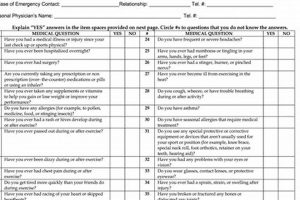
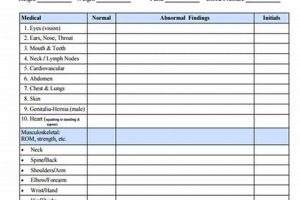
A pre-participation health screening document typically collects comprehensive medical history, including current health status, past injuries, illnesses, and family medical history. For instance, it might inquire about allergies, asthma, cardiac conditions, or prior concussions. This information is often supplemented by a physical examination conducted by a healthcare professional. The examination evaluates various physiological factors, such as height, weight, blood pressure, vision, and cardiovascular health.
These screenings are essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals engaging in physical activity, particularly in organized sports. They help identify potential health risks that might be exacerbated by strenuous exertion. Early detection allows for appropriate medical intervention, preventing potential complications or even life-threatening situations. Historically, these evaluations have evolved from basic checks to comprehensive assessments reflecting advancements in sports medicine and a growing awareness of the importance of preventative care.
This understanding of the health screening process lays the groundwork for further exploration of related topics, including best practices for conducting these evaluations, specific requirements for different activities, and the role of technology in streamlining data collection and analysis.
Tips for Completing Health Screenings
Accurate and complete health information is crucial for effective pre-participation health screenings. The following tips offer guidance for navigating this process.
Tip 1: Honesty is Paramount: Provide complete and truthful information, even if seemingly insignificant. Undisclosed conditions can pose significant risks during physical activity.
Tip 2: Detailed Medical History: Recall prior injuries, illnesses, and family history related to cardiac health, respiratory issues, or other relevant medical conditions. Specific dates, diagnoses, and treatments are helpful.
Tip 3: Medication Awareness: List all current medications, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. This information can help identify potential interactions or contraindications.
Tip 4: Allergy Information: Disclose all known allergies, including drug, food, and environmental allergies. Specify the type of reaction experienced. This is critical for emergency preparedness.
Tip 5: Open Communication: Discuss any concerns or questions with the healthcare professional conducting the evaluation. Clear communication ensures a thorough and personalized assessment.
Tip 6: Parental Involvement (for Minors): Parents or guardians should actively participate in the process for minors, providing accurate information and ensuring the child understands the importance of the screening.
Tip 7: Follow-Up: Adhere to any recommendations or referrals provided by the healthcare professional. This might include further testing or specialist consultations.
Following these guidelines facilitates a comprehensive evaluation, promotes informed decision-making, and contributes to a safer environment for participation in physical activities.
By prioritizing accurate and complete information during health screenings, individuals contribute to their own well-being and support the overall effectiveness of preventative health measures in sports and other physical activities.
1. Comprehensive Medical History
A comprehensive medical history forms the cornerstone of a pre-participation health screening (pfhs) physical form. This detailed record of past and present health conditions provides crucial context for evaluating an individual’s readiness for physical activity. Its thoroughness directly impacts the effectiveness of risk assessment and the development of appropriate safety measures.
- Past Illnesses:
Documentation of previous illnesses, including chronic conditions like asthma or diabetes, informs healthcare professionals about potential vulnerabilities during physical exertion. For example, a history of mononucleosis might necessitate additional cardiac screening before clearance for strenuous activity. Knowing the complete illness history helps tailor activity recommendations to individual needs.
- Previous Injuries:
Prior injuries, particularly musculoskeletal injuries like sprains, fractures, or concussions, are essential to record. A history of ankle sprains, for instance, might indicate a need for preventative measures like ankle bracing or specific training exercises. Understanding past injuries helps assess current joint stability and identify potential areas of weakness.
- Surgical History:
Any surgical procedures, including minimally invasive procedures, should be documented. Knowledge of past surgeries, such as appendectomy or knee surgery, allows healthcare providers to evaluate potential complications or limitations related to physical activity. This information contributes to a more informed assessment of current physical capabilities.
- Family Medical History:
Family history of conditions like heart disease, sudden cardiac death, or specific genetic disorders can indicate increased risk for similar conditions in the individual. This information may prompt further investigation or specialized testing, such as electrocardiograms, to ensure safe participation in physical activity. Understanding family predispositions is key to proactive risk management.
These facets of a comprehensive medical history, when thoroughly documented within the pfhs physical form, empower healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding an individual’s participation in physical activity. This meticulous approach minimizes potential risks and promotes safe engagement in sports and exercise.
