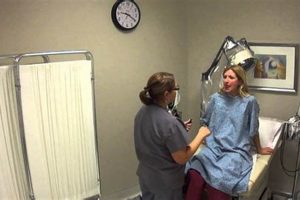
A comprehensive assessment conducted by a hormonal specialist typically involves evaluating vital signs, palpating the thyroid gland, and observing for physical manifestations of endocrine disorders such as changes in skin texture, hair distribution, or body fat distribution. This evaluation may also include a review of medical history and discussion of symptoms.
This specialized assessment is crucial for detecting and managing hormonal imbalances, which can significantly impact overall health and well-being. Early detection of conditions like thyroid disease, diabetes, or adrenal disorders can lead to timely intervention and prevent long-term complications. The evolution of these assessments reflects advancements in medical understanding of the endocrine system and its complex interplay with other bodily functions.
Further exploration of this topic will cover specific components of the assessment, common endocrine disorders diagnosed through this process, and the role of laboratory testing in conjunction with the clinical evaluation.
Tips for an Effective Endocrine Evaluation
Preparation and open communication are key to maximizing the value of a consultation with a hormonal specialist. The following tips can help individuals prepare and ensure a productive appointment.
Tip 1: Maintain a comprehensive medication list. Include all prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements. This information is crucial for assessing potential drug interactions or underlying conditions.
Tip 2: Compile a detailed family history. Many endocrine disorders have a genetic component. Sharing family history regarding hormonal conditions can aid in risk assessment and diagnosis.
Tip 3: Track symptoms and their frequency. A record of symptoms, including their duration and any associated factors, provides valuable insights for the specialist.
Tip 4: Prepare questions beforehand. Compiling a list of questions ensures that all concerns are addressed during the limited appointment time.
Tip 5: Dress comfortably for ease of examination. Certain aspects of the assessment may require access to specific areas of the body.
Tip 6: Be honest and forthcoming about lifestyle factors. Diet, exercise, stress levels, and sleep patterns can significantly influence hormonal health.
Tip 7: Follow any pre-appointment instructions carefully. Some assessments may require fasting or specific dietary restrictions prior to the visit.
By following these recommendations, patients can contribute significantly to a thorough and informative consultation, facilitating accurate diagnosis and effective management of any potential endocrine issues.
This preparation contributes to a more efficient diagnostic process and empowers individuals to actively participate in their healthcare journey. The subsequent section will delve into common diagnostic procedures used in endocrinology.
1. Visual Inspection
Visual inspection plays a crucial role in the endocrinologist physical exam, serving as an initial screening tool for a range of hormonal disorders. This non-invasive procedure involves careful observation of the patient’s overall appearance, focusing on specific areas that can manifest visible signs of endocrine dysfunction. Changes in skin texture, hair distribution, body fat distribution, and the presence of unusual pigmentation or growths can offer valuable clues about underlying hormonal imbalances. For example, hyperpigmentation, particularly in skin creases, can be indicative of Addison’s disease, while excessive hair growth in a female patient might suggest polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). The observation of a goiter, an enlarged thyroid gland, during visual inspection can prompt further investigation for thyroid disorders. This initial visual assessment often guides subsequent stages of the physical exam, influencing which areas require more detailed examination, such as palpation or auscultation.
The effectiveness of visual inspection relies on the clinician’s expertise in recognizing subtle visual cues that might be overlooked by an untrained eye. These observations, combined with information gathered through patient history and other components of the physical exam, contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s endocrine health. The detection of specific visual signs can expedite the diagnostic process, leading to earlier interventions and improved patient outcomes. Furthermore, visual inspection can reveal co-existing conditions or complications associated with endocrine disorders. For instance, the presence of acanthosis nigricans, a darkening and thickening of the skin, can indicate insulin resistance and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Therefore, this seemingly simple visual assessment provides a wealth of information, often serving as the first step toward accurate diagnosis and effective management of endocrine-related conditions.
