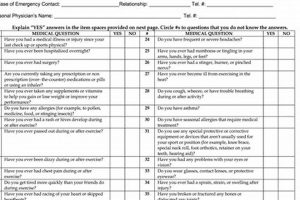
Section 6 of the Pennsylvania Interscholastic Athletic Association (PIAA) Comprehensive Initial Pre-Participation Evaluation (CIPPE) form addresses medical history. This section requires a comprehensive overview of the athlete’s past and current health conditions, including allergies, chronic illnesses, prior injuries, surgeries, and current medications. Providing detailed and accurate information in this section is crucial for ensuring the athlete’s safety and well-being.
The thorough documentation required in this part of the CIPPE serves several critical functions. It allows medical professionals to assess potential risks associated with athletic participation and make informed decisions regarding necessary precautions or restrictions. The historical health data provides valuable context for diagnosing and treating future injuries or illnesses. This comprehensive record also protects both the athlete and the school from liability by demonstrating due diligence in evaluating pre-existing conditions. The information contributes to a more holistic approach to student-athlete healthcare.
This understanding of the CIPPE’s medical history component lays the foundation for a deeper examination of the form’s other sections and their collective role in ensuring student-athlete safety and eligibility. Further exploration will cover topics such as the required physical examination, cardiac screening, and concussion baseline testing.
Tips for Completing the Medical History Section of the PIAA CIPPE Form
Accurate and complete medical information is crucial for athlete safety and appropriate medical care. The following tips provide guidance for completing the medical history section of the PIAA’s Comprehensive Initial Pre-Participation Evaluation (CIPPE) form.
Tip 1: Be Thorough: Disclose all medical conditions, regardless of perceived severity. Seemingly minor issues can sometimes have significant implications for athletic participation. Include details like dates, diagnoses, treatments, and any ongoing management.
Tip 2: List All Medications: Include prescription and over-the-counter medications, supplements, and herbal remedies. Note dosages and frequency. This information is essential for understanding potential drug interactions or contraindications related to sports activities.
Tip 3: Detail Prior Injuries: Describe all previous injuries, even if fully recovered. Include dates, locations, types of injuries, and treatments received. This history can help medical professionals identify potential risk factors for recurring injuries.
Tip 4: Document All Surgeries: Provide details about any surgeries, including dates, procedures performed, and any ongoing complications or limitations. This information is important for assessing potential vulnerabilities related to physical activity.
Tip 5: Address Allergies: List all allergies, including environmental, food, and medication allergies. Specify the type of reaction experienced. This information is critical for emergency preparedness and avoiding potential triggers during practices or competitions.
Tip 6: Provide Family History: Disclose any relevant family history of medical conditions, particularly those with potential implications for athletic participation, such as cardiac conditions or bleeding disorders.
Tip 7: Consult Medical Records: Refer to medical records for accuracy and completeness. This helps ensure that all relevant information is included and avoids omissions or inaccuracies.
Accurate completion of the medical history section facilitates a thorough evaluation of an athlete’s health status. This comprehensive approach promotes informed decision-making regarding participation and contributes to the overall safety and well-being of student-athletes.
This detailed guidance on completing the medical history portion transitions to a broader discussion on the overall importance of the PIAA CIPPE form and its role in safeguarding student-athlete health. The following sections will address other key components of the form and their contributions to a comprehensive pre-participation evaluation.
1. Comprehensive Medical History
Section 6 of the PIAA physical form serves as the repository for the athlete’s comprehensive medical history. This detailed record of past and present health conditions forms the cornerstone of the pre-participation evaluation. The connection between a comprehensive medical history and this section is inextricably linked; the section’s efficacy relies entirely on the thoroughness and accuracy of the information provided. This historical data provides critical context for understanding current health status and potential future risks. For example, a history of asthma influences decisions regarding exercise-induced bronchospasm management, while prior concussions inform return-to-play protocols. The absence of a comprehensive history can lead to misdiagnosis, improper treatment, and increased risk of further injury.
