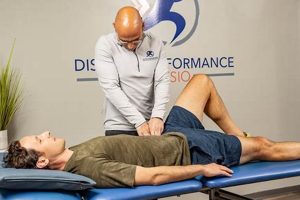
Restoring optimal movement and function in individuals recovering from musculoskeletal injuries or experiencing movement limitations often involves a specialized approach. This process typically emphasizes precise, individualized exercise programs designed to address specific impairments, improve biomechanics, and reduce pain. For instance, a patient recovering from knee surgery might undergo a tailored regimen of strengthening, flexibility, and balance exercises to regain full joint mobility and stability.
Interventions aimed at restoring musculoskeletal health play a vital role in improving patients’ quality of life. By addressing the underlying causes of movement dysfunction, these interventions can alleviate pain, enhance physical function, and promote independence in daily activities. Furthermore, this specialized field has evolved significantly with advances in exercise science, biomechanics, and rehabilitation technology, leading to more effective treatment strategies and improved patient outcomes.
This article will further explore the core principles, techniques, and applications relevant to this specialized area of rehabilitation, examining its role in various conditions and populations. It will also address the importance of individualized treatment plans and the collaborative efforts between therapists and patients in achieving optimal recovery.
Tips for Optimizing Movement and Function
Promoting musculoskeletal health and restoring optimal movement requires a proactive approach. The following tips offer practical guidance for individuals seeking to enhance physical well-being and prevent or manage movement limitations.
Tip 1: Prioritize Proper Posture: Maintaining correct posture during daily activities, whether sitting, standing, or lifting, reduces strain on joints and muscles, minimizing the risk of injury and promoting long-term musculoskeletal health.
Tip 2: Engage in Regular Exercise: A consistent exercise routine incorporating strengthening, flexibility, and cardiovascular activities is essential for building muscle strength, improving joint stability, and enhancing overall physical function.
Tip 3: Incorporate Warm-up and Cool-down Routines: Preparing the body for physical activity with appropriate warm-up exercises and allowing for adequate cool-down afterward helps prevent muscle strains and injuries.
Tip 4: Listen to Your Body: Paying attention to body signals and respecting pain is crucial. Pushing through pain can exacerbate existing injuries and create new ones. Rest and recovery are essential components of any exercise program.
Tip 5: Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment is essential, especially for individuals experiencing pain, injury, or persistent movement limitations.
Tip 6: Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can place undue stress on joints and muscles, increasing the risk of injury and impairing movement. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise supports optimal musculoskeletal function.
Tip 7: Create an Ergonomic Workspace: An ergonomically designed workspace promotes proper posture, reduces strain on the body, and enhances comfort during prolonged periods of sitting or working.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can actively participate in maintaining their musculoskeletal health, improving movement efficiency, and minimizing the risk of future complications. These proactive steps empower individuals to take control of their physical well-being and promote long-term health and mobility.
In conclusion, adopting a proactive approach to musculoskeletal health through informed choices and consistent effort is essential for maintaining optimal physical function and overall well-being. The information presented in this article serves as a foundation for understanding the importance of movement health and provides practical strategies for individuals to implement in their daily lives.
1. Restoring Optimal Movement
Restoring optimal movement represents a central objective within orthocincy physical therapy. Movement limitations, arising from injury, disease, or postural imbalances, can significantly impact an individual’s functional capacity and overall well-being. Orthocincy physical therapy addresses these limitations through targeted interventions designed to enhance mobility, stability, and motor control. The relationship between restoring optimal movement and this specialized approach is one of cause and effect: impaired movement necessitates intervention, and effective intervention leads to restored function. For instance, a patient with limited shoulder mobility due to adhesive capsulitis might undergo manual therapy techniques and prescribed exercises to restore range of motion and improve functional use of the arm. Similarly, a runner with patellofemoral pain syndrome could benefit from gait analysis and corrective exercises to optimize lower extremity biomechanics and reduce pain during running.
The importance of restoring optimal movement as a component of orthocincy physical therapy lies in its direct impact on an individual’s ability to perform daily activities and participate in meaningful life roles. Restoring function enables individuals to regain independence in self-care, work, and recreational pursuits. Furthermore, improvements in movement efficiency can reduce pain, prevent further injury, and enhance overall physical performance. Consider a post-stroke patient relearning basic walking skills; the restoration of even rudimentary movement patterns represents a significant step towards regaining independence and improving quality of life. Likewise, an athlete recovering from an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear relies on regaining full knee function to return to competitive sport.
