Routine medical checkups, even without health coverage, provide a baseline understanding of one’s health status. These examinations can detect potential problems early, sometimes before symptoms arise, allowing for timely intervention and potentially reducing future healthcare costs. For instance, screenings for high blood pressure or cholesterol can identify risk factors for cardiovascular disease, enabling lifestyle changes or medical treatments that might prevent serious illness.
Preventive healthcare plays a vital role in overall well-being and long-term health outcomes. Historically, access to such care has been a challenge for uninsured individuals. However, the increasing availability of free or low-cost clinics, community health centers, and preventative health screenings offered through public health initiatives makes access to these vital services more feasible. Early detection and management of health issues can significantly improve quality of life and potentially reduce the need for more extensive and costly medical interventions later.
This discussion will further explore options for accessing affordable healthcare, strategies for managing healthcare costs without insurance, and the importance of preventive medical services. It will also delve into specific examples of accessible health screenings and resources available to those without traditional health insurance.
Tips for Accessing Affordable Healthcare
Navigating the healthcare system without insurance can be challenging. The following tips offer guidance for accessing necessary medical services, including routine checkups, while minimizing costs.
Tip 1: Utilize Community Health Centers: Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs) offer comprehensive primary care services on a sliding fee scale based on income. Services often include checkups, vaccinations, and management of chronic conditions.
Tip 2: Explore Free and Charitable Clinics: Many communities offer free or low-cost clinics staffed by volunteer healthcare professionals. These clinics often provide basic medical care, including physical examinations and limited diagnostic testing.
Tip 3: Seek Preventative Screenings at Public Health Events: Local health departments and community organizations frequently host events offering free screenings for conditions like high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
Tip 4: Negotiate Directly with Healthcare Providers: Contact physicians’ offices or clinics directly to inquire about discounted rates for cash-paying patients. Some providers offer reduced fees for those without insurance.
Tip 5: Consider Medical Tourism for Certain Procedures: For non-emergency procedures, exploring healthcare options in other countries can sometimes provide significant cost savings.
Tip 6: Research Prescription Assistance Programs: Several pharmaceutical companies offer patient assistance programs that can reduce or eliminate the cost of prescription medications.
Tip 7: Utilize Online Resources and Telemedicine: Some online platforms offer virtual consultations with healthcare professionals at lower costs than traditional in-person visits. These can be helpful for managing certain health conditions.
By utilizing these strategies, individuals can access essential medical services and maintain their health, even without traditional health insurance coverage. Proactive healthcare management contributes significantly to overall well-being and can mitigate potential health risks.
This information provides a starting point for navigating affordable healthcare options. Further research and consultation with healthcare professionals are recommended for individualized guidance.
1. Preventive Care
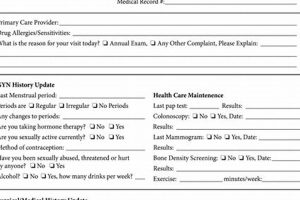
Preventive care plays a crucial role in maintaining health and well-being, particularly for individuals without health insurance. Regular checkups and screenings can detect potential health issues early, potentially reducing the need for more costly interventions later. Accessing preventive care without insurance requires navigating a complex landscape of resources and options.
- Early Detection and Intervention
Early detection of health issues, such as high blood pressure or certain types of cancer, through preventive screenings can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Early intervention often allows for less invasive and less expensive treatment options, minimizing the financial burden often associated with managing more advanced diseases. For example, regular blood pressure monitoring can help prevent strokes, heart attacks, and kidney disease, which can incur substantial costs if left unmanaged. This is particularly relevant for those without insurance, as early detection can prevent the progression to more serious and costly health problems.
- Cost-Effectiveness of Prevention
While the cost of routine checkups may seem daunting without insurance, preventive care often proves more cost-effective in the long run. Managing chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease through regular monitoring and medication can prevent expensive hospitalizations and emergency room visits. For example, managing diabetes through regular checkups, blood sugar monitoring, and medication can prevent complications such as nerve damage, blindness, and kidney failure, which are significantly more expensive to treat. Investing in preventive care, even without insurance, can represent a significant long-term cost saving.