Consider a scenario where an athlete experiences recurring shoulder pain during practice. A comprehensive medical history revealing a previous shoulder dislocation, documented in Section 6, provides valuable insight for the evaluating physician. This information guides the examination, diagnostic testing, and subsequent treatment plan. Without this historical context, the current shoulder pain might be misattributed to a minor strain, potentially delaying appropriate intervention and increasing the risk of re-injury. Another example involves an athlete with a family history of cardiac conditions. This information, disclosed in Section 6, prompts further cardiac screening and evaluation, potentially identifying underlying conditions that might otherwise go undetected. This proactive approach can prevent potentially life-threatening complications during strenuous physical activity.
In conclusion, the significance of a comprehensive medical history within the context of Section 6 of the PIAA physical form cannot be overstated. The thorough documentation of past and present medical conditions, injuries, surgeries, medications, allergies, and family history provides essential information for assessing risk, guiding treatment decisions, and ensuring athlete safety. Challenges in obtaining complete and accurate information underscore the need for collaboration between athletes, parents/guardians, and medical professionals. This collaborative effort ensures the effectiveness of the pre-participation evaluation process and ultimately contributes to the well-being of student-athletes. This meticulous approach to medical history directly contributes to informed decision-making and risk mitigation strategies crucial for protecting student-athlete health and safety.
2. Past and Current Conditions
Section 6 of the PIAA physical form requires detailed disclosure of past and current medical conditions. This information is crucial for assessing an athlete’s fitness for participation and developing appropriate risk management strategies. Understanding the scope of reportable conditions and their potential impact on athletic activity is essential for accurate completion of this section.
- Chronic Illnesses:
Conditions like asthma, diabetes, epilepsy, and heart conditions require careful management in the context of athletic participation. For example, an athlete with asthma must have an asthma action plan in place, while an athlete with diabetes needs to monitor blood glucose levels closely. Disclosing these conditions allows medical professionals to provide appropriate guidance and ensure the athlete’s safety.
- Prior Injuries:
Previous injuries, even if seemingly resolved, can predispose athletes to future problems. A history of ankle sprains, for instance, might indicate a need for ankle support or specific training exercises. Accurate reporting of prior injuries helps prevent re-injury and ensures appropriate preventative measures are implemented.
- Current Musculoskeletal Issues:
Ongoing issues like joint pain, muscle strains, or limited range of motion can significantly impact athletic performance and increase injury risk. Disclosing these conditions allows medical professionals to assess the athlete’s readiness for participation and recommend appropriate modifications or treatment.
- Mental Health Conditions:
Conditions such as anxiety and depression can also influence an athlete’s well-being and performance. While these conditions might not always present direct physical limitations, disclosing them can facilitate access to support services and ensure the athlete receives holistic care.
The detailed disclosure of past and current conditions in Section 6 contributes significantly to the overall effectiveness of the PIAA physical form. This information empowers medical professionals to make informed decisions about an athlete’s eligibility and develop individualized plans to mitigate potential risks. The goal is to maximize athlete safety and well-being while facilitating participation in interscholastic sports. Failure to disclose relevant information can have significant consequences, potentially jeopardizing the athlete’s health and eligibility.
3. Injuries and Surgeries
Section 6 of the PIAA physical form requires comprehensive disclosure of all past injuries and surgeries. This information is critical for assessing potential risks and ensuring athlete safety. Accurate and detailed reporting of injuries and surgeries allows medical professionals to evaluate potential vulnerabilities, recommend appropriate preventative measures, and make informed decisions regarding participation in interscholastic athletics.
- Joint Injuries:
Previous joint injuries, such as sprains, dislocations, or ligament tears, can increase the risk of future problems. For example, an athlete with a history of ankle sprains might require ankle bracing or specific exercises to improve stability. Disclosing these injuries allows medical professionals to assess joint stability, range of motion, and potential long-term consequences. This information informs decisions regarding participation and the need for preventative measures or rehabilitation.
- Fractures:
Previous fractures, even if healed, can weaken bone structure and increase the risk of re-fracture. Details about the location, type, and treatment of previous fractures are essential. This information allows medical professionals to evaluate bone density, healing status, and potential long-term complications. In some cases, further imaging studies might be necessary to ensure complete healing and assess the risk of future fractures.