In summary, the restoration of optimal movement serves as a cornerstone of orthocincy physical therapy. By addressing the underlying causes of movement dysfunction and implementing evidence-based interventions, this specialized field empowers individuals to regain lost function, reduce pain, and improve their overall quality of life. Addressing the complexities of movement limitations requires a comprehensive and individualized approach, and orthocincy physical therapy provides the framework for achieving these crucial rehabilitative goals. Future research and advancements in the field promise continued refinement of treatment strategies and further improvements in patient outcomes.
2. Musculoskeletal Injury Recovery
Musculoskeletal injury recovery represents a critical application of orthocincy physical therapy. Injuries to muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bones, whether acute or chronic, can significantly impair function and diminish quality of life. Orthocincy physical therapy provides a structured, evidence-based approach to restoring function and minimizing disability following such injuries. The relationship between musculoskeletal injury recovery and this specialized approach is inherently intertwined; the injury necessitates intervention, and the specific interventions aim to facilitate recovery. For instance, a rotator cuff tear might require a progressive exercise program to restore shoulder strength and mobility, while a sprained ankle benefits from targeted exercises to improve stability and balance. A vertebral compression fracture might necessitate postural re-education and core strengthening exercises to promote spinal stability and reduce pain.
The importance of musculoskeletal injury recovery within orthocincy physical therapy lies in its capacity to restore individuals’ ability to participate in daily activities, work, and recreational pursuits. Regaining function after injury not only enhances physical capabilities but also promotes psychological well-being and reduces the risk of long-term disability. Consider a carpenter recovering from a wrist fracture; regaining wrist mobility and strength is essential for returning to work and performing essential job tasks. Similarly, an individual recovering from a hip replacement relies on postoperative rehabilitation to regain ambulation and independence in self-care activities. Addressing the specific needs of each individual and tailoring interventions to the nature and severity of the injury form the core of effective musculoskeletal injury recovery.
In summary, musculoskeletal injury recovery represents a cornerstone of orthocincy physical therapy. Through comprehensive assessment, individualized treatment plans, and progressive rehabilitation, this specialized approach facilitates the restoration of function, reduces pain, and minimizes disability following musculoskeletal injuries. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in recognizing the vital role orthocincy physical therapy plays in restoring individuals’ physical capabilities and promoting overall well-being. Future advancements in the field promise to further refine rehabilitation strategies and optimize patient outcomes in musculoskeletal injury recovery.
3. Evidence-based exercise programs
Evidence-based exercise programs constitute a cornerstone of orthocincy physical therapy, ensuring treatment approaches are grounded in scientific rigor and demonstrate effectiveness. These programs rely on the integration of best available research evidence, clinical expertise, and patient values to optimize treatment outcomes. The efficacy of interventions is continually evaluated and refined based on the latest scientific findings, ensuring patients receive the most effective and appropriate care.
- Specificity of Exercise Prescription
Exercise prescription within orthocincy physical therapy emphasizes specificity, tailoring exercises to address the unique needs and impairments of each individual. For example, a patient recovering from a hamstring strain would engage in exercises targeting hamstring flexibility and strength, while an individual with shoulder impingement would perform exercises focused on rotator cuff strengthening and scapular stabilization. The specific nature of these exercises maximizes their impact on the targeted impairments.
- Progressive Overload and Adaptation
Progressive overload, a fundamental principle of exercise physiology, guides the design of evidence-based exercise programs. This principle involves gradually increasing the intensity, duration, or frequency of exercises as the body adapts, stimulating ongoing improvements in strength, endurance, and function. For example, a patient initially performing bicep curls with a 5-pound weight might progress to using a 7-pound weight as strength improves. This progressive approach ensures continuous gains and maximizes the benefits of the exercise program.
- Outcome Measurement and Evaluation
Outcome measurement plays a critical role in evidence-based exercise programs, allowing therapists to objectively track progress and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. Regular assessments of pain levels, range of motion, strength, and functional capacity provide valuable data for modifying treatment plans and ensuring optimal outcomes. For example, tracking a patient’s pain levels using a numerical pain rating scale allows the therapist to monitor the effectiveness of pain management strategies and adjust the treatment plan accordingly.