Visual inspection, while a valuable starting point, has limitations. It does not provide definitive diagnoses and must be complemented by other diagnostic procedures, including laboratory tests and imaging studies. However, the careful observation of visible manifestations during the physical exam often directs the course of further investigations, streamlining the diagnostic process and optimizing resource utilization. Challenges may include subtle or atypical presentations of endocrine disorders, requiring heightened clinical suspicion and experience to interpret visual findings accurately. Therefore, ongoing professional development and awareness of emerging clinical patterns are essential for maximizing the diagnostic potential of visual inspection within the context of a comprehensive endocrine evaluation.
2. Palpation (thyroid, lymph nodes)
Palpation of the thyroid gland and surrounding lymph nodes constitutes a critical component of the endocrinologist physical exam. This hands-on technique provides essential information about the size, shape, texture, and tenderness of these structures, aiding in the detection of potential abnormalities indicative of endocrine disorders.
- Thyroid Gland Assessment
Palpation of the thyroid gland allows the endocrinologist to assess its size, contour, and consistency. Enlargement (goiter), asymmetry, nodules, or unusual firmness can suggest conditions such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroiditis, or thyroid cancer. The presence of tenderness upon palpation might indicate inflammation. Careful examination distinguishes between diffuse enlargement and localized nodules. This direct assessment provides immediate, tangible information, guiding further diagnostic investigations, such as ultrasound or fine-needle aspiration biopsy, if warranted.
- Lymph Node Evaluation
Lymph nodes located in the neck, near the thyroid gland, are also palpated during the exam. Enlarged or tender lymph nodes can be a sign of infection, inflammation, or, in some cases, malignancy. The location, size, and consistency of any palpable lymph nodes offer clues regarding the potential underlying cause. This assessment provides crucial information for differentiating between localized thyroid pathology and systemic conditions affecting the lymphatic system.
- Technique and Positioning
Proper technique is essential for accurate palpation. The patient is typically positioned with the neck slightly extended. The endocrinologist uses their fingertips to gently palpate the thyroid gland, often asking the patient to swallow to facilitate examination. Different approaches, including anterior and posterior palpation, may be used to obtain a comprehensive assessment. The clinician’s experience and anatomical knowledge are crucial for distinguishing normal variations from pathological findings.
- Correlation with Other Findings
Palpation findings are always interpreted in conjunction with other components of the endocrine evaluation, including the patient’s medical history, reported symptoms, and results of laboratory tests. For instance, a palpable thyroid nodule in a patient with elevated thyroid hormone levels might suggest a hyperfunctioning nodule. Integrating palpation findings with other clinical data allows for a more accurate and nuanced understanding of the patient’s condition.
The information obtained through palpation of the thyroid gland and lymph nodes is integral to the overall endocrine assessment. These findings contribute significantly to the development of a differential diagnosis, guiding subsequent investigations and informing treatment decisions. The combination of visual inspection, palpation, and other examination techniques provides a comprehensive picture of the patient’s endocrine health, enabling targeted and individualized management strategies.
3. Vital Signs Assessment
Vital signs assessment, a cornerstone of any medical evaluation, holds particular relevance within the context of an endocrinologist physical exam. These physiological measurements offer valuable insights into the potential impact of hormonal imbalances on various bodily systems. Heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and body temperature can all be affected by endocrine dysfunction. For instance, an elevated heart rate and increased blood pressure might be observed in patients with hyperthyroidism, while a slowed heart rate and low blood pressure could indicate hypothyroidism. Changes in respiratory rate can be associated with conditions affecting the adrenal glands. Careful monitoring of vital signs provides a baseline understanding of the patient’s physiological state and can reveal subtle but important clues regarding the presence and severity of hormonal disorders. This understanding allows for a more targeted approach to diagnostic testing and treatment planning.
The practical significance of vital signs assessment in endocrinology lies in its ability to reveal systemic effects of hormonal imbalances. For example, a patient presenting with fatigue and weight gain might have their initial suspicion of hypothyroidism further supported by a low heart rate and body temperature documented during the vital signs assessment. Conversely, a patient experiencing anxiety and palpitations might have suspected hyperthyroidism corroborated by an elevated heart rate and blood pressure. These seemingly simple measurements offer valuable context, enabling the endocrinologist to connect subjective patient complaints with objective physiological data. This integration of information is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management of complex endocrine disorders.