- Surgeries:
Information about past surgeries, including the type of procedure, date, and any complications, is crucial. Surgical history can significantly influence an athlete’s physical capabilities and limitations. For instance, an athlete who underwent knee surgery might require specific rehabilitation exercises or activity modifications. Disclosing surgical history allows medical professionals to assess post-surgical recovery, potential complications, and functional limitations. This information is essential for determining appropriate activity levels and preventing re-injury.
- Concussions:
Previous concussions require special attention due to the potential for long-term neurological consequences. Accurate reporting of past concussions, including dates, symptoms, and recovery time, is essential. This information informs decisions about return-to-play protocols and the need for further neurological evaluation. Failure to disclose previous concussions can have serious implications, increasing the risk of further brain injury and long-term complications.
The detailed documentation of injuries and surgeries in Section 6 of the PIAA physical form allows for a comprehensive assessment of an athlete’s medical history. This information plays a pivotal role in identifying potential risks, guiding preventative measures, and making informed decisions about participation in interscholastic sports. By understanding the significance of this information, athletes, parents/guardians, and medical professionals can collaborate effectively to ensure athlete safety and well-being.
4. Medications and Allergies
Section 6 of the PIAA physical form necessitates detailed disclosure of all medications and allergies. This information is critical for several reasons. Medications can have significant effects on athletic performance and may interact with other substances or conditions. Allergies can pose serious health risks, particularly in the context of strenuous physical activity. Accurate reporting of medications and allergies allows medical professionals to assess potential risks, guide appropriate management strategies, and ensure the athlete’s safety.
Consider an athlete taking medication for a heart condition. This information is crucial for understanding potential exercise limitations or necessary precautions. Another example involves an athlete with a severe nut allergy. Knowledge of this allergy allows for appropriate emergency preparedness and avoidance of potential triggers during practices and competitions. In both cases, disclosing this information in Section 6 facilitates informed decision-making and contributes to the athlete’s well-being. The omission of such details could have serious consequences, ranging from adverse drug reactions to life-threatening allergic reactions. For instance, an athlete with asthma who fails to disclose their use of an inhaler may experience breathing difficulties during strenuous exercise. Similarly, an athlete with a known allergy to bee stings who does not communicate this information may not receive prompt and appropriate medical attention in the event of an allergic reaction.
Comprehensive disclosure of medications and allergies in Section 6 of the PIAA physical form is paramount for safeguarding athlete health and safety. This information allows medical professionals to assess potential risks, tailor treatment plans, and implement preventative measures. Challenges in obtaining complete and accurate information underscore the need for collaboration between athletes, parents/guardians, and medical professionals. This collaborative effort is essential for ensuring the effectiveness of the pre-participation evaluation and protecting student-athletes from preventable health risks. The practical significance of this understanding lies in its contribution to informed decision-making regarding athlete participation, appropriate medical management, and emergency preparedness. It forms a critical component of the comprehensive approach to student-athlete healthcare embodied by the PIAA physical form.
5. Family Medical History
Section 6 of the PIAA physical form includes a dedicated section for family medical history. This component plays a crucial role in assessing potential genetic predispositions to certain medical conditions that may impact an athlete’s safety and eligibility for participation. Specific conditions, such as sudden cardiac death, Marfan syndrome, and sickle cell trait, have known genetic components. Knowledge of a family history of these conditions allows for targeted screening and preventative measures. This proactive approach can identify potential risks and guide appropriate medical management, ultimately safeguarding athlete health and well-being.
Consider an athlete with a family history of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), a condition that can cause sudden cardiac death during strenuous exercise. Disclosing this family history in Section 6 prompts further cardiac evaluation, such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) or echocardiogram. Early detection of HCM allows for appropriate medical intervention, including activity restrictions or medication, which can significantly reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death. Another example involves an athlete with a family history of Marfan syndrome, a connective tissue disorder that can affect the cardiovascular system. Knowledge of this family history prompts careful evaluation of the athlete’s cardiovascular system and skeletal structure. Early diagnosis of Marfan syndrome allows for appropriate monitoring and management, reducing the risk of complications such as aortic dissection.
