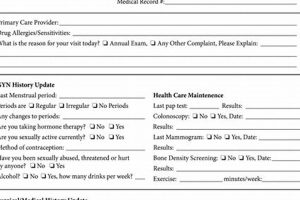
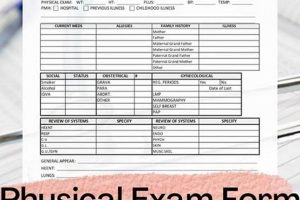
A standardized document used to record the findings of a medical evaluation specifically designed for individuals working in healthcare settings typically includes sections for vital signs, review of systems, and detailed physical assessments relevant to occupational health risks. Such forms may also incorporate specific screenings or tests related to the worker’s job responsibilities or potential exposures, like immunizations or respiratory fitness evaluations. An example might include a dedicated space for documenting tuberculosis screening results or fit testing for respirators.
These assessments are crucial for ensuring the health and safety of healthcare professionals, patients, and the overall healthcare environment. Regular evaluations can identify potential health issues early, facilitate preventative measures, and help manage existing conditions. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of disease transmission, reduces work-related injuries, and supports a healthy and productive workforce. Historically, these evaluations evolved alongside increasing awareness of occupational hazards and the importance of preventative medicine in healthcare settings.
This article will explore the various components of these assessments, including recommended frequencies, legal considerations, and the role of occupational health professionals in administering and interpreting them. Further discussion will address specific examples of how these assessments contribute to a safer and healthier workplace.
Tips for Effective Use of Health Evaluation Records
Proper utilization of health evaluation documentation ensures accurate record-keeping, facilitates proactive healthcare management, and supports a safe work environment. The following tips offer guidance for maximizing the effectiveness of these important records.
Tip 1: Ensure Completeness and Accuracy. All sections of the form should be completed thoroughly and accurately. Missing information or inaccuracies can compromise the quality of care and hinder effective health management.
Tip 2: Maintain Confidentiality. Health information is sensitive and confidential. Proper storage and access protocols must be followed to protect worker privacy.
Tip 3: Regular Review and Updates. Health evaluations should be conducted regularly, and records updated accordingly. This allows for timely identification of changes in health status and facilitates appropriate interventions.
Tip 4: Clear Communication. Open communication between healthcare professionals and workers regarding the results of the evaluation is essential for shared decision-making and effective health management.
Tip 5: Adherence to Regulatory Requirements. All documentation must comply with relevant regulatory standards and guidelines regarding health evaluations and record-keeping.
Tip 6: Utilize Standardized Forms. Employing standardized forms promotes consistency in data collection and facilitates accurate comparisons and trend analysis.
Tip 7: Secure Electronic Storage. Whenever possible, utilize secure electronic systems for storing and managing health records, enhancing accessibility and data security.
By following these tips, healthcare organizations can ensure accurate, comprehensive, and confidential health records, promoting a healthier and safer workplace for all.
These practical considerations contribute to the broader goal of proactive healthcare management within the healthcare industry, as detailed in the following conclusion.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formats are essential for physical exam forms used by healthcare workers. Standardization ensures consistent data collection across different practitioners and facilities. This consistency allows for easier comparison of results, identification of trends, and improved data analysis for research or epidemiological studies. A standardized format also simplifies data entry into electronic health records systems, reducing errors and enhancing efficiency. For example, consistent placement of fields for blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate allows for quick access to vital information and facilitates efficient review by healthcare providers. Without standardization, variations in format can lead to misinterpretation, overlooked information, and difficulties in tracking health trends over time.
Utilizing a standardized format provides several practical advantages. It streamlines training for personnel using the forms, reducing the likelihood of errors and omissions. Standardized forms can also be easily adapted for use in electronic systems, facilitating efficient data management and analysis. Moreover, standardized formats support compliance with regulatory requirements regarding health record keeping and data privacy. For instance, dedicated sections for documenting specific vaccinations or exposure incidents help ensure adherence to reporting mandates and facilitate epidemiological tracking.
In conclusion, the use of a standardized format for physical exam forms offers substantial benefits for healthcare workers and the healthcare system as a whole. It promotes accuracy, efficiency, and comparability of data, enabling better health monitoring, improved trend analysis, and informed decision-making. While challenges may arise in adapting standardized forms to specific needs or integrating them with existing systems, the overall advantages of standardization significantly outweigh these challenges, contributing to more effective and reliable healthcare practices.
2. Relevant Medical History
Comprehensive medical history is a cornerstone of effective healthcare for all individuals, but it holds particular significance for healthcare workers. Within the context of a physical exam form for healthcare workers, relevant medical history provides crucial context for interpreting current findings, identifying potential risks, and guiding preventative measures. A thorough understanding of past medical conditions, exposures, and family history allows for a more nuanced and proactive approach to occupational health management.
- Past Medical Conditions
Documentation of pre-existing conditions, such as asthma, allergies, or chronic illnesses, informs healthcare providers about potential vulnerabilities and guides appropriate precautions. For example, a healthcare worker with a history of latex allergy requires alternative glove options to prevent reactions. Knowledge of prior musculoskeletal injuries can inform work restrictions or modifications to minimize re-injury risk.
