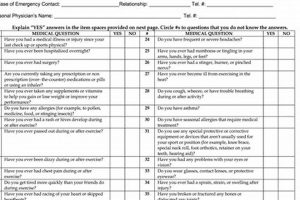
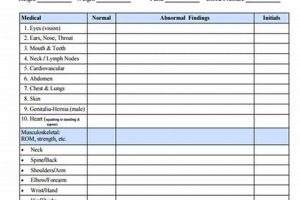
The required medical evaluation for athlete participation in the National Association of Intercollegiate Athletics (NAIA) involves a comprehensive assessment of an individual’s health status to ensure their safety and eligibility for competition. This process typically includes a review of medical history, a physical examination, and may involve additional assessments as deemed necessary by the examining physician.
A pre-participation medical clearance safeguards student-athlete well-being, mitigating the risks associated with strenuous physical activity. It allows medical professionals to identify potential health concerns that might predispose an athlete to injury or illness, enabling preventative measures and appropriate management strategies. This process also helps ensure fair competition by verifying athlete eligibility according to established health standards. Historically, such evaluations have evolved alongside advancements in sports medicine, reflecting a growing understanding of the complex relationship between athletic performance and overall health.
Further exploration of this topic will cover specific components of the evaluation process, common medical concerns encountered, and resources available to athletes and institutions navigating these requirements.
Successfully completing the required medical evaluation ensures eligibility for participation in NAIA athletics. The following tips offer guidance for athletes and institutions involved in this process.
Tip 1: Schedule Evaluations Early: Securing appointments with medical professionals well in advance of the intended participation date avoids potential delays and ensures timely clearance. This proactive approach allows ample time for any necessary follow-up appointments or consultations.
Tip 2: Compile Comprehensive Medical History: Gathering detailed medical records, including prior diagnoses, treatments, and medications, facilitates a thorough evaluation. A complete history enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding an athlete’s readiness for competition.
Tip 3: Disclose All Medical Information: Open communication with medical professionals regarding all current and past health concerns is crucial. Accurate and complete disclosure, even seemingly minor issues, helps ensure appropriate medical oversight and prevents potential complications.
Tip 4: Understand the Evaluation Components: Familiarizing oneself with the required components of the medical evaluation, such as the physical examination and any specific tests or screenings, allows athletes to prepare accordingly.
Tip 5: Follow Up on Recommendations: Adhering to any recommendations or referrals provided by the examining physician demonstrates a commitment to athlete health and safety. Timely follow-up ensures any identified health concerns are addressed appropriately.
Tip 6: Maintain Open Communication with Athletic Staff: Maintaining regular communication with athletic trainers and other relevant staff regarding any health changes or concerns throughout the season promotes a collaborative approach to athlete well-being.
Tip 7: Keep Records Organized: Maintaining organized and accessible copies of all medical documentation facilitates efficient communication and ensures compliance with NAIA regulations.
Following these recommendations promotes a smooth and efficient medical evaluation process, prioritizing athlete health and safety while ensuring eligibility for competition.
These guidelines provide a foundational understanding of the importance of the pre-participation medical evaluation. The subsequent sections will delve deeper into specific aspects of NAIA eligibility requirements.
1. Medical History
A comprehensive medical history forms the cornerstone of the NAIA sports physical form, providing essential context for evaluating an athlete’s readiness for competition. This detailed record of past health issues, injuries, and treatments allows medical professionals to identify potential risk factors and make informed decisions regarding participation. A thorough medical history is crucial for ensuring athlete safety and maintaining a level playing field.
- Previous Injuries:
Documentation of prior injuries, including fractures, sprains, and concussions, is critical. For example, a history of multiple ankle sprains might necessitate preventative measures like ankle bracing. Understanding the nature and extent of past injuries allows for targeted assessments during the physical examination and informs decisions regarding return-to-play protocols within the NAIA framework.
- Pre-existing Conditions:
Chronic illnesses like asthma, diabetes, or heart conditions require careful management in the context of athletic participation. Disclosing such conditions, along with current treatment plans, enables medical professionals to assess potential risks and implement appropriate safeguards. This information is crucial for tailoring training regimens and ensuring the athlete’s well-being while adhering to NAIA regulations.