- Integration of Manual Therapy and Modalities
While exercise forms the core of orthocincy physical therapy, evidence-based practice often integrates manual therapy techniques and therapeutic modalities to complement exercise interventions. Manual therapy, such as joint mobilization and soft tissue manipulation, can address specific joint restrictions or muscle imbalances. Therapeutic modalities, like ultrasound or electrical stimulation, may be used to manage pain and inflammation. Integrating these techniques into evidence-based exercise programs provides a comprehensive approach to rehabilitation.
These facets of evidence-based exercise programs highlight their crucial role in orthocincy physical therapy. By grounding interventions in scientific evidence, emphasizing specificity, and incorporating progressive overload and outcome measurement, orthocincy physical therapy ensures that treatment approaches are both effective and tailored to the unique needs of each individual. This commitment to evidence-based practice drives continuous improvement in patient care and outcomes within this specialized field.
4. Individualized Treatment Plans
Individualized treatment plans represent a cornerstone of orthocincy physical therapy. Recognizing that each individual presents with unique impairments, functional limitations, and health goals, orthocincy physical therapy emphasizes the development of tailored treatment strategies. This personalized approach considers factors such as age, activity level, pre-existing conditions, and specific movement limitations to create a plan that optimizes outcomes. The relationship between individualized treatment plans and this specialized approach is symbiotic; the variability inherent in patient presentations necessitates individualized plans, and the effectiveness of the approach relies on this customization. For example, a young athlete recovering from an ACL tear will have different rehabilitation goals and requirements compared to an older adult recovering from a hip replacement, even if both require exercises to improve lower extremity strength and mobility. Similarly, an office worker with chronic neck pain will require a different approach than a construction worker with a rotator cuff injury, even if both benefit from postural correction and strengthening exercises. This highlights the crucial need for individualized approaches.
The importance of individualized treatment plans within orthocincy physical therapy stems from their capacity to maximize functional gains and improve overall patient outcomes. By addressing specific needs and tailoring interventions to the individual’s capabilities and goals, therapists can optimize the effectiveness of treatment, minimize the risk of re-injury, and enhance patient adherence to the prescribed program. Consider a musician with carpal tunnel syndrome; their treatment plan will likely focus on restoring wrist mobility, nerve gliding exercises, and modifying playing techniques to minimize strain. In contrast, a swimmer with shoulder impingement will require a program that addresses rotator cuff strengthening, scapular stabilization, and stroke mechanics. These examples demonstrate the practical significance of tailoring interventions to the individual’s specific needs and activity demands.
In summary, individualized treatment plans form an integral part of orthocincy physical therapy, ensuring treatment effectiveness and maximizing patient outcomes. The variability in patient presentations underscores the importance of this personalized approach. Addressing specific impairments, considering individual goals, and tailoring interventions to the patient’s unique circumstances optimize the recovery process, promoting both functional gains and long-term musculoskeletal health. Challenges include effectively gathering comprehensive patient information and adapting treatment plans based on ongoing progress, but the benefits of individualized care within orthocincy physical therapy remain significant. Continued research and development of assessment tools and treatment strategies will further enhance the precision and efficacy of individualized treatment plans within this field.
5. Pain reduction and management
Pain reduction and management represent integral components of orthocincy physical therapy. Pain, whether acute or chronic, often accompanies musculoskeletal conditions and injuries, significantly impacting an individual’s function and quality of life. Orthocincy physical therapy addresses pain through a multifaceted approach, combining various interventions to alleviate symptoms, address underlying causes, and improve overall function. The relationship between pain reduction and management and this specialized approach is bidirectional: pain motivates individuals to seek intervention, and effective intervention aims to mitigate pain and improve function. For instance, a patient with low back pain might receive manual therapy techniques to address joint restrictions and muscle spasms, combined with therapeutic exercises to improve core stability and reduce pain triggers. Similarly, an individual with osteoarthritis of the knee may benefit from a combination of modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation to manage inflammation and pain, along with exercises to improve joint mobility and strengthen surrounding muscles. This demonstrates the integrated nature of pain management within orthocincy physical therapy.