2. Current Health Status
Current health status plays a vital role within a pre-participation health screening (pfhs) physical form. It provides a snapshot of an individual’s present physical condition, influencing eligibility for physical activity and informing necessary precautions. Accurate reporting of current health issues is crucial for effective risk assessment.
Several factors within current health status directly impact participation decisions. Active infections, such as a respiratory infection or skin infection, might temporarily restrict involvement in sports to prevent spread or exacerbate the illness. Chronic conditions, like asthma or diabetes, necessitate careful management and individualized exercise plans. Recent injuries, even minor ones, require evaluation to determine readiness for activity and prevent re-injury. Medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, are documented to identify potential interactions or effects on performance. Allergies, particularly those with potential for severe reactions, necessitate emergency preparedness and activity modifications. For example, an athlete with poorly controlled asthma might require adjusted training intensity or access to an inhaler during practice. An individual recovering from a recent concussion might require gradual return-to-play protocols to minimize risk of further injury.
Accurate documentation of current health status empowers healthcare professionals to assess immediate risks, personalize activity recommendations, and implement appropriate safety measures. This careful evaluation contributes to a safer and more effective approach to physical activity participation. Ignoring current health issues can lead to adverse events, emphasizing the practical significance of accurate reporting within the pfhs physical form.
3. Physician Examination
The physician examination constitutes a critical component of the pre-participation health screening (pfhs) physical form. It provides an objective assessment of an individual’s physical condition, complementing the subjective information gathered through medical history. This examination facilitates identification of potential health concerns that might not be apparent through self-reporting alone. The examination typically includes evaluation of cardiovascular health, including heart rate and blood pressure; pulmonary function through auscultation of the lungs; musculoskeletal integrity, assessing range of motion and joint stability; and neurological function, evaluating reflexes and balance. For example, a heart murmur detected during the examination might necessitate further cardiac evaluation, such as an echocardiogram, before clearance for strenuous activity. Similarly, limited range of motion in a joint might indicate a previous injury requiring further investigation or rehabilitation.
The physician examination serves several essential functions within the pfhs process. It corroborates information provided in the medical history, verifying self-reported conditions. It identifies previously undiagnosed conditions or asymptomatic abnormalities that could pose risks during physical activity. It allows for personalized recommendations regarding activity limitations or modifications based on individual physical findings. Furthermore, it provides an opportunity for health education and counseling, promoting awareness of potential health risks and preventative measures. For instance, an individual with elevated blood pressure might receive guidance on lifestyle modifications to improve cardiovascular health. An athlete with a history of concussions might receive education on concussion prevention and management.
In summary, the physician examination is integral to the effectiveness of the pfhs physical form. It provides an objective assessment of physical health, facilitates early identification of potential risks, and informs personalized recommendations for safe participation in physical activity. This comprehensive approach enhances the protective value of pre-participation health screenings, contributing to a safer and healthier environment for individuals engaging in sports and exercise.
4. Informed Consent
Informed consent represents a crucial ethical and legal component of the pre-participation health screening (pfhs) physical form process. It signifies an individual’s autonomous authorization to participate in an activity after receiving comprehensive information about the inherent risks and benefits. This understanding encompasses the purpose of the screening, the nature of the examination, potential implications of the findings, and alternatives to participation. Informed consent ensures individuals possess the necessary knowledge to make voluntary and informed decisions regarding their health and physical activity involvement. For instance, an athlete must understand the potential risks associated with sports participation, such as injuries or exacerbations of pre-existing conditions, before providing consent for the screening and subsequent involvement in activities.
Several factors contribute to valid informed consent within the pfhs context. Disclosure of pertinent information, including the scope of the examination, potential diagnostic tests, and possible outcomes, is fundamental. Comprehension of this information is equally critical; healthcare professionals must ensure individuals understand the explanations provided, addressing any questions or concerns. Voluntariness emphasizes the absence of coercion or undue influence in the decision-making process. Individuals must feel empowered to decline participation without fear of reprisal or negative consequences. Competence to consent signifies the individual’s capacity to understand the information presented and make reasoned judgments. For minors, parental or guardian consent is typically required, reflecting their legal responsibility for the child’s well-being. Documentation of informed consent, often through a signed form, provides evidence of the process and protects both the individual and the organization administering the screening.
Informed consent safeguards individual autonomy and promotes ethical practices within pre-participation health screenings. It fosters trust between individuals and healthcare providers, facilitating open communication and shared decision-making. Adherence to informed consent principles reinforces the integrity of the pfhs process, ensuring its effectiveness in promoting safe and responsible participation in physical activity. Challenges may arise in ensuring comprehension in individuals with limited health literacy or cognitive impairments, requiring tailored communication strategies. Adequate resources and training for healthcare professionals are essential to navigate these challenges and uphold the ethical principles of informed consent.