- Navigating Resources for the Uninsured
Several resources exist to help uninsured individuals access preventive care. Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs) offer services on a sliding fee scale based on income. Free clinics and community health events often provide free screenings for various health conditions. Additionally, some healthcare providers offer discounted rates for cash-paying patients. Understanding these resources can empower individuals to prioritize their health, even without traditional insurance coverage.
- Long-Term Health and Financial Implications
Consistent preventive care contributes significantly to long-term health and can mitigate the financial risks associated with unexpected illnesses. By managing chronic conditions and identifying potential problems early, individuals can maintain a higher quality of life and potentially reduce the long-term financial burden of healthcare. This proactive approach to health management is especially important for those without insurance, as it can help minimize the risk of catastrophic health expenses.
Accessing preventive care without insurance requires proactive planning and resourcefulness. By understanding the importance of early detection, utilizing available resources, and recognizing the long-term financial implications of neglecting preventive care, individuals can take control of their health and well-being, mitigating potential health risks and financial burdens. A focus on prevention often leads to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs over time, regardless of insurance status.
2. Cost Considerations
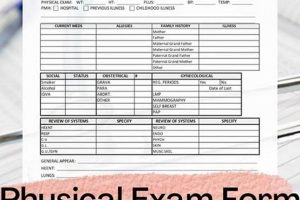
Cost considerations are central to the decision-making process for individuals seeking medical care without insurance. Financial constraints can create significant barriers to accessing routine checkups and preventive services. Understanding the various cost factors associated with medical care and exploring available resources are essential for navigating healthcare without insurance. The following facets explore key cost considerations related to accessing medical examinations without insurance coverage.
- Clinic Fees and Service Charges
The cost of a physical exam can vary significantly depending on the provider and the services included. Free clinics and community health centers often offer reduced fees or sliding-scale payment options based on income. Private clinics may offer discounted cash prices for uninsured patients, but these can still be substantial. Understanding the fee structure of different healthcare providers is essential for making informed decisions and budgeting appropriately.
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Testing Costs
Medical examinations may necessitate laboratory tests, such as blood work or urinalysis, and diagnostic procedures, like X-rays or EKGs. These tests and procedures incur additional costs, which can vary depending on the facility and the type of test. Patients should inquire about the cost of these services beforehand and explore options for reducing expenses, such as negotiating with providers or seeking financial assistance programs.
- Medication Expenses
If a medical examination reveals a condition requiring medication, the cost of prescriptions adds another layer of financial complexity for uninsured individuals. Prescription medication costs can be substantial, especially for long-term conditions. Exploring options such as generic medications, patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical companies, and online pharmacies can help mitigate these expenses.
- Long-Term Cost Implications of Foregoing Care
While the upfront cost of a medical examination without insurance may seem prohibitive, delaying or forgoing necessary care can lead to more serious and costly health issues in the future. Untreated conditions can progress, requiring more extensive and expensive interventions later. Investing in preventive care, even without insurance, can ultimately save money and improve long-term health outcomes.
Navigating the healthcare system without insurance requires careful consideration of cost factors at each stage, from the initial examination to potential follow-up care and medication. Proactive planning, research, and communication with healthcare providers are essential for minimizing costs and maximizing access to necessary medical services. Understanding the financial implications of delaying or forgoing care underscores the importance of prioritizing preventive health, even in the face of financial constraints.
3. Community Resources
Access to routine medical examinations without insurance often relies heavily on community resources. These resources provide crucial support for individuals seeking affordable healthcare options. Understanding the role of these resources is essential for navigating the complexities of healthcare access without traditional insurance coverage.