The importance of pain reduction and management within orthocincy physical therapy lies in its ability to facilitate functional recovery and enhance overall well-being. Reducing pain enables individuals to engage more effectively in therapeutic exercises, promoting improved mobility, strength, and functional capacity. Furthermore, effective pain management contributes to improved sleep quality, reduced reliance on medication, and enhanced participation in daily activities and social roles. Consider a patient with chronic shoulder pain limiting their ability to perform overhead activities; by addressing pain through manual therapy and targeted exercises, they can regain functional use of their arm and participate in activities they previously enjoyed. Likewise, an individual with plantar fasciitis experiencing significant foot pain might benefit from interventions such as stretching, orthotics, and manual therapy to reduce pain and restore their ability to walk and engage in weight-bearing activities comfortably. These examples highlight the practical implications of effective pain management within the context of orthocincy physical therapy.
In summary, pain reduction and management represent essential elements of orthocincy physical therapy. By employing a multifaceted approach that integrates various interventions, orthocincy physical therapy addresses pain’s complex nature and its impact on function and well-being. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in appreciating the crucial role pain management plays in facilitating recovery, improving function, and enhancing individuals’ overall quality of life. Challenges include effectively assessing and addressing both the physiological and psychological aspects of pain, and tailoring interventions to individual needs and responses. Continued research and advancements in pain management techniques will further refine the approach and optimize outcomes within this specialized field.
6. Improved Biomechanics and Function
Improved biomechanics and function represent core outcomes of orthocincy physical therapy. Biomechanics, the study of human movement, plays a crucial role in understanding how forces act on the musculoskeletal system. Dysfunctional movement patterns, often stemming from injury, weakness, or postural imbalances, can lead to pain, decreased performance, and increased risk of further injury. Orthocincy physical therapy addresses these issues by analyzing movement patterns, identifying biomechanical faults, and implementing corrective strategies to optimize movement efficiency and restore function. The relationship between improved biomechanics and function and this specialized approach is one of reciprocal influence: dysfunctional biomechanics necessitates intervention, and effective intervention leads to improved biomechanics and subsequent functional gains. For example, a runner with excessive pronation (inward rolling of the foot) might benefit from orthotics and exercises to strengthen the supporting musculature of the foot and ankle, improving running mechanics and reducing the risk of injuries like plantar fasciitis or shin splints. Similarly, a golfer with limited hip rotation might undergo targeted mobility and strengthening exercises to improve swing mechanics, enhance power, and reduce the risk of back injuries. These examples illustrate the connection between addressing biomechanical deficits and achieving improved functional outcomes.
The importance of improved biomechanics and function within orthocincy physical therapy lies in their direct impact on an individual’s ability to perform daily activities, participate in recreational pursuits, and achieve optimal physical performance. Optimizing movement patterns reduces stress on joints and tissues, minimizes pain, and enhances efficiency in activities ranging from basic movements like walking and lifting to complex tasks involved in sports or occupational duties. Consider a patient recovering from a stroke who exhibits gait abnormalities; improving their gait biomechanics through targeted exercises and assistive devices can enhance their walking speed, endurance, and overall mobility, promoting independence in daily life. Likewise, an athlete with a jumping deficiency might undergo plyometric training to improve lower extremity power and biomechanics, enhancing their jumping performance and reducing the risk of injury. These practical applications underscore the significance of addressing biomechanics in various contexts.
In summary, improved biomechanics and function constitute integral goals within orthocincy physical therapy. By analyzing movement, identifying biomechanical faults, and implementing corrective strategies, this specialized approach optimizes movement efficiency, reduces pain, and enhances functional capacity. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in recognizing the fundamental role biomechanics plays in movement health and overall well-being. Challenges include accurately assessing complex biomechanical factors and developing individualized interventions that effectively address these factors. Continued research and advancements in movement analysis technology and therapeutic techniques will further refine this approach and optimize outcomes within this specialized field.
