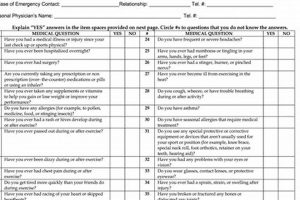
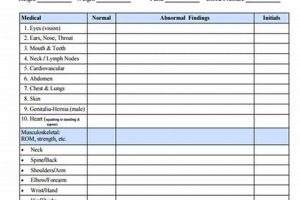
Hardcopy documents used in professional settings encompass a wide range of materials, including job applications, performance reviews, time sheets, expense reports, and various agreements. These tangible records often serve as primary source documentation for personnel matters, financial transactions, and legal compliance. For example, a signed employee handbook acknowledgement provides concrete evidence of an employee’s understanding of company policies.
Maintaining physical documentation offers several advantages in specific circumstances. These records can be readily accessible even without internet connectivity or power, offering a reliable backup in case of digital system failures. The tangible nature of physical forms can also reinforce the significance of certain processes, such as signing a contract or submitting a formal complaint. Historically, paper-based systems were the standard for record-keeping, and many organizations still rely on them, particularly in environments with limited technological resources or for specific regulatory requirements. Though digital systems are becoming increasingly prevalent, physical documents retain relevance and practicality in many workplaces.
This article will further explore the various types of workplace forms, their specific applications, best practices for their management, and the ongoing transition towards digital alternatives.
Tips for Effective Management of Hardcopy Workplace Documents
Proper handling of physical forms is essential for maintaining organized records and ensuring efficient workflow. The following tips offer guidance for maximizing the utility and longevity of these documents.
Tip 1: Standardize Forms: Utilizing consistent templates for common documents promotes clarity, simplifies data entry, and facilitates efficient retrieval.
Tip 2: Secure Storage: Storing documents in designated, secure locations protects sensitive information and prevents loss or damage. Consider locked cabinets or dedicated storage rooms with controlled access.
Tip 3: Implement a Clear Filing System: A well-defined filing system, whether alphabetical, numerical, or chronological, ensures quick and easy access to specific documents. Regularly purge outdated or obsolete files to maintain efficiency.
Tip 4: Use Durable Materials: Opting for high-quality paper and ink ensures document legibility over time and minimizes the risk of fading or smudging.
Tip 5: Ensure Proper Completion: All required fields should be accurately and legibly completed to avoid ambiguities and potential processing delays. Provide clear instructions for filling out forms to minimize errors.
Tip 6: Maintain Version Control: When revising forms, clearly indicate the version number and date to prevent confusion and ensure the use of the most up-to-date version.
Tip 7: Consider Digitization: While maintaining physical copies may be necessary for certain documents, explore digitizing records where possible to improve accessibility and reduce storage space.
Adhering to these practices contributes significantly to streamlined operations, regulatory compliance, and informed decision-making.
By understanding the importance and effective management of hardcopy documentation, organizations can optimize their processes and ensure the integrity of their records. The subsequent sections will delve into specific examples and further explore the evolving landscape of document management in the modern workplace.
1. Template Design
Template design plays a crucial role in the effectiveness and usability of printable physical forms for work. A well-designed template ensures clarity, consistency, and ease of completion, contributing to accurate data collection and efficient processing. This section explores key facets of template design.
- Layout and Structure
A logical layout guides the user through the form, ensuring all necessary information is captured. Clear section headings, appropriate spacing, and intuitive flow contribute to efficient completion and reduce errors. For example, a job application form might group personal information, education history, and work experience into distinct sections. Effective layout minimizes confusion and improves the overall user experience.
- Typography and Readability
Font selection, size, and spacing significantly impact readability. A clear, legible font in an appropriate size ensures accessibility and reduces eye strain. Sufficient white space prevents the form from appearing cluttered and improves comprehension. For instance, using a sans-serif font like Arial or Calibri in a size 12 point or larger ensures clarity, particularly for forms with extensive text.
- Data Field Design
Careful consideration of data field types, size, and placement ensures accurate data capture. Providing clear instructions and using appropriate input fields (e.g., checkboxes, radio buttons, text fields) simplifies the process for the user. For example, using dropdown menus for predefined options, such as country or state, reduces manual entry and ensures data consistency. Clear labeling of each field eliminates ambiguity.
- Branding and Aesthetics
Incorporating company branding elements, such as logos and color schemes, reinforces professional identity and promotes brand recognition. While aesthetics are important, they should not compromise functionality or readability. A subtle background color or a strategically placed logo can enhance the form’s visual appeal without detracting from its primary purpose.