- Free and Charitable Clinics
Free and charitable clinics represent a cornerstone of healthcare access for uninsured individuals. These clinics, often staffed by volunteer medical professionals, provide basic medical services, including physical examinations, at no or low cost. Eligibility criteria may vary depending on location and specific clinic policies. For example, some clinics may serve only individuals below a certain income threshold, while others may focus on specific populations, such as the homeless or undocumented immigrants. The availability of these clinics significantly expands access to essential medical services for those without insurance.
- Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs)
FQHCs offer comprehensive primary care services, including physical examinations, on a sliding fee scale based on income. These centers provide crucial access points for preventive care and management of chronic conditions. FQHCs play a vital role in providing continuous and comprehensive care, particularly for individuals with limited financial resources. For instance, individuals can access routine checkups, vaccinations, and management of conditions like diabetes or hypertension at a cost aligned with their ability to pay. This makes consistent healthcare management more attainable for those without insurance.
- Public Health Departments and Community Health Events
Local public health departments and community organizations frequently offer free health screenings and educational programs. These events provide opportunities for individuals to receive basic health assessments, including blood pressure checks, cholesterol screenings, and diabetes testing. Such initiatives promote early detection and disease prevention, particularly for those who may not otherwise have access to routine medical care. For example, free flu shot clinics and health fairs provide access to preventive services and raise awareness about important health issues within the community.
- State and Local Programs for the Uninsured
Various state and local programs offer specific resources and assistance for uninsured residents. These programs may provide access to subsidized healthcare services, prescription assistance, or guidance on navigating the healthcare system. For example, some states offer programs that provide temporary or limited health insurance coverage to individuals who do not qualify for other forms of insurance. Researching and understanding available state and local programs is crucial for maximizing access to affordable healthcare options.
Community resources provide a critical safety net for individuals seeking medical examinations and preventive care without health insurance. Utilizing these resources requires proactive research and engagement with local organizations. By understanding the range of available services and eligibility criteria, individuals can effectively navigate the complexities of healthcare access and prioritize their well-being, even without traditional insurance coverage. These resources are essential for bridging the gap in healthcare access and ensuring that essential medical services are available to all members of the community, regardless of insurance status.
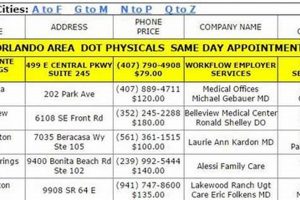
4. Affordable Options
Affordable options represent a critical link between healthcare access and the uninsured population. The availability of low-cost or no-cost medical examinations directly influences whether individuals without insurance seek preventive care. Cost often serves as a significant barrier, deterring those with limited financial resources from obtaining necessary medical services. A direct correlation exists between the affordability of healthcare and the likelihood of early detection and intervention for various health conditions. For instance, accessible blood pressure screenings at community health centers can lead to early diagnosis and management of hypertension, potentially preventing more severe cardiovascular complications later. Conversely, the absence of affordable options can lead to delayed diagnoses and increased healthcare costs in the long run. When routine medical examinations are financially accessible, individuals are more likely to engage with the healthcare system proactively, improving overall health outcomes.
Several factors influence the affordability of healthcare options for the uninsured. Government-funded programs, such as Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs), play a crucial role in providing subsidized care. Charitable organizations and free clinics also contribute significantly to the landscape of affordable healthcare, offering services based on donations and volunteer efforts. Sliding-scale fee structures, based on income and family size, further enhance accessibility for those with limited financial means. Negotiated discounts with healthcare providers represent another avenue for reducing costs, particularly for cash-paying patients. Furthermore, advancements in telemedicine offer opportunities for remote consultations and monitoring, potentially reducing the need for costly in-person visits. The interplay of these factors determines the spectrum of affordable options available to uninsured individuals.
Understanding the landscape of affordable options is essential for navigating healthcare without insurance. Strategic utilization of available resources requires proactive research and planning. Individuals must identify local free clinics, FQHCs, and community health events offering low-cost or no-cost examinations. Furthermore, understanding eligibility criteria for various programs is crucial for maximizing access to available benefits. Ultimately, the accessibility of affordable options directly impacts individual health outcomes and the overall well-being of the community. Addressing the financial barriers to healthcare remains a significant challenge, requiring ongoing efforts to expand access to affordable and quality medical services for all, regardless of insurance status.