- Prior Surgeries:
Surgical history, including the type of surgery, date, and any complications, offers valuable insights into an athlete’s physical condition. Knowledge of previous surgeries, such as knee arthroscopy or appendectomy, informs the physician’s assessment during the physical examination and guides decisions regarding activity limitations or necessary modifications within the NAIA context.
- Medications and Allergies:
A complete list of current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, is essential for understanding potential drug interactions or side effects that might impact athletic performance. Similarly, disclosing any known allergies, particularly to medications or environmental factors, helps prevent adverse reactions and ensures prompt medical intervention if needed. This information contributes to a comprehensive understanding of an athlete’s health status within the NAIA sports physical form.
The medical history, in conjunction with the other components of the NAIA sports physical form, provides a holistic view of an athlete’s health profile. This information facilitates effective communication between athletes, medical professionals, and athletic staff, ultimately promoting safe and fair competition within the NAIA framework. A thorough medical history is not merely a formality; it is a vital tool for safeguarding athlete well-being and upholding the integrity of collegiate athletics.
2. Physical Examination
The physical examination constitutes a critical component of the NAIA sports physical form, providing a real-time assessment of an athlete’s current physical condition. This hands-on evaluation complements the medical history, offering insights into potential musculoskeletal issues, cardiovascular health, and overall well-being. A thorough physical examination is essential for identifying potential risks and ensuring athlete safety within the NAIA regulatory framework.
- Cardiovascular Assessment:
This assessment typically involves listening to the heart and lungs, measuring blood pressure, and evaluating pulse rate. It aims to detect potential cardiac abnormalities that might pose a risk during strenuous activity. For example, detecting a heart murmur might necessitate further evaluation by a cardiologist before clearance for participation is granted. This component is crucial for mitigating the risk of sudden cardiac events in athletes.
- Musculoskeletal Evaluation:
This evaluation assesses the athlete’s range of motion, joint stability, and muscle strength. It involves examining the major joints of the body, looking for signs of previous injuries, instability, or imbalances that might predispose the athlete to future injury. For instance, limited range of motion in the shoulder joint might indicate a rotator cuff issue requiring further investigation and potential rehabilitation before participation.
- Neurological Screening:
Basic neurological screening, including reflexes, balance, and coordination tests, can help identify underlying neurological issues. This screening might involve tests like the Romberg test for balance or assessment of deep tendon reflexes. Such assessments are crucial for detecting conditions that could impact an athlete’s ability to safely participate in their sport.
- Visual Acuity:
Assessing visual acuity is important for sports requiring optimal vision. Impaired vision can significantly impact performance and increase the risk of injury. Therefore, the physical examination often includes a basic eye chart test to ensure adequate vision or identify the need for corrective lenses.
The physical examination findings, combined with the athlete’s medical history and other components of the NAIA sports physical form, inform the physician’s final clearance decision. This comprehensive approach ensures that athletes are medically fit to participate, minimizing the risk of injury and promoting a safe and competitive environment within the NAIA framework.
3. Physician Clearance
Physician clearance represents the culmination of the NAIA sports physical form process. It signifies that a qualified medical professional has reviewed the athlete’s medical history, conducted a thorough physical examination, and deemed the athlete medically eligible to participate in intercollegiate athletics. This clearance is not merely a formality but a critical safeguard, protecting athlete well-being and ensuring fair competition within the NAIA.
- Evaluation of Medical History:
The physician carefully considers the athlete’s disclosed medical history, including past injuries, pre-existing conditions, and surgeries. This evaluation assesses potential risks associated with specific conditions, such as a previous concussion or asthma. The physician determines whether these conditions might pose a threat to the athlete’s health during strenuous activity or require specific management strategies within the context of NAIA competition.
- Assessment of Physical Examination Findings:
Findings from the physical examination, including cardiovascular assessment, musculoskeletal evaluation, and neurological screening, are integral to the clearance decision. For instance, abnormal heart sounds or limited joint mobility might necessitate further investigation or specialized consultations before clearance can be granted. The physician synthesizes these findings to form a comprehensive picture of the athlete’s current physical state.
- Determination of Eligibility:
Based on the combined assessment of medical history and physical examination findings, the physician determines whether the athlete meets the NAIA’s medical eligibility requirements. This decision considers the specific demands of the sport and the potential impact of any pre-existing conditions. If cleared, the athlete receives formal documentation confirming their eligibility to participate.
