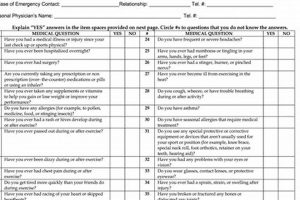
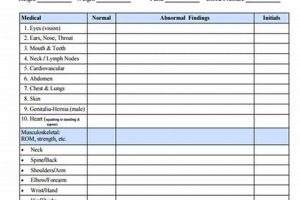
A pre-participation examination for athletics is a crucial prerequisite for student involvement in organized sports. This evaluation typically involves a comprehensive medical history review, including current health status, past injuries, and family medical background. The physical assessment often includes checks of vital signs, vision, cardiovascular health, and musculoskeletal function. A sample document might include sections for physician signature, parental consent, and emergency contact information.
These evaluations serve to identify potential health concerns that could pose a risk during athletic activities. Early detection allows for appropriate medical management and may prevent serious complications. Such preventative measures contribute to a safer sporting environment for all participants. The practice has evolved over time, becoming more standardized and comprehensive in response to growing awareness of sport-related health risks.
This article will further explore specific components of the examination, relevant regulatory guidelines, and best practices for implementation in various sporting contexts.
Tips for Pre-Participation Sports Physicals
Completing a sports physical effectively involves careful preparation and open communication. The following tips offer guidance for students, parents, and guardians navigating this important process.
Tip 1: Schedule the examination well in advance of the intended sports season. This allows ample time to address any identified health concerns and ensures eligibility for participation from the outset.
Tip 2: Gather all necessary medical information. This includes immunization records, details of past injuries or illnesses, and any relevant family medical history. Having this information readily available streamlines the evaluation process.
Tip 3: Communicate openly with the healthcare provider. Provide complete and accurate information regarding current health status, medications, and any experienced symptoms, even if seemingly minor.
Tip 4: Follow any recommendations provided by the healthcare provider. This may involve further testing, specialist referrals, or specific activity modifications to ensure safe participation.
Tip 5: Maintain open communication with coaches and athletic trainers. Inform them of any existing medical conditions or restrictions to ensure appropriate support and supervision during training and competition.
Tip 6: Keep the completed form readily accessible. Ensure a copy is provided to the relevant school or sporting organization as required.
Tip 7: Understand the importance of periodic re-evaluations. Health conditions can change over time. Regular check-ups help ensure ongoing fitness for participation.
Following these tips contributes to a safer and more effective pre-participation process, promoting the health and well-being of student athletes.
By prioritizing these preparatory steps, athletes can ensure a smoother and more informed experience, facilitating safe and successful participation in their chosen sport.
1. Medical History
Medical history constitutes a critical component of pre-participation sports physicals. It provides crucial context for understanding an athlete’s current health status and potential predispositions to future injuries or illnesses. A comprehensive medical history encompasses previous injuries, illnesses, surgeries, hospitalizations, allergies, medications, and family medical history. This information allows healthcare professionals to assess risk factors pertinent to sports participation. For instance, a history of asthma might indicate a higher risk of exercise-induced bronchospasm, while a family history of sudden cardiac death could necessitate further cardiac evaluation. The absence of a complete medical history can lead to overlooking potential health concerns, potentially jeopardizing an athlete’s safety.
Analyzing medical history within the context of a sports physical allows for individualized assessment and risk stratification. Knowledge of prior concussions, for example, informs return-to-play decisions and guides preventative strategies. Similarly, awareness of pre-existing conditions like diabetes or epilepsy enables appropriate management strategies to be implemented during training and competition. A thorough medical history, therefore, facilitates informed decision-making regarding safe participation in sports. Failure to collect a detailed medical history can have significant consequences, potentially delaying diagnosis and treatment of underlying conditions. For instance, an undisclosed history of knee injuries might increase the risk of re-injury if appropriate preventative measures are not taken. Similarly, overlooking a family history of heart conditions could have life-threatening consequences.
In summary, a comprehensive medical history serves as a cornerstone of pre-participation sports physicals. It provides essential insights into an athlete’s health background, facilitating accurate risk assessment and personalized recommendations for safe sports participation. The absence of a detailed medical history can hinder effective evaluation and compromise athlete safety. Therefore, prioritizing the thorough collection and analysis of medical history is paramount for promoting the well-being of student-athletes.
2. Physical Examination
The physical examination is a crucial component of the pre-participation sports physical form, providing objective data about an athlete’s current physical condition. This hands-on assessment, conducted by a qualified healthcare professional, complements the information gathered through the medical history, enabling a more comprehensive evaluation of an athlete’s readiness for sports participation.