- Immunization History
A complete immunization record is crucial for healthcare workers due to their potential exposure to infectious diseases. Documentation of vaccinations, titers, and prior infections provides critical information for determining immunity status and guiding recommendations for booster shots or prophylactic measures. This information is particularly relevant for preventing the spread of vaccine-preventable illnesses within healthcare settings.
- Exposure History
Healthcare workers frequently encounter infectious agents, hazardous materials, and stressful situations. Documenting prior exposures to bloodborne pathogens, chemicals, or radiation allows for appropriate monitoring and follow-up. For example, a documented needlestick injury requires post-exposure prophylaxis and follow-up testing. Recording exposure to specific allergens or irritants can aid in diagnosing and managing occupational asthma or dermatitis.
- Family History
While not directly related to occupational health, family history provides insights into genetic predispositions that may influence a healthcare worker’s risk for certain conditions. A family history of heart disease, for example, may prompt closer monitoring of cardiovascular health. Knowledge of hereditary cancers can inform screening recommendations and preventative strategies.
The information gleaned from a thorough medical history provides critical context for the physical examination and informs personalized recommendations for health maintenance and disease prevention. By integrating relevant medical history into physical exam forms for healthcare workers, healthcare providers can ensure a comprehensive and proactive approach to occupational health management, promoting a safer and healthier work environment.
3. Comprehensive Physical Assessment
Comprehensive physical assessments constitute a critical component of physical exam forms for healthcare workers. These assessments provide a baseline understanding of current health status, enabling early detection of potential health concerns and facilitating preventative interventions. They also offer valuable insights into the worker’s fitness for specific job duties, ensuring both individual well-being and patient safety.
- Cardiovascular Evaluation
Evaluating cardiovascular health is paramount, given the physical demands often placed on healthcare professionals. Auscultation of the heart, blood pressure measurement, and assessment of peripheral pulses provide crucial data for identifying potential risks like hypertension, heart murmurs, or peripheral artery disease. Early detection of such conditions allows for timely intervention and minimizes the risk of adverse events during work activities.
- Respiratory Assessment
Respiratory health is of particular concern for healthcare workers due to potential exposure to airborne pathogens and environmental irritants. Assessment includes auscultation of the lungs, evaluation of respiratory rate and effort, and pulse oximetry. These measures help identify conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or latent infections, allowing for appropriate protective measures and treatment strategies.
- Musculoskeletal Examination
Healthcare work frequently involves physically demanding tasks, making musculoskeletal assessment essential. Evaluating range of motion, muscle strength, and joint stability helps identify existing injuries, musculoskeletal imbalances, or risk factors for future problems. This information informs ergonomic recommendations, preventative exercises, and potential work modifications to minimize the risk of work-related musculoskeletal disorders.
- Neurological Examination
Neurological assessment, including evaluation of reflexes, cranial nerves, and sensory function, provides insights into the integrity of the nervous system. Early detection of neurological deficits or abnormalities can be crucial for diagnosing and managing conditions that could impact job performance and patient safety. This component is particularly important for healthcare workers involved in tasks requiring fine motor skills, precise movements, or rapid decision-making.
These facets of a comprehensive physical assessment, documented within the physical exam form, collectively contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the healthcare worker’s health status. This information is essential for fostering a safe and healthy work environment, enabling informed decisions regarding work assignments, preventative measures, and necessary accommodations to support both individual well-being and the delivery of high-quality patient care.
4. Occupational Hazard Screening
Occupational hazard screening forms an integral part of physical exam forms for healthcare workers. This screening process aims to identify and assess potential risks associated with specific job duties and the healthcare environment. Its inclusion in the physical exam form underscores the importance of proactive risk management in maintaining a healthy and safe workplace for healthcare professionals.
- Exposure to Infectious Diseases
Healthcare workers face significant risks of exposure to infectious diseases, including bloodborne pathogens like HIV and Hepatitis B and C, as well as airborne illnesses like tuberculosis and influenza. Screening may involve assessing immunization status, conducting tuberculosis skin tests or blood tests, and evaluating potential exposure incidents. This information is crucial for determining appropriate preventative measures, including vaccinations, post-exposure prophylaxis, and infection control practices.
- Chemical and Hazardous Material Exposure
Healthcare settings utilize various chemicals and hazardous materials, including cleaning agents, disinfectants, and chemotherapeutic drugs. Occupational hazard screening assesses potential exposures through workplace assessments, review of material safety data sheets, and biological monitoring if necessary. This information informs safety protocols, including the use of personal protective equipment and proper handling and disposal procedures.
- Ergonomic Risk Factors
Healthcare workers often perform physically demanding tasks, including lifting and transferring patients, which can pose ergonomic risks. Screening involves evaluating work postures, repetitive movements, and lifting techniques. This assessment informs recommendations for ergonomic adjustments, safe lifting practices, and preventative exercises to minimize the risk of musculoskeletal injuries.