- Recommendations and Restrictions:
In some cases, clearance might be granted with specific recommendations or restrictions. An athlete with a history of ankle sprains, for example, might be cleared with the recommendation of ankle bracing during practices and competitions. These recommendations aim to mitigate potential risks and ensure the athlete’s safe participation within the NAIA framework. Such restrictions are documented and communicated to the athlete and relevant athletic staff.
Physician clearance serves as the final gatekeeper in the NAIA sports physical form process. It ensures that athletes meet the necessary health standards for safe participation, protecting both individual well-being and the integrity of intercollegiate competition. This crucial step underscores the NAIA’s commitment to athlete safety and fair play.
4. Immunization Records
Immunization records constitute a critical component of the NAIA sports physical form, reflecting a commitment to preventative healthcare and disease control within the collegiate athletic environment. Maintaining updated immunization records safeguards athlete health and minimizes the risk of outbreaks within teams and across the broader campus community. This section explores the multifaceted role of immunization records in the NAIA’s athlete eligibility process.
- Verification of Immunity:
Immunization records provide documented evidence of immunity to preventable diseases, such as measles, mumps, rubella, and tetanus. This verification helps ensure that athletes have received recommended vaccinations, minimizing their susceptibility to these illnesses. Maintaining adequate immunity safeguards not only individual athletes but also the collective health of teams and the broader campus population, reducing the potential for outbreaks.
- Compliance with NAIA Regulations:
The NAIA mandates specific immunization requirements for athlete participation, aligning with broader public health guidelines. Submission of immunization records demonstrates compliance with these regulations, ensuring eligibility for competition. Failure to provide adequate documentation of immunity can lead to restrictions on participation, underscoring the importance of maintaining updated records.
- Protection Against Outbreaks:
Within the close-knit environment of athletic teams, communicable diseases can spread rapidly. Comprehensive immunization records act as a protective barrier, reducing the likelihood of outbreaks and safeguarding team performance. By ensuring a high level of immunity within teams, the NAIA minimizes disruptions to training schedules and competition calendars, promoting a healthy and competitive environment.
- Promoting Public Health:
Requiring immunization records aligns with broader public health initiatives aimed at preventing and controlling the spread of infectious diseases. By emphasizing the importance of vaccinations, the NAIA contributes to the creation of a healthier campus environment and reinforces the role of preventative healthcare in the athletic community. This proactive approach benefits not only athletes but also the broader campus population.
In summary, immunization records are not merely a procedural requirement but a vital component of the NAIA sports physical form, reflecting a commitment to athlete well-being and public health. By verifying immunity, ensuring compliance with regulations, and minimizing the risk of outbreaks, these records contribute significantly to a safer and healthier athletic environment within the NAIA framework.
5. Cardiovascular Screening
Cardiovascular screening plays a vital role within the NAIA sports physical form, serving as a critical safeguard against potential cardiac risks associated with strenuous athletic activity. This screening process aims to identify underlying heart conditions that might predispose athletes to adverse events during competition. Conditions such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), a thickening of the heart muscle, or congenital heart defects can remain asymptomatic yet pose significant risks during intense physical exertion. Detecting these conditions through cardiovascular screening allows for appropriate medical intervention, potentially preventing life-threatening situations. For instance, an athlete with undiagnosed HCM might experience sudden cardiac arrest during a game, while timely screening and subsequent management could mitigate this risk. The inclusion of cardiovascular screening within the NAIA sports physical form demonstrates a commitment to athlete safety and reflects a proactive approach to risk management in collegiate sports.
Practical implementation of cardiovascular screening within the NAIA context often involves a combination of non-invasive procedures. Auscultation, listening to the heart with a stethoscope, allows physicians to detect abnormal heart sounds, such as murmurs. Electrocardiograms (ECGs) provide a visual representation of the heart’s electrical activity, aiding in the identification of arrhythmias or other electrical abnormalities. In some cases, more comprehensive evaluations, such as echocardiograms, might be recommended to further assess cardiac structure and function. The specific components of cardiovascular screening can vary based on individual risk factors and institutional protocols. However, the underlying goal remains consistent: to identify potential cardiac risks and ensure the safety of student-athletes participating in NAIA competition. The information gleaned from these screenings informs decisions regarding eligibility and guides appropriate medical management, contributing significantly to a safer and healthier athletic environment.