5. Early Detection
Early detection of underlying health conditions represents a cornerstone of preventive medicine and holds particular significance for individuals lacking health insurance. Routine physical examinations, even without insurance coverage, provide crucial opportunities for identifying potential health risks before they escalate into more serious and costly medical problems. This proactive approach to healthcare empowers individuals to take control of their health, mitigating potential long-term complications and financial burdens. The connection between early detection and routine physicals for the uninsured is multifaceted, involving a complex interplay of access, affordability, and health outcomes.
Consider the case of an individual who, despite lacking insurance, accesses a free community health clinic for a routine checkup. During the examination, elevated blood pressure is detected. This early detection allows for prompt lifestyle interventions, such as dietary changes and increased physical activity, potentially preventing the development of hypertension and its associated complications, such as heart disease or stroke. Without access to that routine physical, the individual might have remained unaware of the underlying issue until experiencing more severe symptoms, potentially requiring more extensive and costly medical interventions. This underscores the practical significance of early detection through accessible physical examinations, even in the absence of traditional insurance.
Early detection through routine physicals, even without insurance, offers several tangible benefits. Timely identification of chronic conditions like diabetes or high cholesterol allows for early intervention and management, improving long-term health outcomes and reducing the risk of costly complications. Furthermore, early detection of certain cancers significantly increases the likelihood of successful treatment and survival. While financial constraints often pose barriers to accessing healthcare for the uninsured, prioritizing preventive measures like routine physicals can ultimately reduce overall healthcare expenditures by mitigating the need for more intensive and expensive interventions later. Navigating the healthcare system without insurance requires proactive engagement with community resources and affordable healthcare options. Understanding the profound impact of early detection underscores the importance of seeking routine medical care, regardless of insurance status, to protect long-term health and well-being.
6. Financial Planning
Financial planning plays a crucial role in navigating healthcare expenses, particularly for individuals without health insurance. The absence of insurance coverage necessitates proactive financial strategies to mitigate the potential costs associated with medical care, including routine physical examinations. Effective financial planning empowers individuals to prioritize preventive healthcare while managing the financial risks associated with unexpected illnesses or injuries. This proactive approach to healthcare finance requires careful consideration of various factors, including budgeting, saving, and exploring affordable healthcare options.
- Budgeting for Routine Checkups
Allocating funds specifically for routine physical examinations and preventive screenings becomes essential when managing healthcare expenses without insurance. Creating a dedicated healthcare budget allows individuals to anticipate and plan for these costs, minimizing the financial strain of unexpected medical bills. For example, setting aside a small amount each month can accumulate to cover the cost of an annual physical or necessary lab tests. This proactive budgeting strategy helps prioritize preventive care and avoids delaying essential checkups due to financial constraints.
- Establishing an Emergency Medical Fund
An emergency medical fund provides a financial safety net for unexpected medical expenses, such as emergency room visits or urgent care needs. This fund serves as a critical resource for individuals without insurance, protecting them from the potentially devastating financial consequences of unforeseen illnesses or injuries. For instance, an emergency fund can cover the cost of unexpected diagnostic tests, prescription medications, or even a short hospital stay, mitigating the financial burden of such events.
- Exploring Affordable Healthcare Options
Navigating the healthcare system without insurance requires diligent research and exploration of affordable options. Free clinics, community health centers, and sliding-scale services offer cost-effective solutions for routine checkups and preventive care. Understanding the resources available within the community empowers individuals to access necessary medical services while minimizing expenses. For example, researching local free clinics or community health centers offering low-cost physical exams can significantly reduce the financial burden of routine healthcare.
- Negotiating Healthcare Costs and Payment Plans
Directly negotiating with healthcare providers regarding fees and payment plans offers another avenue for managing healthcare expenses without insurance. Many providers offer discounted rates for cash-paying patients or are willing to establish flexible payment plans to accommodate individual financial circumstances. Open communication with healthcare providers about financial constraints can lead to mutually agreeable payment arrangements, facilitating access to necessary medical services while minimizing financial strain.
