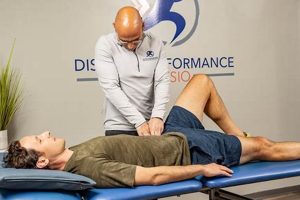
Controlled movements and specialized exercises form the core of both therapeutic approaches. One emphasizes core strengthening and postural alignment through low-impact exercises often performed on specialized equipment or mats. The other employs a variety of techniques, including exercise, manual therapy, and modalities, to address pain, improve mobility, and restore function. Often, these two disciplines are utilized in conjunction to maximize patient outcomes.
Integrating these methodologies can offer significant advantages for individuals seeking pain relief, improved flexibility, enhanced strength, and overall functional improvement. This combined approach may prove particularly beneficial for rehabilitation after injury or surgery, management of chronic conditions, and prevention of future musculoskeletal problems. The complementary nature of these practices has gained increasing recognition within the healthcare community.
This article will delve into the specifics of each practice, explore the synergy achieved through their combined application, and discuss the various conditions that can benefit from this integrative approach. It will also examine the evidence supporting the effectiveness of this combined treatment strategy and highlight the potential for personalized care plans tailored to individual needs and goals.
Tips for Optimizing Movement and Wellness
These practical strategies offer guidance for incorporating core principles of therapeutic exercise and body awareness into daily life. These tips can contribute to injury prevention, improved posture, and enhanced physical function.
Tip 1: Maintain Neutral Spine: Awareness of spinal alignment is crucial. Whether standing, sitting, or lifting, maintaining a neutral spine reduces strain and promotes proper posture. Imagine a straight line running through the ears, shoulders, and hips.
Tip 2: Engage the Core: Activating core muscles provides stability and support for all movements. Visualize drawing the navel towards the spine to engage these deep stabilizing muscles.
Tip 3: Focus on Controlled Movements: Execute exercises with precision and control rather than speed. This maximizes muscle engagement and minimizes the risk of injury.
Tip 4: Breathe Deeply and Consistently: Proper breathing facilitates movement and oxygenates muscles. Coordinate breath with exercise, inhaling during preparatory phases and exhaling during exertion.
Tip 5: Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any signs of pain or discomfort. Respect these signals and modify or cease activity as needed. Consult a healthcare professional if pain persists.
Tip 6: Prioritize Consistency: Regular practice, even in short durations, yields greater benefits than sporadic, intense sessions. Integrating these principles into daily routines can lead to lasting improvements.
Tip 7: Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting qualified practitioners can provide personalized instruction, tailored exercise plans, and address specific needs or limitations.
Implementing these strategies can lead to noticeable improvements in physical well-being, promoting strength, flexibility, and overall movement quality. Consistent application of these principles supports long-term musculoskeletal health.
By understanding and applying these fundamental concepts, individuals can cultivate a deeper awareness of their bodies and adopt healthier movement patterns for lasting benefits. This awareness forms the foundation for a proactive approach to physical well-being.
1. Core Strengthening
Core strengthening plays a vital role in both Pilates and physical therapy, serving as a foundation for improved posture, movement efficiency, and injury prevention. A strong core provides stability and support for the spine and pelvis, influencing overall body mechanics and functional capacity. This section explores the multifaceted nature of core strengthening within these disciplines.
- Spinal Stability:
A strong core stabilizes the spine, reducing the risk of back pain and injury. This stability is crucial for everyday activities like lifting, bending, and twisting, as well as for athletic performance. In Pilates, exercises like the “Hundred” and “Roll-Up” target deep core muscles to enhance spinal stability. Physical therapy often incorporates core strengthening exercises to rehabilitate back injuries and improve postural control.
- Balance and Coordination:
Core strength is essential for maintaining balance and coordination. The core muscles act as a central stabilizing force, allowing for controlled movements and improved proprioception (body awareness). Pilates exercises on unstable surfaces, such as the reformer or stability ball, challenge balance and further enhance core activation. Physical therapy utilizes balance training in conjunction with core strengthening to improve functional mobility and reduce fall risk, particularly in older adults or individuals recovering from injury.
- Efficient Force Transfer:
A strong core facilitates efficient force transfer throughout the body. This is crucial for athletic activities, where power generation and movement efficiency are paramount. For example, a strong core allows a tennis player to generate more power in their serve or a runner to maintain efficient stride mechanics. Both Pilates and physical therapy incorporate exercises that promote core strength and power transfer, improving overall athletic performance and functional capacity.
- Injury Prevention:
Core strengthening is a key component of injury prevention programs. A stable core reduces strain on the spine and surrounding muscles, minimizing the risk of injuries related to lifting, twisting, or repetitive movements. In physical therapy, core strengthening is often prescribed to prevent recurrence of back injuries and improve overall musculoskeletal health. Pilates complements this approach by emphasizing proper body mechanics and core engagement during exercise, fostering long-term injury prevention.
