribute significantly to enhanced quality of life. This personalized approach underscores the shift from standardized protocols to patient-centered care in contemporary rehabilitation practice.
3. Evidence-Based Techniques
Evidence-based techniques are fundamental to quality physical therapy, representing a shift from tradition-based practices to interventions supported by rigorous research and scientific evidence. This approach ensures treatment efficacy, optimizes patient outcomes, and elevates the overall standard of care. Utilizing techniques validated by scientific data minimizes risks, maximizes benefits, and promotes confidence in the rehabilitation process. For instance, studies demonstrating the effectiveness of specific manual therapy techniques for low back pain inform clinical practice, leading to more targeted and successful interventions. This reliance on empirical data distinguishes quality physical therapy from approaches lacking a strong scientific foundation.
Employing evidence-based techniques fosters continuous improvement and refinement within the field of physical therapy. Research findings contribute to the development of new treatment protocols and the modification of existing ones, ensuring that clinical practice aligns with the latest scientific advancements. Furthermore, this approach promotes critical thinking and informed decision-making among practitioners, leading to more individualized and effective treatment plans. For example, a therapist might integrate new exercise protocols based on recent research demonstrating their superior effectiveness in improving balance and reducing fall risk in older adults. This ongoing integration of research findings ensures that patients receive the most up-to-date and effective care.
Ultimately, the integration of evidence-based techniques strengthens the credibility and effectiveness of physical therapy. This commitment to scientific rigor reinforces the profession’s role in healthcare and empowers patients to make informed decisions about their treatment. While challenges remain in disseminating and implementing research findings across diverse clinical settings, the emphasis on evidence-based practice remains paramount in delivering quality physical therapy and achieving optimal patient outcomes. This scientific foundation positions physical therapy as a dynamic and evolving field, committed to providing the most effective and evidence-informed care possible.
4. Functional Restoration
Functional restoration represents a core objective of quality physical therapy, emphasizing the restoration of patient abilities and participation in meaningful activities. It moves beyond addressing symptoms to focus on improving overall functional capacity and quality of life. This approach recognizes that true recovery involves regaining the ability to perform daily tasks, engage in work or leisure activities, and participate fully in society.
- Activity-Specific Training:
Functional restoration emphasizes activity-specific training, tailoring exercises and interventions to replicate the demands of real-life situations. For example, a therapist might design a program for a golfer that includes exercises mimicking the golf swing, promoting a safe and effective return to the sport. This approach contrasts with generic exercises, focusing on movements directly relevant to the patient’s desired activities.
- Progressive Overload and Adaptation:
Functional restoration incorporates principles of progressive overload and adaptation, gradually increasing the demands placed on the body to promote strength, endurance, and functional capacity. This might involve progressively increasing the weight lifted during strengthening exercises or the duration of a functional task. This gradual progression challenges the body to adapt and improve, leading to enhanced functional performance.
- Compensatory Strategies and Assistive Devices:
When full restoration is not feasible, functional restoration incorporates compensatory strategies and assistive devices to maximize independence and participation. This might involve teaching a patient with limited mobility how to use adaptive equipment for dressing or recommending modifications to their home environment to facilitate safe movement. This approach emphasizes maximizing functional independence regardless of the extent of impairment.
- Outcome Measurement and Goal Attainment:
Functional restoration utilizes outcome measures to track progress and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. These measures might assess factors such as range of motion, strength, balance, and functional performance in specific activities. Regular assessment ensures that the program is meeting the patient’s goals and allows for adjustments as needed. This data-driven approach ensures accountability and optimizes the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes.
These facets of functional restoration underscore its importance in quality physical therapy. By focusing on restoring activity, promoting adaptation, and maximizing independence, functional restoration empowers individuals to regain control over their lives and achieve meaningful improvements in their overall well-being. This emphasis on functional outcomes distinguishes quality physical therapy from approaches that solely address symptoms, highlighting the importance of restoring not just physical capacity, but also the ability to live a full and active life.