These interconnected facets of template design contribute significantly to the overall utility and effectiveness of printable physical forms in the workplace. A well-designed template streamlines data collection, reduces errors, and improves the user experience, ultimately contributing to more efficient and effective organizational processes. By prioritizing clear and user-friendly design, organizations can maximize the value of their physical forms and ensure they serve their intended purpose effectively.
2. Data Fields
Data fields constitute the core components of printable physical forms, serving as designated spaces for specific information. Their design and arrangement directly impact data accuracy, completeness, and subsequent processing efficiency. Effective data fields facilitate seamless data capture and minimize ambiguity, ensuring the collected information aligns with its intended purpose. For instance, a data field requesting “Date of Birth” necessitates a specific format (e.g., MM/DD/YYYY) to prevent misinterpretation. Clear field labels and accompanying instructions further enhance clarity and minimize potential errors.
Careful consideration of data field types optimizes data collection and subsequent analysis. Employing checkboxes for binary options, radio buttons for exclusive selections, and text fields for free-form input ensures data integrity and simplifies processing. A performance review form, for example, might use rating scales within data fields to quantify employee performance against specific criteria. Furthermore, strategically placing related data fields in proximity enhances user comprehension and streamlines the completion process. A well-structured form logically groups related information, minimizing cognitive load and facilitating efficient data entry.
Understanding the critical role of data fields in printable physical forms enables effective form design and contributes to streamlined data management processes. Optimizing data fields for clarity, accuracy, and ease of use ultimately enhances organizational efficiency. Challenges, however, can arise when transferring data from physical forms to digital systems. Ensuring compatibility between physical form design and digital data entry systems minimizes data entry errors and facilitates seamless integration. Addressing these challenges reinforces the importance of thoughtful data field design within the broader context of document management.
3. Paper Quality
Paper quality significantly impacts the utility, longevity, and overall impression conveyed by printable physical forms in professional settings. Selecting appropriate paper stock ensures documents withstand regular handling, maintain legibility over time, and project a professional image. This seemingly minor detail plays a crucial role in the effectiveness and perceived value of workplace documentation.
- Durability and Handling
The durability of paper directly relates to its resistance to tearing, creasing, and general wear and tear. Higher weight and stronger fibers contribute to greater resilience, particularly important for frequently handled documents like employee handbooks or training manuals. A durable paper stock ensures documents remain intact and legible despite repeated use, preserving their integrity and extending their lifespan.
- Print Quality and Legibility
Paper characteristics, such as smoothness and brightness, influence print clarity and ink absorption. A smoother surface allows for crisper text and sharper images, while appropriate brightness enhances contrast, making the content easier to read. This is particularly relevant for forms with fine print or intricate details, where optimal print quality is essential for accurate interpretation.
- Impression and Professionalism
The choice of paper stock subtly communicates professionalism and attention to detail. A higher quality paper conveys a sense of formality and importance, enhancing the perceived value of the document. For example, using premium paper for client agreements or official certificates reinforces the significance of these documents and projects a professional image.
- Archival Properties
For long-term storage, paper with archival qualities is essential. Acid-free and lignin-free paper resists deterioration over time, preserving the integrity of the document for extended periods. This is crucial for records requiring long-term retention, such as legal documents or historical archives, ensuring their readability and usability for years to come.
Careful consideration of paper quality contributes significantly to the effectiveness and longevity of printable physical forms in the workplace. Selecting appropriate paper stock ensures documents not only fulfill their functional purpose but also convey a sense of professionalism and attention to detail, reflecting positively on the organization. Balancing cost considerations with the specific requirements of each document type allows for informed decisions that optimize both practicality and impact.
4. Legal Validity
Legal validity concerning printable physical forms in the workplace hinges on several critical factors, impacting their enforceability and admissibility in legal proceedings. Original signatures, proper witnessing requirements, and adherence to specific legal stipulations dictate the extent to which these documents hold up under scrutiny. For example, an employment contract lacking the required signatures may be deemed unenforceable, highlighting the crucial link between proper execution and legal standing. Similarly, specific legal clauses, such as non-compete agreements or intellectual property waivers, often necessitate physical signatures to establish their validity.