7. Enhanced Quality of Life
Enhanced quality of life represents a fundamental objective of orthocincy physical therapy. Musculoskeletal conditions and injuries can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities, participate in valued roles, and experience overall well-being. Orthocincy physical therapy aims to mitigate these limitations by restoring function, reducing pain, and improving physical capacity, ultimately contributing to an enhanced quality of life. The relationship between enhanced quality of life and this specialized approach is one of cause and effect: impaired function diminishes quality of life, while effective intervention aims to restore function and thereby enhance it. For instance, an individual with chronic back pain limiting their ability to engage in social activities and perform work tasks might experience a significant improvement in quality of life following a course of orthocincy physical therapy that reduces pain and improves functional mobility. Similarly, an older adult experiencing balance difficulties and fear of falling could regain confidence and independence through a balance training program, leading to an enhanced quality of life through reduced fall risk and increased participation in daily activities.
The importance of enhanced quality of life as a component of orthocincy physical therapy lies in its recognition that physical health and well-being are integral to overall life satisfaction. Restoring function and reducing pain not only improve physical capabilities but also empower individuals to engage more fully in meaningful activities, social interactions, and personal pursuits. Consider a child with cerebral palsy undergoing physical therapy to improve motor skills and independence in self-care; the gains achieved through therapy directly translate to an enhanced quality of life for both the child and their family. Likewise, an athlete recovering from a sports injury aims to return to their pre-injury level of performance, and achieving this goal through rehabilitation contributes significantly to their overall sense of well-being and quality of life. These practical applications highlight the far-reaching impact of orthocincy physical therapy beyond the purely physical realm.
In summary, enhanced quality of life represents a central outcome and driving principle within orthocincy physical therapy. By addressing the functional limitations and pain associated with musculoskeletal conditions, this specialized approach empowers individuals to regain lost abilities, participate more fully in life’s activities, and experience a greater sense of overall well-being. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in appreciating the holistic nature of orthocincy physical therapy and its focus on improving not just physical function, but also the overall quality of individuals’ lives. Challenges include effectively measuring and quantifying quality of life improvements and tailoring interventions to address the diverse factors that contribute to individual well-being. Continued research exploring the multifaceted relationship between physical function, pain, and quality of life will further enhance the effectiveness and patient-centeredness of orthocincy physical therapy interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding this specialized approach to physical rehabilitation.
Question 1: What conditions benefit from this specialized approach?
Numerous conditions, including post-surgical rehabilitation, arthritis, back pain, sports injuries, and balance disorders, can benefit. The approach adapts to individual needs, addressing specific impairments and functional limitations.
Question 2: How does this approach differ from traditional physical therapy?
While sharing core principles with traditional physical therapy, this approach frequently emphasizes precise, individualized exercise programs targeting specific biomechanical and functional deficits to optimize movement quality.
Question 3: What is the typical duration of a treatment program?
Treatment duration varies depending on individual needs and the nature of the condition. Some individuals may experience benefits within a few weeks, while others may require a longer duration of care.
Question 4: Is this approach suitable for all age groups?
Interventions can be adapted to individuals of all ages and activity levels, from pediatric patients to older adults. Treatment plans consider age-related physiological differences and specific functional goals.
Question 5: How can individuals find a qualified practitioner?
Recommendations from healthcare providers, online directories specializing in this approach, and professional organizations can assist individuals in locating qualified practitioners.
Question 6: What is the role of patient engagement in the rehabilitation process?
Active patient participation is crucial for successful outcomes. Adherence to prescribed exercise programs, open communication with the therapist, and active engagement in the recovery process contribute significantly to achieving optimal results.
Understanding these key aspects empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their care. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the suitability of this approach for specific conditions and individual needs.
Further exploration of specific applications and advancements in this specialized field will be discussed in subsequent sections.
Conclusion
This exploration of orthocincy physical therapy has highlighted its comprehensive approach to restoring optimal movement and function. Key aspects discussed include the importance of individualized treatment plans, evidence-based exercise programs, and the integration of pain management strategies. The significance of addressing biomechanical factors and the ultimate goal of enhancing patients’ quality of life have also been emphasized. Orthocincy physical therapy offers a structured framework for addressing a wide range of musculoskeletal conditions and injuries, promoting recovery, and improving overall well-being.
The evolving landscape of rehabilitation underscores the continued need for specialized approaches like orthocincy physical therapy. Further research and advancements in movement science, exercise physiology, and pain management promise to refine treatment strategies and further optimize patient outcomes. The focus on restoring function, reducing pain, and improving quality of life positions orthocincy physical therapy as a valuable resource for individuals seeking to regain or maintain optimal musculoskeletal health and physical capacity.