Financial planning provides a framework for managing healthcare expenses, empowering individuals without insurance to prioritize preventive care and mitigate the financial risks associated with unexpected medical needs. By incorporating budgeting, saving, and resource exploration into their financial plans, individuals can proactively manage healthcare costs, ensuring access to essential services like routine physical examinations while safeguarding their financial well-being. This proactive approach to healthcare finance enables informed decision-making and fosters a sense of control over healthcare expenses, even in the absence of traditional insurance coverage. It underscores the crucial link between financial planning and access to essential healthcare services for the uninsured population.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding access to physical examinations and other healthcare services without health insurance. Understanding the available options and resources is crucial for navigating the complexities of healthcare access for the uninsured.
Question 1: How can one find affordable physical exams without insurance?
Several resources offer affordable or free physical exams. Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs) provide services on a sliding fee scale based on income. Free clinics and community health events often offer free screenings and examinations. Additionally, some private physicians offer discounted rates for cash-paying patients. Researching local options is crucial.
Question 2: What are the potential risks of delaying or forgoing routine physicals due to lack of insurance?
Delaying or forgoing routine physicals can lead to delayed diagnoses of serious health conditions. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment and improved health outcomes. Preventive care, even without insurance, is often more cost-effective in the long run by preventing costly interventions for advanced diseases.
Question 3: Do free clinics offer the same quality of care as private practices?
Free clinics are typically staffed by licensed medical professionals, including physicians, nurses, and other healthcare providers, often on a volunteer basis. They strive to provide high-quality care, though the range of services offered may differ from private practices due to resource limitations. Focusing on preventive services and basic medical needs is common.
Question 4: What documents are typically required when visiting a free clinic or FQHC?
Requirements vary depending on the specific clinic. Proof of income or residency may be necessary for services at FQHCs due to their sliding fee scales. Free clinics often have less stringent requirements, focusing on serving the uninsured regardless of documentation status. Contacting the specific clinic in advance is recommended.
Question 5: How can one access prescription medications affordably without insurance?
Several options exist for reducing prescription medication costs. Patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical companies can significantly lower or eliminate medication costs. Generic medications are typically less expensive than brand-name drugs. GoodRx and similar online resources offer coupons and price comparisons for different pharmacies.
Question 6: Besides routine physicals, what other preventive services are important for the uninsured?
Essential preventive services include age-appropriate screenings for various cancers, vaccinations, and management of chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension. Access to affordable preventive dental and vision care is also important for overall health and well-being. Community resources and public health initiatives often offer access to these services.
Accessing healthcare without insurance requires proactive planning and resourcefulness. Understanding the available options and engaging with local community organizations can significantly improve access to affordable and quality care. Prioritizing preventive health, even without insurance, leads to better long-term health outcomes.
This information serves as a general overview. Consultation with healthcare professionals and further research are recommended for personalized guidance.
Conclusion
Access to routine medical examinations, even without the benefit of health insurance, remains a critical component of individual and public health. This exploration has highlighted the importance of preventive care in mitigating long-term health risks and the potential financial burdens associated with untreated medical conditions. Various avenues, including community health centers, free clinics, and public health initiatives, offer crucial access points for affordable healthcare services. Strategic financial planning, coupled with proactive engagement with these resources, empowers individuals to prioritize their well-being, regardless of insurance status. The availability of affordable options directly influences the likelihood of early detection and intervention, ultimately shaping long-term health outcomes.
Healthcare access should not be determined by insurance coverage. Continued efforts to expand access to affordable preventive care, strengthen community resources, and promote health literacy remain essential for ensuring equitable healthcare access for all. The pursuit of accessible healthcare is a shared responsibility, requiring ongoing dialogue and collaboration among healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations. Investing in preventive health represents an investment in a healthier future, benefiting individuals and the broader community alike.