- Cardiovascular Assessment
This involves evaluating heart rate, rhythm, blood pressure, and auscultation for murmurs. It aims to identify potential underlying cardiac conditions that could pose risks during strenuous activity. For example, detecting a heart murmur might necessitate further investigation, such as an echocardiogram, before clearing the athlete for participation. This component is vital for preventing sudden cardiac events during sports.
- Pulmonary Evaluation
Assessment of lung function through auscultation and, if necessary, spirometry helps identify respiratory conditions such as asthma or exercise-induced bronchospasm. This information can guide appropriate management strategies, including the use of inhalers or other interventions, to ensure safe participation. Undiagnosed respiratory issues can significantly impair athletic performance and pose health risks.
- Musculoskeletal Screening
This evaluation assesses joint stability, range of motion, and muscle strength. It aims to identify pre-existing injuries, anatomical abnormalities, or muscle imbalances that could predispose an athlete to further injury. For instance, identifying limited range of motion in the shoulder might indicate a previous injury or underlying instability, requiring further investigation or targeted rehabilitation. This screening contributes to injury prevention and promotes optimal athletic performance.
- Neurological Examination
This assessment includes evaluation of reflexes, balance, and coordination. It can help identify neurological conditions or previous injuries that could impact athletic performance or pose safety risks. For example, assessing balance and coordination can be particularly important in contact sports where head injuries are a concern. This examination contributes to a comprehensive understanding of the athlete’s neurological health in the context of sports participation.
These facets of the physical examination, documented within the sports physical form, collectively contribute to a thorough understanding of the athlete’s current physical state. This information, combined with the athlete’s medical history, informs the healthcare provider’s decision regarding clearance for sports participation, ultimately promoting athlete safety and well-being. The physical examination provides a vital snapshot of the athlete’s physical condition at a specific point in time, contributing essential data for informed decision-making about safe participation in sports.
3. Cardiovascular Assessment
Cardiovascular assessment forms an integral part of pre-participation sports physicals, serving as a critical screening tool for identifying potential cardiac conditions that could pose risks during athletic activity. This assessment typically includes evaluating heart rate and rhythm, blood pressure measurement, and auscultation for murmurs. It aims to detect underlying conditions, such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or congenital heart defects, which might not manifest during routine activities but could become life-threatening under the stress of intense exercise. For example, a seemingly healthy athlete with an undiagnosed heart condition could experience sudden cardiac arrest during strenuous exertion. Therefore, a thorough cardiovascular assessment within the context of a sports physical can be life-saving.
The importance of cardiovascular assessment is further underscored by the potential for strenuous exercise to exacerbate underlying cardiac conditions. Intense physical activity places increased demands on the cardiovascular system. Pre-existing conditions, even if asymptomatic at rest, can become symptomatic or even life-threatening during vigorous exertion. For example, an athlete with an undiagnosed arrhythmia might experience palpitations, dizziness, or syncope during intense training or competition. A thorough cardiovascular assessment allows for early detection and appropriate management of such conditions, mitigating the risks associated with sports participation. Failure to conduct a thorough cardiovascular assessment can have severe consequences, including sudden cardiac death. This underscores the critical role of this assessment in ensuring athlete safety and well-being.
In summary, cardiovascular assessment is not merely a formality within the sports physical process; it represents a fundamental safeguard for athletes. It provides critical information about cardiac health, enabling early detection of potentially life-threatening conditions. This, in turn, allows for appropriate medical intervention and informed decision-making regarding safe participation in sports. The inclusion of a comprehensive cardiovascular assessment within pre-participation sports physicals is, therefore, paramount for promoting the health and safety of all athletes.
4. Musculoskeletal Evaluation
Musculoskeletal evaluation constitutes a critical component of the pre-participation sports physical form, serving to identify existing or potential musculoskeletal issues that could affect an athlete’s ability to safely participate in sports. This evaluation focuses on assessing joint stability, range of motion, strength, and flexibility. It aims to uncover any underlying conditions, such as previous injuries, joint laxity, muscle imbalances, or postural abnormalities, that could predispose an athlete to future injury. For example, an athlete with a history of ankle sprains might exhibit decreased ankle stability, increasing their risk of re-injury. Similarly, identifying significant discrepancies in leg length or muscle strength could indicate an increased risk of overuse injuries. A thorough musculoskeletal evaluation, therefore, provides valuable insights for injury prevention and performance optimization.
The practical significance of a comprehensive musculoskeletal evaluation lies in its ability to inform individualized training and conditioning programs. Identifying areas of weakness or instability allows for targeted interventions, such as strengthening exercises or bracing, to mitigate injury risk. For instance, an athlete with weak core muscles might benefit from a core strengthening program to improve stability and reduce the risk of lower back injuries. Similarly, an athlete with limited flexibility might benefit from targeted stretching exercises to improve range of motion and prevent muscle strains. Furthermore, the musculoskeletal evaluation can identify athletes who may require further specialized assessment, such as referral to a sports medicine physician or physical therapist, for more in-depth evaluation and management of specific conditions. Early identification and intervention can significantly impact long-term athletic health and performance.