5. Pain Management
Effective pain management is integral to quality physical therapy, significantly influencing patient comfort, adherence to treatment, and overall functional outcomes. Uncontrolled pain can hinder progress, limit participation in therapeutic activities, and negatively impact quality of life. Addressing pain effectively is not merely a secondary concern but a fundamental component of successful rehabilitation. For example, a patient experiencing severe back pain may struggle to engage in prescribed exercises, impeding progress and potentially prolonging recovery. Therefore, comprehensive pain management strategies are essential for optimizing patient outcomes and ensuring a positive rehabilitation experience. These strategies often involve a multi-faceted approach, combining various techniques to address both the underlying causes and the sensory experience of pain. This can include modalities like heat or ice, manual therapy techniques to address soft tissue restrictions, and therapeutic exercises to improve strength and mobility.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of pain is crucial for effective management within the context of physical therapy. Pain can stem from various sources, including tissue damage, inflammation, nerve irritation, and psychosocial factors. A thorough assessment helps identify the underlying causes of pain, guiding the selection of appropriate interventions. For instance, pain arising from nerve impingement requires a different approach than pain caused by muscle strain. Quality physical therapy utilizes a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies to manage pain effectively. Non-pharmacological approaches, such as manual therapy, therapeutic exercise, and patient education on pain management techniques, empower patients to actively participate in their recovery and minimize reliance on medication for pain relief.
Successful pain management within physical therapy facilitates engagement in therapeutic activities, promoting functional restoration and improving overall outcomes. By reducing pain, patients can participate more fully in exercises, stretches, and other interventions designed to improve mobility, strength, and function. This, in turn, contributes to a faster recovery, improved quality of life, and reduced risk of long-term disability. However, it’s important to recognize that pain management is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Individualized strategies, tailored to specific patient needs and conditions, are essential for achieving optimal results. The interplay between pain management and functional restoration highlights the interconnectedness of these elements within quality physical therapy, emphasizing the importance of a holistic approach to patient care. Addressing both pain and function is crucial for achieving meaningful and sustainable improvements in patient well-being.
6. Patient Education
Patient education represents a crucial component of quality physical therapy, empowering individuals to actively participate in their recovery and achieve long-term health benefits. Effective education extends beyond simply providing information; it fosters understanding, promotes self-management, and cultivates a collaborative partnership between the patient and therapist. This approach recognizes that informed patients are more likely to adhere to treatment plans, make healthy lifestyle choices, and achieve sustainable improvements in their physical well-being.
- Understanding the Condition and Treatment Plan:
Comprehensive education equips patients with a clear understanding of their condition, the rationale behind the prescribed treatment plan, and the expected trajectory of recovery. This knowledge fosters realistic expectations, reduces anxiety, and promotes active engagement in the rehabilitation process. For instance, a patient with a rotator cuff tear benefits from understanding the healing process, the purpose of specific exercises, and the anticipated timeframe for regaining full function. This understanding fosters adherence to the prescribed program and empowers the patient to take an active role in their recovery.
- Self-Management Strategies and Home Exercise Programs:
Patient education emphasizes self-management strategies, equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills to manage their condition independently. This includes instruction on proper body mechanics, pain management techniques, and home exercise programs. A patient recovering from back surgery, for example, learns proper lifting techniques, strategies for managing pain flares, and a personalized home exercise program to maintain strength and flexibility. These self-management skills empower patients to continue their progress beyond the clinical setting and minimize the risk of recurrence.
- Promoting Adherence and Motivation:
Effective patient education fosters adherence to treatment plans and enhances motivation. When patients understand the benefits of specific interventions and the potential consequences of non-compliance, they are more likely to follow through with prescribed exercises and lifestyle modifications. A therapist might explain to a patient with osteoarthritis how regular exercise can reduce pain and improve joint function, motivating them to adhere to their home exercise program. This proactive approach enhances the effectiveness of treatment and promotes long-term health benefits.