These facets of core strengthening highlight the integral role it plays in both Pilates and physical therapy. By developing a strong and stable core, individuals can improve posture, enhance movement efficiency, prevent injuries, and achieve optimal physical function. The synergistic application of Pilates and physical therapy principles maximizes the benefits of core strengthening, promoting overall well-being and facilitating a proactive approach to musculoskeletal health.
2. Postural Alignment
Postural alignment represents a cornerstone of both Pilates and physical therapy, impacting musculoskeletal health, functional movement, and overall well-being. Optimal postural alignment involves maintaining the body’s natural curves and ensuring proper skeletal alignment, minimizing stress on joints, muscles, and ligaments. This balanced posture contributes to efficient movement patterns and reduces the risk of pain and injury. Deviations from optimal alignment, often stemming from habitual movement patterns, prolonged static postures, or muscular imbalances, can contribute to various musculoskeletal issues. Addressing these postural deviations is a central focus within both disciplines.
Pilates emphasizes postural awareness and control through targeted exercises that strengthen core muscles, improve flexibility, and promote balanced muscle development. These exercises often focus on restoring the natural curves of the spine and promoting neutral pelvic alignment. Physical therapy utilizes postural assessment and corrective exercises to address specific postural deviations, such as forward head posture, rounded shoulders, or excessive lumbar lordosis. Therapeutic interventions may include manual therapy, stretching, strengthening exercises, and patient education on proper body mechanics. For example, an individual with forward head posture might benefit from exercises that strengthen the deep neck flexor muscles and stretch the tight posterior neck muscles. Combining Pilates principles with physical therapy techniques offers a comprehensive approach to postural correction.
Understanding the principles of postural alignment provides a foundation for injury prevention and improved movement quality. Maintaining optimal posture reduces stress on joints and soft tissues, minimizing the risk of overuse injuries and chronic pain. Improved postural alignment also contributes to efficient biomechanics, enhancing athletic performance and functional capacity. Furthermore, addressing postural imbalances can alleviate existing pain and improve overall body awareness. Integrating postural alignment principles into daily life, through mindful movement and ergonomic considerations, promotes long-term musculoskeletal health and enhances overall well-being.
3. Movement Control
Movement control represents a critical intersection between Pilates and physical therapy, emphasizing precision, stability, and coordinated muscle activation for optimal function. This integrated approach addresses not only gross motor skills but also the subtle nuances of movement, fostering efficient, pain-free motion. Deficits in movement control can contribute to musculoskeletal imbalances, decreased performance, and increased injury risk. These deficits may arise from various factors, including injury, sedentary lifestyles, or repetitive strain. Addressing these underlying issues through targeted interventions enhances both physical performance and overall well-being.
Pilates exercises cultivate precise movement control through focused, low-impact movements that challenge core stability and promote neuromuscular coordination. For example, the “Teaser” requires precise control of the abdominal muscles to maintain a balanced posture while articulating the spine. Physical therapy utilizes therapeutic exercises and manual techniques to restore movement control in injured or dysfunctional areas. A therapist might employ proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) techniques to enhance muscle activation and improve joint stability. In the case of a shoulder injury, targeted exercises might focus on restoring scapular control and rotator cuff function to optimize shoulder movement mechanics. The combined approach of Pilates and physical therapy provides a comprehensive framework for enhancing movement control, addressing both the underlying causes of dysfunction and improving functional capacity.
The practical significance of refined movement control extends to everyday activities and athletic performance. Improved movement efficiency reduces strain on joints and soft tissues, minimizing the risk of injury. Enhanced neuromuscular coordination contributes to greater agility, balance, and overall functional capacity. In athletic contexts, improved movement control translates to enhanced performance, reduced injury risk, and optimized biomechanics. This integrated approach empowers individuals to move with greater ease, efficiency, and confidence, promoting long-term musculoskeletal health and enhancing overall quality of life. The ability to control movement with precision and stability forms the foundation for a healthy, active lifestyle.
4. Injury Rehabilitation
Injury rehabilitation represents a crucial application of Pilates and physical therapy principles, facilitating the restoration of function, reduction of pain, and prevention of re-injury. These methodologies offer a comprehensive approach to recovery, addressing the multifaceted nature of musculoskeletal injuries. The integration of Pilates and physical therapy provides a synergistic approach to rehabilitation, maximizing patient outcomes and promoting long-term musculoskeletal health. Addressing the underlying causes of injury, rather than solely managing symptoms, is paramount for effective rehabilitation.