The inclusion of family medical history in Section 6 underscores the comprehensive approach of the PIAA physical form in assessing athlete health. This information provides valuable insights into potential genetic predispositions and facilitates early detection of potentially life-threatening conditions. Challenges in obtaining complete and accurate family medical history information highlight the importance of communication between athletes, parents/guardians, and medical professionals. Accurate reporting of family medical history is essential for ensuring the efficacy of the pre-participation evaluation and promoting informed decision-making regarding athlete safety and eligibility. This proactive approach to risk assessment is fundamental to protecting student-athletes and fostering a safe and healthy environment for interscholastic sports participation.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the medical history component of the Pennsylvania Interscholastic Athletic Association (PIAA) physical form, specifically Section 6. Clear and accurate completion of this section is crucial for ensuring athlete safety and eligibility.
Question 1: Why is a comprehensive medical history necessary for athletic participation?
A comprehensive medical history provides essential context for evaluating an athlete’s current health status and potential risks associated with sports participation. This information guides medical professionals in making informed decisions regarding necessary precautions, activity modifications, or further medical evaluation.
Question 2: What specific information should be included in the medical history section?
This section requires disclosure of all past and current medical conditions, including chronic illnesses, prior injuries, surgeries, medications, allergies, and family medical history. Detailed information about dates, diagnoses, treatments, and ongoing management should be provided.
Question 3: What are the potential consequences of omitting or inaccurately reporting medical information?
Omitting or inaccurately reporting medical information can have serious consequences, potentially jeopardizing the athlete’s health and eligibility for participation. Incomplete information may lead to misdiagnosis, improper treatment, and increased risk of further injury.
Question 4: How does family medical history contribute to the pre-participation evaluation?
Family medical history provides insights into potential genetic predispositions to certain medical conditions, such as sudden cardiac death or Marfan syndrome. This information can prompt further screening and preventative measures, safeguarding athlete health.
Question 5: What if an athlete is unsure about certain aspects of their medical history?
Athletes should consult with parents/guardians and medical providers to clarify any uncertainties regarding their medical history. Reviewing medical records can ensure accuracy and completeness of the information provided.
Question 6: How does accurate completion of the medical history section benefit the athlete?
Accurate completion of the medical history section allows for a comprehensive assessment of the athlete’s health status, contributing to informed decision-making regarding participation and the development of individualized plans to mitigate potential risks.
Accurate and comprehensive disclosure of medical information is paramount for promoting athlete safety and well-being. Open communication between athletes, parents/guardians, and medical professionals is essential for ensuring the effectiveness of the pre-participation evaluation process.
The following sections will delve into specific aspects of the PIAA physical form, providing further guidance on completing each section accurately and understanding its significance in the context of interscholastic athletics.
Conclusion
This exploration of Section 6 of the PIAA physical form has underscored its critical role in safeguarding student-athlete health and well-being. The section’s comprehensive approach to medical history, encompassing past and current conditions, injuries, surgeries, medications, allergies, and family history, provides essential information for assessing risk, guiding treatment decisions, and ensuring athlete safety. Accurate completion of this section facilitates informed decision-making regarding participation eligibility and the development of individualized plans to mitigate potential risks. The information provided serves as a cornerstone for the pre-participation evaluation process, enabling medical professionals to make sound judgments about an athlete’s readiness for interscholastic sports.
The significance of Section 6 extends beyond mere compliance with regulatory requirements. It represents a commitment to prioritizing the health and safety of student-athletes. Accurate and thorough completion of this section is not merely a formality but a crucial step in fostering a safe and supportive environment for athletic participation. This proactive approach to risk assessment and medical management is fundamental to protecting young athletes and ensuring their long-term well-being. The responsibility for accurate and complete disclosure rests with all stakeholders, including athletes, parents/guardians, and medical professionals. This shared responsibility reflects a collective commitment to promoting a culture of safety and well-being within interscholastic athletics. The continued emphasis on comprehensive medical history evaluations will undoubtedly contribute to a healthier and safer future for student-athletes.