The integration of cardiovascular screening into the NAIA sports physical form underscores the importance of proactive health management in collegiate athletics. While not all cardiac conditions are preventable, early detection through comprehensive screening allows for timely intervention and risk mitigation. This proactive approach not only protects athlete health and safety but also promotes informed decision-making regarding participation. Challenges remain in ensuring equitable access to comprehensive cardiovascular screening and navigating the complexities of interpreting results. However, the continued emphasis on cardiovascular health within the NAIA framework reinforces the commitment to prioritizing athlete well-being and fostering a safe and competitive environment for all participants.
6. Orthopedic Assessment
Orthopedic assessment within the NAIA sports physical form serves as a critical component in evaluating musculoskeletal health and identifying potential risks that could impact an athlete’s participation and performance. This assessment focuses on evaluating the structural integrity and functional capacity of the musculoskeletal system, encompassing bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. A thorough orthopedic evaluation helps identify pre-existing injuries, anatomical abnormalities, or functional limitations that might predispose an athlete to future injury or exacerbate existing conditions during the demanding physical activities inherent in collegiate sports. For example, an athlete with a history of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury might exhibit instability in the knee joint during specific maneuvers, increasing their risk of re-injury. Similarly, identifying discrepancies in leg length or limitations in hip range of motion can provide valuable insights into potential biomechanical imbalances that might contribute to overuse injuries or performance limitations. Therefore, orthopedic assessment provides essential information for informed decision-making regarding an athlete’s readiness for participation and guides preventative strategies or rehabilitation programs aimed at minimizing risk and optimizing performance within the NAIA framework.
Practical application of orthopedic assessment within the NAIA sports physical form typically involves a series of targeted examinations. Range of motion testing assesses the flexibility and mobility of joints, identifying any limitations or asymmetries that might indicate underlying issues. Palpation, the process of examining the body by touch, allows medical professionals to assess tissue texture, identify areas of tenderness, and detect potential abnormalities in bone or soft tissue structures. Specific orthopedic tests, such as the Lachman test for ACL integrity or the Apprehension test for shoulder instability, provide further insights into joint stability and function. Strength testing evaluates muscle function and identifies potential imbalances that might contribute to injury. The findings from these assessments, combined with the athlete’s medical history and other components of the physical form, inform the physician’s overall evaluation of musculoskeletal health and contribute to the final clearance decision. This comprehensive approach aims to minimize the risk of musculoskeletal injuries and ensure athlete safety within the context of NAIA competition.
In summary, orthopedic assessment serves as a cornerstone of the NAIA sports physical form, providing essential information for safeguarding athlete health and promoting optimal performance. By identifying pre-existing conditions, functional limitations, and potential risk factors, this comprehensive assessment allows for informed decision-making regarding participation and guides preventative or rehabilitative strategies. Challenges remain in standardizing orthopedic assessment procedures and ensuring consistent application across institutions. However, the continued emphasis on musculoskeletal health within the NAIA framework reinforces the commitment to athlete well-being and highlights the importance of proactive injury prevention in collegiate sports. Orthopedic assessment, combined with other components of the sports physical form, contributes significantly to creating a safer and more competitive athletic environment within the NAIA.
7. Consent and Signatures
Consent and signatures represent a crucial legal and ethical component of the NAIA sports physical form, establishing a framework of informed agreement and accountability within the collegiate athletic environment. The act of signing the form signifies an athlete’s acknowledgment and acceptance of the inherent risks associated with participation in intercollegiate sports. This informed consent ensures athletes understand the physical demands and potential dangers involved in their chosen sport, acknowledging the possibility of injury despite adherence to safety protocols. Furthermore, the signature affirms the athlete’s agreement to abide by the NAIA’s rules and regulations regarding eligibility, conduct, and health and safety protocols. For instance, an athlete signing the form acknowledges their responsibility to report any injuries or health concerns to the appropriate medical staff and to comply with any prescribed treatment plans or activity restrictions. This shared understanding between the athlete, the institution, and the NAIA establishes a foundation of trust and promotes a culture of responsible participation. Consent also extends to the authorization for medical treatment in the event of an injury or emergency during athletic activities. This pre-authorization streamlines the process of providing necessary medical care, potentially minimizing delays that could exacerbate an athlete’s condition.