In summary, musculoskeletal evaluation plays a vital role in pre-participation sports physicals. It provides crucial information about an athlete’s musculoskeletal system, enabling identification of potential risk factors for injury. This information, in turn, informs preventative strategies, individualized training programs, and appropriate referrals for specialized care. The thoroughness of this evaluation contributes significantly to athlete safety, performance optimization, and long-term musculoskeletal health. Integrating a robust musculoskeletal evaluation into pre-participation sports physicals remains a cornerstone of responsible athletic healthcare.
5. Vision Screening
Vision screening within the context of a pre-participation sports physical serves as a crucial assessment of visual acuity and overall eye health. Adequate vision plays a vital role in athletic performance, impacting depth perception, peripheral awareness, hand-eye coordination, and reaction time. These visual skills are essential for successful participation in a wide range of sports, from baseball and basketball to tennis and soccer. Impaired vision can hinder an athlete’s ability to accurately track objects, judge distances, and react effectively to changing game situations, potentially increasing the risk of injury to themselves and others. For instance, an athlete with undiagnosed nearsightedness might misjudge the distance to a fly ball, leading to a collision with a teammate or an unsuccessful catch. Similarly, impaired peripheral vision could increase the risk of collisions in sports like soccer or hockey. Therefore, incorporating vision screening into the sports physical helps ensure that athletes possess the necessary visual skills for safe and effective participation.
Vision screening during the sports physical typically involves assessing visual acuity using a standard eye chart. This assessment can identify refractive errors such as nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), and astigmatism. Early detection of these conditions allows for appropriate corrective measures, such as eyeglasses or contact lenses, to be implemented. Furthermore, vision screening can detect other eye conditions, such as strabismus (eye misalignment) or amblyopia (lazy eye), which might require further evaluation and specialized treatment by an ophthalmologist or optometrist. Addressing these issues before sports participation can optimize visual function and enhance athletic performance. A comprehensive eye examination can also detect potentially serious eye conditions like glaucoma or cataracts, even in young athletes. Early detection and treatment of these conditions can prevent irreversible vision loss.
In summary, vision screening represents a vital component of the pre-participation sports physical, safeguarding athlete safety and optimizing performance. It facilitates early detection and correction of visual impairments, enabling athletes to fully participate in their chosen sport without the hindrance of compromised vision. This screening, combined with other aspects of the sports physical, contributes to a comprehensive assessment of an athlete’s readiness for safe and successful sports participation. Failing to address visual impairments can have far-reaching implications, affecting not only athletic performance but also academic performance and overall quality of life. Therefore, prioritizing vision screening within the pre-participation sports physical is essential for promoting the overall well-being of student-athletes.
6. Physician Clearance
Physician clearance represents the culmination of the pre-participation sports physical evaluation. It signifies that a qualified healthcare professional has reviewed the athlete’s medical history, conducted a comprehensive physical examination, and deemed the athlete medically eligible to participate in their chosen sport. This clearance, documented on the sports physical form, is not merely a formality but a critical safeguard, protecting athletes from potential health risks associated with sports participation. It demonstrates that potential health concerns have been identified and addressed, minimizing the risk of exacerbating pre-existing conditions or incurring new injuries. For instance, an athlete with a history of concussions might receive clearance conditional upon completing a specific return-to-play protocol, ensuring their brain has adequately recovered before resuming contact sports. Similarly, an athlete with asthma might receive clearance with specific instructions regarding medication usage and management of exercise-induced bronchospasm. Without physician clearance, participation in sports could pose significant health risks.
The practical significance of physician clearance lies in its ability to facilitate informed decision-making regarding athlete safety and eligibility. It provides coaches, athletic trainers, and school officials with essential information regarding an athlete’s health status, enabling them to implement appropriate safety protocols and modifications as needed. For example, knowledge of an athlete’s pre-existing knee injury might prompt coaches to modify training drills or limit playing time to prevent re-injury. Similarly, awareness of an athlete’s diabetes might necessitate adjustments to hydration protocols during practice and competition. Physician clearance, therefore, serves as a critical communication tool, ensuring that all stakeholders are aware of an athlete’s health needs and can collaborate to create a safe and supportive athletic environment. This understanding fosters a culture of safety and responsibility within the sports community.
In summary, physician clearance represents a critical juncture within the pre-participation sports physical process. It signifies a comprehensive assessment of an athlete’s health status and their readiness for sports participation. This clearance, documented on the sports physical form, acts as a safeguard, protecting athletes from potential health risks and informing decisions related to training, competition, and overall athlete management. The absence of physician clearance exposes athletes to unnecessary risks and undermines efforts to create a safe and supportive athletic environment. Therefore, prioritizing physician clearance as an essential component of pre-participation sports physicals remains fundamental to promoting athlete health and well-being.