Maintaining meticulous records of document creation, distribution, and retention further strengthens legal validity. Documented proof of delivery, such as signed receipts or tracked mail confirmations, can be crucial in establishing a clear timeline and verifying compliance. Proper retention policies, adhering to legal and regulatory requirements for document storage duration, ensure accessibility should legal disputes arise. For instance, maintaining accurate records of employee acknowledgment of company policies protects organizations against potential liability claims. Consideration must also be given to the evolving legal landscape surrounding electronic signatures and digital documentation, as their acceptance and enforceability vary depending on jurisdiction and specific regulations.
Understanding the factors influencing legal validity is essential for ensuring compliance and mitigating potential legal risks. Proper execution, documentation, and retention practices safeguard the enforceability of printable physical forms, contributing to a secure and legally sound operational environment. The intersection of physical documentation and digital record-keeping presents ongoing challenges, emphasizing the need for adaptable strategies that maintain legal validity while leveraging technological advancements. Successfully navigating these complexities contributes to organizational integrity and minimizes legal vulnerabilities.
5. Storage Methods
Effective storage methods are crucial for preserving the integrity and accessibility of printable physical forms in the workplace. Proper storage safeguards sensitive information, ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, and facilitates efficient retrieval when needed. A well-defined storage strategy contributes significantly to organizational efficiency and minimizes the risk of document loss or damage. The following facets highlight key considerations for optimizing storage practices.
- Environmental Control
Maintaining a controlled environment safeguards documents from deterioration. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure significantly impact paper longevity. Excessive humidity can lead to mold growth, while direct sunlight can cause fading and discoloration. Climate-controlled storage areas, or specialized document storage containers, mitigate these risks, preserving document integrity over time.
- Security and Access Control
Protecting sensitive information necessitates secure storage solutions with restricted access. Confidential employee records, financial documents, and legal agreements require safeguarding against unauthorized access or theft. Implementing access control measures, such as locked cabinets, designated storage rooms, or controlled access systems, ensures only authorized personnel can access sensitive information, maintaining confidentiality and compliance with data protection regulations.
- Organization and Retrieval Systems
Efficient retrieval hinges on a well-organized filing system. Implementing a clear and consistent system, whether alphabetical, numerical, or chronological, allows for quick and easy access to specific documents. Utilizing indexing systems, cross-referencing, or digital databases further enhances retrieval efficiency, minimizing time spent searching for specific files. A well-defined system streamlines workflows and ensures information is readily available when needed.
- Offsite Storage and Disaster Recovery
Protecting against unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or fires, requires a robust disaster recovery plan. Offsite storage provides a secure backup location for critical documents, ensuring business continuity in the event of unforeseen circumstances. Regularly backing up essential records and storing them in a secure offsite location minimizes the risk of permanent data loss and facilitates business recovery in emergency situations.
Strategic implementation of these storage methods contributes significantly to the long-term preservation and accessibility of printable physical forms. A comprehensive approach to storage, encompassing environmental control, security measures, efficient organization, and disaster recovery planning, safeguards valuable information and ensures its availability when required. Integrating these practices with evolving digital document management systems allows organizations to adapt to changing technological landscapes while maintaining the integrity and accessibility of essential records.
6. Archival Practices
Archival practices play a crucial role in the long-term preservation and management of printable physical forms in the workplace. These practices ensure the accessibility and integrity of vital records, supporting legal compliance, historical research, and informed decision-making. Effective archival strategies encompass a range of considerations, from document selection and preservation techniques to storage environments and retrieval systems. For example, organizations must determine which documents warrant long-term preservation based on legal requirements, historical significance, and operational needs. Personnel records, financial statements, and legal agreements often necessitate extended retention periods due to regulatory mandates or potential future litigation.
Proper preservation techniques safeguard documents from deterioration due to environmental factors or handling. Utilizing acid-free storage materials, protecting documents from direct sunlight and excessive humidity, and implementing careful handling procedures contribute to document longevity. A museum archiving historical photographs, for example, utilizes specialized archival-quality sleeves and climate-controlled storage to prevent degradation and preserve these valuable artifacts. Furthermore, efficient retrieval systems are essential for accessing archived materials. Detailed indexing, cataloging, and cross-referencing facilitate quick and accurate retrieval of specific documents, even within extensive archives. A library, for instance, employs a comprehensive cataloging system to manage its collection and enable patrons to locate specific books or documents efficiently.