Pilates, with its focus on core strengthening, postural control, and precise movement patterns, provides a valuable framework for restoring function after injury. Following a knee injury, for example, Pilates exercises can help strengthen supporting muscles, improve joint stability, and restore proper movement mechanics. Physical therapy complements this approach by addressing specific tissue impairments, utilizing manual therapy techniques to reduce pain and inflammation, and prescribing targeted exercises to improve range of motion and strength. A physical therapist might utilize modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation to facilitate tissue healing and pain management. The combined approach addresses both the localized injury and the broader kinetic chain, optimizing functional recovery and minimizing the risk of compensatory movement patterns. For instance, rehabilitation for a rotator cuff tear might involve Pilates exercises to improve scapular stability and postural alignment, combined with physical therapy modalities to reduce pain and inflammation, and specific exercises to strengthen the rotator cuff muscles.
Effective injury rehabilitation requires a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s specific needs and goals. Tailored rehabilitation programs consider the nature and severity of the injury, the individual’s physical condition, and their functional requirements. The collaborative nature of Pilates and physical therapy allows for a personalized approach, ensuring optimal recovery and long-term functional outcomes. By addressing the underlying causes of injury and promoting optimal movement patterns, this integrated approach empowers individuals to regain function, reduce pain, and prevent future injuries. This holistic approach to rehabilitation emphasizes not just the restoration of physical function, but also the promotion of overall well-being and the empowerment of individuals to actively participate in their recovery process.
5. Pain Management
Pain management represents a significant component within the integrated framework of Pilates and physical therapy. These disciplines offer a non-pharmacological approach to addressing pain, focusing on restoring function, improving movement mechanics, and promoting overall well-being. Chronic pain, often arising from musculoskeletal imbalances, injuries, or underlying medical conditions, can significantly impact quality of life. Addressing pain through movement-based therapies provides a pathway towards reclaiming functional capacity and reducing reliance on medication.
- Core Strengthening and Stability:
A strong core provides stability and support for the spine, reducing strain and alleviating back pain. Pilates exercises, such as the “Bridge” and “Plank,” target deep core muscles, enhancing spinal stability and reducing pain associated with lumbar instability or poor posture. Physical therapy complements this by addressing specific muscle weaknesses or imbalances that contribute to pain. For example, strengthening the transverse abdominis, a key core muscle, can significantly reduce lower back pain.
- Improved Flexibility and Range of Motion:
Restricted movement and muscle tightness can contribute to pain and limit functional capacity. Pilates exercises incorporate stretching and lengthening movements, improving flexibility and restoring optimal range of motion. Physical therapy utilizes manual therapy techniques, such as soft tissue mobilization and joint mobilization, to address specific restrictions and improve joint mobility. Increased flexibility in the hamstrings, for example, can alleviate lower back pain and improve posture.
- Postural Correction and Alignment:
Poor posture can place undue stress on joints and muscles, leading to pain and dysfunction. Pilates emphasizes postural awareness and correction through exercises that strengthen postural muscles and improve body alignment. Physical therapy employs postural assessments and corrective exercises to address specific postural deviations, such as forward head posture or rounded shoulders. Correcting postural imbalances can reduce neck and shoulder pain and improve overall musculoskeletal health.
- Neuromuscular Control and Movement Re-education:
Dysfunctional movement patterns can exacerbate pain and contribute to further injury. Pilates and physical therapy focus on re-educating movement patterns, improving neuromuscular control, and promoting efficient, pain-free movement. Following a knee injury, for example, targeted exercises and manual therapy can restore proper patellar tracking and reduce pain associated with patellofemoral pain syndrome. Improving movement mechanics reduces stress on injured tissues and promotes functional recovery.
By addressing the underlying causes of pain through movement-based interventions, Pilates and physical therapy offer a pathway towards long-term pain management and improved quality of life. These integrated approaches empower individuals to regain control over their bodies, reduce reliance on medication, and cultivate sustainable strategies for managing pain. The emphasis on functional movement, core stability, and postural correction provides a holistic approach to pain management, fostering overall well-being and enhancing physical capacity.
6. Functional Restoration
Functional restoration represents a central objective within the combined application of Pilates and physical therapy. It emphasizes regaining the ability to perform essential daily activities and participate in meaningful life roles. Restoring functional capacity often necessitates addressing underlying impairments such as limited range of motion, muscle weakness, postural imbalances, and pain. These impairments can arise from injury, surgery, chronic conditions, or deconditioning. A structured, progressive approach is essential to guide individuals towards achieving functional goals, whether that involves returning to work, participating in recreational activities, or simply performing tasks of daily living with greater ease and independence. Cause and effect relationships are carefully considered; for example, limited hip mobility can restrict functional activities such as walking or climbing stairs. Addressing this underlying impairment through targeted interventions facilitates improved functional capacity.