7. Parental Consent
Parental consent forms an indispensable component of the pre-participation sports physical process, particularly for minors. This consent acknowledges inherent risks associated with sports participation and authorizes medical evaluation and treatment as needed. The consent process ensures parents or guardians are fully informed about potential physical and psychological demands of the sport, enabling informed decision-making regarding their child’s participation. It represents a legal and ethical safeguard, protecting both the athlete and the sporting organization. For instance, if a minor sustains an injury during practice or a game, parental consent allows medical personnel to administer necessary treatment without delay. Absence of such consent could hinder timely medical intervention, potentially exacerbating the injury. Furthermore, parental consent reinforces shared responsibility for athlete well-being, fostering collaboration between parents, coaches, and medical professionals.
The practical significance of parental consent extends beyond immediate medical treatment. It allows for open communication between parents and medical providers, ensuring any pre-existing medical conditions or specific health needs are addressed. This information informs the development of individualized training plans and safety protocols tailored to the athlete’s specific requirements. For example, a parent might inform the coaching staff about their child’s history of asthma, prompting adjustments to training intensity and ensuring appropriate medical supervision during strenuous activities. This collaboration promotes a safe and supportive athletic environment, minimizing potential risks and maximizing athlete well-being. Furthermore, parental consent ensures compliance with legal and ethical guidelines regarding medical treatment of minors, protecting both the athlete and the sporting organization from potential liability issues. This shared understanding of responsibilities and open communication strengthens the athlete support system.
In summary, parental consent represents a cornerstone of responsible athletic participation for minors. It provides a legal and ethical framework for medical treatment and facilitates open communication between parents, medical professionals, and coaching staff. This collaborative approach fosters a safer and more supportive athletic environment, promoting athlete well-being and ensuring adherence to established guidelines. Securing informed parental consent remains a critical step in the pre-participation sports physical process, demonstrating a commitment to athlete safety and responsible sports participation. This shared understanding reinforces a culture of care and accountability within the youth sports community.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding pre-participation physical examinations for sports.
Question 1: How often is a sports physical required?
Typically, a sports physical is required annually or before each new sports season. Specific requirements may vary depending on the state or governing athletic organization.
Question 2: What if a medical condition is identified during the physical?
If a potential medical concern arises during the examination, further evaluation or treatment might be recommended before clearance for participation. This could involve specialist referrals, additional testing, or specific treatment plans.
Question 3: Can any healthcare provider conduct a sports physical?
While specific regulations vary, generally, licensed physicians, physician assistants, or nurse practitioners can conduct sports physicals. It’s essential to verify the qualifications of the healthcare provider based on local regulations.
Question 4: What should athletes bring to their sports physical appointment?
Athletes should bring a completed medical history form, a list of current medications, immunization records, and any relevant medical documentation pertaining to previous injuries or illnesses. Wearing comfortable clothing suitable for a physical examination is also recommended.
Question 5: What is the difference between a sports physical and a regular check-up?
While both involve assessing overall health, a sports physical focuses specifically on identifying conditions that could pose a risk during athletic activity. It emphasizes musculoskeletal and cardiovascular assessments relevant to sports participation, whereas a regular check-up might encompass a broader range of health concerns.
Question 6: What happens if an athlete fails to complete a required sports physical?
Failure to complete a required pre-participation physical examination typically results in ineligibility for participation in organized sports. This policy prioritizes athlete safety and ensures all participants have undergone necessary medical evaluation.
Understanding these frequently asked questions contributes to a smoother and more informed experience with pre-participation sports physicals, promoting athlete safety and well-being.
For further information or specific requirements, consulting with a healthcare professional or the relevant governing athletic organization is advised.
Conclusion
This exploration of pre-participation physical examinations for sports has underscored their crucial role in safeguarding athlete health and well-being. From comprehensive medical history reviews and thorough physical assessments to specific evaluations of cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems, each component contributes to a comprehensive understanding of an athlete’s readiness for participation. Furthermore, vision screening and the essential physician clearance, grounded in informed parental consent, complete this vital process. These examinations serve not merely as administrative requirements but as proactive measures to identify and address potential health risks, ensuring safer and more informed participation in sports.
Prioritizing these evaluations demonstrates a commitment to athlete well-being, fostering a culture of safety and responsibility within the sports community. These preventative measures are an investment in long-term athletic health and performance, contributing to a more positive and sustainable sporting experience for all. Continual refinement of these evaluations, informed by evolving medical knowledge and best practices, will further enhance their effectiveness in protecting athletes and promoting a safer sporting future.