Implementing robust archival practices safeguards valuable organizational knowledge and ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. These practices contribute to informed decision-making by providing access to historical data and supporting research initiatives. Challenges, however, arise as organizations transition towards digital record-keeping. Integrating physical archival practices with digital asset management systems requires careful planning and execution to ensure long-term accessibility and data integrity. Successfully navigating this evolving landscape necessitates adaptable strategies that bridge the gap between traditional archival methods and the demands of the digital age.
7. Accessibility Considerations
Accessibility considerations are integral to the design and implementation of printable physical forms in the workplace. These considerations ensure inclusivity and equal access to information for all employees, regardless of disability. Addressing accessibility needs not only promotes equitable participation but also fulfills legal obligations and fosters a more inclusive work environment. For instance, providing large-print versions of forms accommodates employees with visual impairments, while Braille or tactile formats cater to the needs of visually impaired individuals. Furthermore, ensuring forms are compatible with assistive technologies, such as screen readers, enables access for employees with a range of disabilities. A job application form, for example, should be designed with clear headings and appropriate spacing to facilitate navigation for screen reader users.
Practical implementation of accessibility considerations extends beyond format variations. Font selection, color contrast, and layout all contribute to usability. Using a clear, sans-serif font in a sufficiently large size enhances readability for individuals with visual impairments. Adequate color contrast between text and background ensures legibility and minimizes eye strain. A well-structured layout with clear headings and logical flow facilitates comprehension and navigation for all users, including those with cognitive or learning disabilities. An expense report form, for example, benefits from a clear, structured layout with distinct sections for different expense categories, facilitating accurate completion by all employees.
Integrating accessibility considerations into the design and distribution of printable physical forms demonstrates a commitment to inclusivity and fosters a more equitable workplace. Meeting diverse needs ensures all employees can access and utilize essential information, regardless of ability. Challenges, however, remain in maintaining accessibility while transitioning towards digital document workflows. Ensuring digital forms adhere to accessibility standards, such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines), is crucial for maintaining inclusivity in the evolving digital landscape. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing attention and adaptation to ensure equal access to information for all employees in the modern workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the use and management of hardcopy documents in professional settings.
Question 1: When are physical forms preferable to digital alternatives in the workplace?
Physical forms remain relevant in situations requiring original signatures for legal validity, environments lacking reliable technology infrastructure, or processes benefiting from the tangible nature of paper records.
Question 2: What are the best practices for securely storing confidential hardcopy documents?
Secure storage involves utilizing locked cabinets or designated rooms with controlled access, implementing clear access protocols, and regularly auditing stored materials.
Question 3: How can organizations ensure the long-term preservation of essential physical records?
Long-term preservation necessitates using archival-quality materials, maintaining controlled storage environments, and implementing robust disaster recovery plans.
Question 4: What legal requirements must be considered when using printable physical forms for official purposes?
Legal requirements vary by jurisdiction and document type, often encompassing stipulations regarding original signatures, witness requirements, and retention periods. Consulting legal counsel is advisable to ensure compliance.
Question 5: How can organizations balance the need for physical records with increasing digitization efforts?
Organizations can adopt hybrid approaches, digitizing readily accessible records while maintaining physical copies of essential or legally required documents. Careful consideration should be given to document accessibility and data security during the digitization process.
Question 6: What strategies can improve the accessibility of printable physical forms for employees with disabilities?
Accessibility improvements include providing large-print versions, Braille formats, and ensuring compatibility with assistive technologies. Form design should prioritize clear layout, sufficient color contrast, and readily navigable data fields.
Understanding these frequently asked questions facilitates informed decision-making regarding the effective management and utilization of hardcopy documents in the evolving workplace landscape.
For further information on specific document types and their applications, consult the subsequent sections of this article.
Printable Physical Forms for Work
This exploration of printable physical forms for work has highlighted their continued relevance in modern professional environments. From template design and data field optimization to legal validity and archival practices, the multifaceted nature of these documents necessitates careful consideration. Effective management of physical forms contributes to streamlined workflows, legal compliance, and the preservation of vital organizational records. Despite the increasing prevalence of digital solutions, specific circumstances, such as legal requirements or the need for original signatures, necessitate the continued use of hardcopy documentation. Accessibility considerations remain paramount, ensuring inclusivity for all employees regardless of ability.
Organizations must adapt their document management strategies to balance the utility of printable physical forms with the evolving landscape of digital record-keeping. A thoughtful approach to form design, storage, and accessibility ensures these documents continue to serve their essential purpose effectively. The ongoing interplay between physical and digital documentation necessitates ongoing evaluation and adaptation to meet the dynamic needs of the modern workplace.