The integration of Pilates and physical therapy provides a comprehensive framework for functional restoration. Pilates exercises enhance core strength, postural control, and movement efficiency, laying the foundation for functional movement patterns. Physical therapy complements this approach by addressing specific impairments, utilizing manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and modalities to restore optimal biomechanics. For instance, an individual recovering from a stroke might utilize Pilates to improve core stability and balance, while physical therapy focuses on regaining upper extremity function and gait training. Real-life examples illustrate the practical significance of this integrated approach. A construction worker recovering from a back injury might utilize both modalities to regain the strength and mobility needed to return to work safely. Similarly, an athlete recovering from an ACL tear might integrate Pilates and physical therapy to restore knee stability, improve neuromuscular control, and regain pre-injury performance levels. The goal is to restore not just physical capacity, but also the confidence and self-efficacy necessary to fully participate in life’s activities.
Successfully achieving functional restoration requires a collaborative and patient-centered approach. Thorough assessments identify specific functional limitations and inform the development of individualized treatment plans. Regular monitoring and reassessment ensure that the program remains aligned with the individual’s progress and evolving needs. Challenges such as pain, fear of movement, or psychological factors can impede progress. Addressing these challenges through integrated pain management strategies, graded exposure, and psychological support optimizes the likelihood of achieving functional goals. Ultimately, functional restoration empowers individuals to regain independence, improve quality of life, and return to meaningful activities. This outcome represents a fundamental goal shared by both Pilates and physical therapy, underscoring the synergistic power of their combined application.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the integration of Pilates and physical therapy, providing clarity on their combined benefits and applications.
Question 1: How do Pilates and physical therapy complement each other in rehabilitation?
Pilates emphasizes core strengthening, postural control, and precise movement patterns, creating a solid foundation for functional recovery. Physical therapy addresses specific impairments through targeted exercises, manual therapy, and modalities, facilitating tissue healing and restoring optimal biomechanics. The combined approach optimizes rehabilitation outcomes.
Question 2: Is Pilates suitable for individuals with chronic pain?
When appropriately modified and supervised by qualified practitioners, Pilates can be highly effective for managing chronic pain. The focus on core strengthening, flexibility, and postural correction can alleviate pain stemming from musculoskeletal imbalances and improve overall function. However, consulting a healthcare professional is essential to determine suitability and ensure safe implementation.
Question 3: Can Pilates replace traditional physical therapy?
While Pilates offers numerous benefits, it does not replace traditional physical therapy, particularly in cases of injury or specific medical conditions requiring specialized interventions. Physical therapy provides comprehensive assessments, diagnoses, and treatment plans tailored to individual needs. Pilates can serve as a valuable adjunct to physical therapy, enhancing core strength, flexibility, and movement control.
Question 4: What conditions can benefit from the combined approach of Pilates and physical therapy?
A wide range of conditions, including back pain, neck pain, arthritis, osteoporosis, post-surgical rehabilitation, and balance disorders, can benefit from this integrated approach. The combined modalities address musculoskeletal imbalances, improve functional capacity, and enhance overall well-being.
Question 5: How does one find qualified practitioners for Pilates and physical therapy?
Seeking recommendations from healthcare providers, researching certified Pilates instructors with specialized training in rehabilitation, and verifying physical therapists’ credentials and experience are crucial steps in finding qualified practitioners. Ensuring practitioners possess relevant certifications and experience within their respective fields is essential for safe and effective treatment.
Question 6: What is the typical duration of a combined Pilates and physical therapy program?
Program duration varies based on individual needs, goals, and the specific condition being addressed. Some individuals may experience benefits within a few weeks, while others may require longer-term programs for optimal results. Consistency and adherence to the prescribed program are key factors influencing treatment outcomes.
Understanding the complementary nature of these disciplines empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their healthcare and pursue comprehensive strategies for achieving optimal physical well-being.
The next section will delve into specific case studies illustrating the practical application and benefits of integrating Pilates and physical therapy for various conditions.
Conclusion
This exploration of Pilates and physical therapy has highlighted their complementary nature and synergistic potential within various healthcare contexts. Their combined application offers a comprehensive approach to movement rehabilitation, pain management, and functional restoration. Key benefits include enhanced core strength, improved postural alignment, refined movement control, and optimized injury recovery. The integration of these methodologies addresses not only physical impairments but also promotes overall well-being and empowers individuals to actively participate in their healthcare journey.
The evolving landscape of healthcare increasingly emphasizes integrative approaches that prioritize patient-centered care and address the multifaceted nature of health and well-being. Pilates and physical therapy, when strategically combined, offer a valuable model for achieving optimal functional outcomes and enhancing quality of life. Further research exploring the long-term effects and broader applications of this integrated approach promises to unlock even greater potential for improving musculoskeletal health and promoting lifelong wellness.