Beyond the athlete’s consent, the NAIA sports physical form often requires signatures from other key stakeholders. Parental or guardian signatures are typically required for athletes under a certain age, ensuring legal consent for participation and medical treatment. Physician signatures validate the completion of the medical evaluation and confirm the athlete’s medical eligibility based on the assessment findings. These signatures document the professional evaluation and attest to the athlete’s suitability for participation within the NAIA framework. The presence of these multiple signatures reinforces the collaborative nature of the process, emphasizing the shared responsibility for athlete health and safety. It underscores the commitment of all parties involvedthe athlete, parents or guardians, physicians, and the institutionto upholding the NAIA’s standards of ethical conduct and athlete well-being.
In conclusion, consent and signatures on the NAIA sports physical form represent more than just a procedural formality; they embody a commitment to ethical principles, legal compliance, and shared responsibility. These signatures establish a framework of informed agreement, ensuring athletes understand the inherent risks of participation and agree to abide by established rules and regulations. They also facilitate timely medical treatment and reinforce the collaborative efforts of all stakeholders in promoting athlete health and safety within the NAIA. Ensuring proper documentation and understanding of the consent process is crucial for mitigating legal risks and fostering a culture of transparency and accountability within collegiate athletics. The emphasis on informed consent and appropriate signatures underscores the NAIA’s dedication to athlete well-being and reinforces the importance of ethical conduct in intercollegiate sports.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the NAIA sports physical form, providing clarity on key aspects of the process and requirements.
Question 1: What is the purpose of the NAIA sports physical form?
The form ensures athlete eligibility for competition by verifying compliance with established health and safety standards, mitigating risks associated with strenuous physical activity.
Question 2: Who is required to complete the NAIA sports physical form?
All student-athletes intending to participate in NAIA-sanctioned sports are required to complete and submit the form before engaging in any competitive activities.
Question 3: Where can one obtain the NAIA sports physical form?
The official form is typically available through the NAIA website and respective institutional athletic departments. Institutions may also utilize their own specific versions, provided they meet NAIA requirements.
Question 4: What are the key components of the NAIA sports physical form?
Key components include a comprehensive medical history, a thorough physical examination conducted by a qualified medical professional, immunization records, cardiovascular screening, orthopedic assessment, and consent signatures from the athlete, parent/guardian (if applicable), and physician.
Question 5: How often is the NAIA sports physical form required?
Typically, completion is required annually. However, specific requirements may vary by institution and sport. Consult with the relevant athletic department for specific guidance.
Question 6: What happens if a medical condition is identified during the evaluation process?
If a medical condition is identified, the examining physician may recommend further evaluation, treatment, or activity modifications to ensure athlete safety. Clearance for participation might be contingent upon adherence to these recommendations.
Understanding these aspects of the NAIA sports physical form process promotes informed participation and safeguards athlete health and well-being.
For additional information and resources, consult the official NAIA website or contact the respective institutional athletic department.
Conclusion
This exploration of the NAIA sports physical form has highlighted its crucial role in safeguarding athlete health and ensuring fair competition within the NAIA framework. From comprehensive medical histories and thorough physical examinations to cardiovascular screenings and orthopedic assessments, each component contributes to a holistic evaluation of an athlete’s readiness for participation. The importance of informed consent, appropriate signatures, and adherence to immunization requirements further underscores the NAIA’s commitment to athlete well-being and responsible conduct. Understanding these elements provides valuable insights into the comprehensive nature of the process and its significance in promoting a safe and competitive athletic environment.
The NAIA sports physical form serves as a vital tool for mitigating risks, promoting informed participation, and upholding the integrity of collegiate athletics. Continued emphasis on preventative healthcare, comprehensive evaluations, and athlete education will further enhance the effectiveness of this process in safeguarding student-athlete well-being. Prioritizing these elements strengthens the foundation of a healthy and competitive athletic landscape within the NAIA, contributing to a more sustainable and enriching experience for all participants.