- Stress and Mental Health Concerns
The demanding nature of healthcare work, coupled with exposure to emotionally challenging situations, can contribute to stress, burnout, and mental health concerns. Screening may include questionnaires or interviews to assess stress levels, coping mechanisms, and potential mental health risks. This information can guide interventions such as stress management programs, access to mental health resources, and workplace modifications to promote a supportive and healthy work environment.
By incorporating these occupational hazard screenings into physical exam forms, healthcare organizations demonstrate a commitment to proactive risk management and worker safety. These assessments provide valuable data for developing targeted interventions, implementing preventative measures, and fostering a healthier and safer work environment for all healthcare professionals. This ultimately contributes to improved patient care and a more resilient healthcare system.
5. Confidentiality and Security
Confidentiality and security are paramount in the context of physical exam forms for healthcare workers. These forms contain sensitive personal and medical information, requiring stringent safeguards to protect worker privacy and comply with legal and ethical obligations. Failure to maintain confidentiality can have serious consequences, including legal repercussions, damage to reputation, and erosion of trust between healthcare workers and their employers.
Several regulations and guidelines govern the confidentiality of health information, including HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States. These regulations mandate strict controls on access, use, and disclosure of protected health information. Physical exam forms must be stored securely, whether in physical files or electronic systems, with access limited to authorized personnel. Appropriate safeguards must be implemented to prevent unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of this sensitive information. For example, physical files should be stored in locked cabinets, and electronic systems should employ robust access controls, encryption, and audit trails. Any breaches in confidentiality must be reported and addressed promptly according to established protocols.
Maintaining confidentiality fosters trust between healthcare workers and their employers, encouraging open communication about health concerns. This trust is essential for effective occupational health management and ensures that healthcare workers feel comfortable seeking necessary medical attention without fear of stigma or discrimination. Robust security measures also protect against potential misuse of information, such as identity theft or discrimination based on health status. Adherence to strict confidentiality and security protocols demonstrates a commitment to ethical practice, legal compliance, and the well-being of healthcare professionals, ultimately contributing to a safer and more trustworthy healthcare environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding health evaluations for healthcare professionals.
Question 1: What is the typical frequency of mandatory health evaluations for healthcare personnel?
The frequency of required health evaluations varies depending on the specific job duties, potential exposures, and regulatory requirements. Some roles may necessitate annual assessments, while others might require more frequent evaluations, particularly following specific exposures or incidents.
Question 2: Who is responsible for conducting these health evaluations?
Occupational health professionals, including physicians, nurses, and physician assistants specializing in occupational health, typically conduct these evaluations. In some cases, primary care providers may also perform these assessments, provided they possess the necessary expertise and familiarity with occupational health guidelines.
Question 3: Are healthcare workers required to undergo these evaluations as a condition of employment?
In many cases, health evaluations are a prerequisite for employment in healthcare settings. This requirement ensures that healthcare professionals are fit for duty and minimizes the risk of transmitting infections or other health concerns to patients.
Question 4: What happens if a health issue is identified during the evaluation?
If a health concern is identified, appropriate follow-up actions will be determined based on the specific issue. This may involve referral to a specialist, further testing, treatment recommendations, or temporary work modifications to ensure the worker’s health and safety.
Question 5: Are there any legal requirements related to maintaining records of these evaluations?
Stringent regulatory requirements govern the maintenance and confidentiality of health records for healthcare workers. These requirements vary by jurisdiction but generally mandate secure storage, controlled access, and strict adherence to privacy regulations.
Question 6: How do these evaluations contribute to patient safety?
Regular health evaluations contribute significantly to patient safety by minimizing the risk of disease transmission from healthcare workers to patients. These assessments also ensure that healthcare professionals are fit to perform their duties, reducing the risk of errors or adverse events related to worker health.
Understanding these key aspects of health evaluations for healthcare professionals promotes a culture of safety and well-being within healthcare settings. Prioritizing worker health ultimately benefits both individual professionals and the patients they serve.
Further exploration of specific components within these evaluations will be addressed in the subsequent sections.
Conclusion
Systematic health evaluations, documented through standardized physical examination forms, are indispensable for safeguarding the well-being of healthcare professionals and ensuring patient safety. This exploration has highlighted the critical components of these evaluations, including the importance of comprehensive medical history, thorough physical assessments, targeted occupational hazard screenings, and stringent confidentiality protocols. Each element contributes to a proactive approach to occupational health management, enabling early identification of potential risks and facilitating timely interventions.
Prioritizing the health and safety of healthcare workers is not merely an ethical imperative; it is a strategic investment in a robust and resilient healthcare system. Continued refinement of evaluation procedures, informed by evolving research and best practices, will further enhance the efficacy of these assessments in mitigating occupational risks and promoting a healthier and safer work environment for all healthcare professionals. This commitment to proactive healthcare management is essential for maintaining a high-quality healthcare workforce capable of meeting the ever-increasing demands of a complex and evolving healthcare landscape.