- Health Literacy and Shared Decision-Making:
Patient education promotes health literacy and empowers individuals to actively participate in shared decision-making regarding their care. This collaborative approach fosters a strong therapeutic alliance, enhances patient satisfaction, and improves overall outcomes. For example, a therapist might discuss different treatment options with a patient experiencing knee pain, explaining the risks and benefits of each approach and involving the patient in the decision-making process. This collaborative approach ensures that treatment plans align with patient preferences and values, promoting autonomy and optimizing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
These facets of patient education highlight its integral role in quality physical therapy. By empowering patients with knowledge, self-management skills, and a sense of ownership over their recovery, effective education optimizes treatment outcomes, promotes long-term health and well-being, and transforms patients into active participants in their rehabilitation journey. This emphasis on patient education underscores the shift from a paternalistic model of care to a collaborative partnership, recognizing the importance of patient engagement in achieving optimal and sustainable results. Ultimately, patient education is not merely an adjunct to treatment, but a fundamental pillar of quality physical therapy, crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of interventions and empowering individuals to achieve their full functional potential.
Frequently Asked Questions about Effective Physical Therapy
This section addresses common inquiries regarding effective rehabilitation, providing concise and informative responses to facilitate informed decision-making and promote a clearer understanding of the rehabilitation process.
Question 1: How does one differentiate between qualified and unqualified practitioners?
Verification of credentials, including licensure, certifications, and specialized training, is crucial. Furthermore, considering experience, patient testimonials, and professional affiliations can provide valuable insights into a practitioner’s qualifications and reputation.
Question 2: What is the typical duration of a rehabilitation program?
Program duration varies depending on individual needs, the nature of the condition, and the desired functional outcomes. Some individuals may require short-term intervention, while others may benefit from more extended programs. Realistic timelines are established collaboratively between the patient and practitioner based on thorough assessments and individualized goals.
Question 3: Are all rehabilitation approaches supported by scientific evidence?
While the field strives for evidence-based practice, not all interventions possess equal levels of scientific support. Prioritizing treatments with robust research backing ensures optimal efficacy and minimizes the risk of ineffective or potentially harmful interventions. Inquiries about the evidence supporting specific treatment approaches are encouraged.
Question 4: What role does patient adherence play in successful rehabilitation?
Patient adherence is paramount to successful outcomes. Active participation in prescribed exercises, consistent attendance at therapy sessions, and adherence to home exercise programs significantly influence the effectiveness of interventions. Open communication with practitioners regarding any challenges or concerns is essential for optimizing adherence and achieving desired results.
Question 5: How can individuals locate reputable rehabilitation facilities or clinics?
Seeking referrals from healthcare providers, consulting online directories of licensed practitioners, and considering recommendations from trusted sources can assist in identifying reputable facilities. Evaluating factors such as facility accreditation, practitioner credentials, and patient testimonials further supports informed decision-making.
Question 6: What can one expect during an initial evaluation with a practitioner?
An initial evaluation typically involves a comprehensive assessment of medical history, current symptoms, and functional limitations. Practitioners may conduct physical examinations, assess range of motion, and evaluate strength and balance. This comprehensive assessment informs the development of an individualized treatment plan tailored to specific patient needs and goals.
These responses provide foundational knowledge for individuals seeking effective rehabilitative care. Understanding these aspects empowers individuals to navigate the rehabilitation process with confidence and make informed decisions that optimize their potential for successful outcomes.
The following sections will delve deeper into specific treatment modalities and approaches commonly utilized in effective rehabilitation programs.
Conclusion
Effective, patient-centered rehabilitative care hinges on a confluence of factors: skilled practitioners employing evidence-based techniques, individualized programs tailored to specific needs and goals, and a commitment to functional restoration, comprehensive pain management, and thorough patient education. These elements, when integrated seamlessly, empower individuals to regain lost function, manage pain effectively, and achieve lasting improvements in their physical well-being. This holistic approach underscores the importance of viewing rehabilitation not merely as a treatment for specific conditions, but as a comprehensive process of restoring overall health and quality of life.
The pursuit of optimal physical function and well-being necessitates a proactive and informed approach to rehabilitation. Individuals seeking such care are encouraged to prioritize evidence-based interventions delivered by qualified practitioners within a patient-centered framework. Through informed decision-making and active participation in the rehabilitation process, individuals can unlock their full potential for recovery and experience the transformative benefits of effective rehabilitative care, ultimately leading to a healthier and more fulfilling life.