5. Clearance for Participation
Clearance for participation represents the culmination of the pre-participation health screening (pfhs) physical form process. It signifies an individual’s medical eligibility to engage in specific physical activities based on the comprehensive evaluation of health information, physical examination findings, and any additional diagnostic testing. This clearance serves as a safeguard, minimizing potential health risks associated with physical exertion. The pfhs physical form provides the foundational data upon which clearance decisions are made. A thorough and accurate pfhs form facilitates informed medical judgments regarding an individual’s readiness for activity. For instance, an athlete with a history of concussions might require clearance from a neurologist before returning to contact sports. An individual with uncontrolled asthma might require specialized management strategies and clearance from a pulmonologist before engaging in high-intensity exercise. Conversely, an individual with no significant health concerns might receive unconditional clearance based on a normal pfhs physical form and examination.
The connection between clearance for participation and the pfhs physical form operates on a cause-and-effect basis. The information documented within the pfhs form, coupled with the physician’s examination findings, directly influences the decision regarding clearance. Incomplete or inaccurate information within the pfhs form can compromise the validity of the clearance process, potentially placing individuals at risk. Conversely, a comprehensive and accurate pfhs form, combined with a thorough physical examination, empowers healthcare professionals to make informed decisions that prioritize individual safety and well-being. The practical significance of this understanding lies in its contribution to risk mitigation and injury prevention. Clearance for participation, based on a robust pfhs process, reduces the likelihood of adverse events during physical activity. This systematic approach benefits both individual participants and the organizations responsible for their well-being.
In summary, clearance for participation represents a critical outcome of the pfhs physical form process. It signifies medical approval for activity based on a comprehensive evaluation of health information. The quality and accuracy of the pfhs form directly impact the validity and effectiveness of clearance decisions. Understanding this connection is paramount for promoting safe and responsible participation in physical activities, minimizing potential health risks, and fostering a culture of preventative care in sports and exercise. Challenges may arise in situations with complex medical histories or limited access to specialized medical expertise, necessitating careful consideration of individual circumstances and collaborative decision-making among healthcare professionals and stakeholders.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding pre-participation health screenings and the associated physical form.
Question 1: Who requires a pre-participation health screening?
Individuals of all ages engaging in organized sports or strenuous physical activity typically require a pre-participation health screening. Specific requirements may vary depending on the organization or governing body.
Question 2: What information is typically included in a pre-participation health screening form?
The form generally requests comprehensive medical history, including current health status, past illnesses, injuries, medications, allergies, and family medical history. It may also include questions about lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise habits.
Question 3: What is the role of the physician in the pre-participation health screening process?
The physician reviews the completed health screening form, conducts a physical examination, and assesses the individual’s readiness for physical activity. They may recommend further evaluation or specialized testing if necessary.
Question 4: What happens if a potential health concern is identified during the screening?
If a potential health concern is identified, the physician may recommend further evaluation, treatment, or activity modifications. Clearance for participation might be delayed until the concern is addressed appropriately.
Question 5: How often should pre-participation health screenings be conducted?
The frequency of screenings depends on factors such as age, health status, and the type of activity. Annual screenings are often recommended, particularly for adolescents participating in organized sports.
Question 6: Where can one obtain a pre-participation health screening form?
Forms are often available through schools, sports organizations, healthcare providers, or online resources specific to governing bodies for particular activities.
Thorough pre-participation health screenings are essential for promoting safe and informed engagement in physical activities. Understanding the process and addressing common questions facilitates proactive health management and informed decision-making.
For further information on specific requirements or recommendations, consulting with a healthcare professional or referring to relevant organizational guidelines is advised. This FAQ section serves as a general guide and should not replace professional medical advice.
Conclusion
Pre-participation health screening physical forms represent a cornerstone of preventative healthcare in sports and other physical activities. Exploration of this topic has illuminated the crucial role these forms play in assessing individual health status, identifying potential risks, and informing decisions regarding safe participation. Key elements, including comprehensive medical history, current health status, physician examination, informed consent, and clearance for participation, contribute synergistically to the effectiveness of this process. The information gleaned from accurately completed forms empowers healthcare professionals to make informed judgments regarding activity suitability, implement preventative measures, and promote overall well-being for individuals engaging in physical exertion.
Prioritizing the accurate and thorough completion of pre-participation health screening physical forms strengthens the foundation of safe and responsible activity engagement. This proactive approach benefits individuals, organizations, and the broader community by minimizing preventable health risks and fostering a culture of informed decision-making in sports and exercise. Continued emphasis on the importance of pre-participation health screenings contributes to a healthier and safer future for all involved in physical activity.