Integrating vital signs assessment into the broader context of the endocrinologist physical exam enhances the diagnostic process. While vital sign abnormalities alone rarely provide a definitive diagnosis, they serve as important indicators of potential hormonal dysfunction. Furthermore, tracking vital signs over time allows for monitoring treatment efficacy and identifying potential complications. Challenges may arise in interpreting vital signs in patients with coexisting medical conditions that could independently influence these measurements. Therefore, careful consideration of the patient’s complete medical history and other examination findings is essential for accurate interpretation. Vital signs assessment, while a routine procedure, provides essential information that contributes significantly to the comprehensive evaluation and management of endocrine disorders.
4. Medical History Review
Medical history review forms an integral part of the endocrinologist physical exam, providing crucial context for interpreting physical findings and developing a differential diagnosis. This process involves gathering comprehensive information about past illnesses, surgeries, medications, allergies, family history, and lifestyle factors. Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and autoimmune disorders can influence endocrine function and must be considered. Family history of endocrine conditions, like thyroid disease or diabetes, significantly increases an individual’s risk. Medications, including steroids or hormonal contraceptives, can impact hormone levels and should be carefully documented. Lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, and stress levels, also play a role in endocrine health. For instance, a patient presenting with weight gain and fatigue might have a history of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in their family, increasing the likelihood of a similar diagnosis. Similarly, a patient on long-term steroid therapy might exhibit symptoms mimicking Cushing’s syndrome. Understanding the interplay between medical history and presenting symptoms allows for a more focused and efficient diagnostic approach.
The practical significance of a thorough medical history review lies in its ability to guide diagnostic testing and inform treatment decisions. A history of previous thyroid surgery, for example, would alert the endocrinologist to the possibility of hypothyroidism and the need for thyroid hormone replacement. Similarly, a family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndromes would necessitate specific genetic testing and surveillance for related endocrine tumors. Furthermore, knowledge of a patient’s medication list helps avoid potential drug interactions or identify medications that might be contributing to endocrine dysfunction. By carefully considering the patient’s medical history alongside physical exam findings, the endocrinologist can develop a personalized management plan that addresses the individual’s unique circumstances and risk factors. For example, a patient with a history of recurrent kidney stones and elevated calcium levels might be investigated for hyperparathyroidism, even in the absence of overt physical signs. This proactive approach allows for early detection and intervention, potentially preventing long-term complications.
Integrating the medical history review within the broader context of the endocrinologist physical exam enhances the diagnostic accuracy and improves patient outcomes. The challenges lie in obtaining a complete and accurate history, particularly from patients with complex medical backgrounds or cognitive impairments. Effective communication skills and the ability to build rapport with patients are crucial for eliciting relevant information. Furthermore, cultural sensitivities and language barriers must be considered to ensure accurate and comprehensive data collection. The medical history review, while a seemingly straightforward process, requires careful attention to detail and a nuanced understanding of how past experiences can influence current health status within the complex interplay of the endocrine system. This information forms the bedrock of effective endocrine care, guiding diagnostic decisions, shaping treatment strategies, and ultimately, optimizing patient well-being.
5. Symptom Discussion
Symptom discussion constitutes a cornerstone of the endocrinologist physical exam, providing essential subjective data that complements objective physical findings. Open communication regarding experienced symptoms allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the patient’s condition and guides further diagnostic investigation.
- Nature of Symptoms
Detailed descriptions of symptoms, including their onset, duration, frequency, and severity, offer valuable insights into the potential underlying endocrine disorder. For example, gradual weight gain accompanied by fatigue and cold intolerance might suggest hypothyroidism, while rapid weight loss with increased appetite and heat intolerance could indicate hyperthyroidism. Understanding the specific characteristics of reported symptoms aids in differentiating between various endocrine conditions.
- Associated Symptoms
Exploring associated symptoms provides a more complete picture of the patient’s health status. Symptoms often cluster together, offering clues regarding the affected endocrine gland or system. For instance, a patient reporting excessive thirst and frequent urination, along with unexplained weight loss, might be experiencing symptoms of diabetes. Recognizing these symptom clusters helps streamline the diagnostic process.
- Impact on Daily Life
Understanding how symptoms impact a patient’s daily life provides valuable context and underscores the need for appropriate intervention. Symptoms such as fatigue, mood swings, or changes in libido can significantly affect quality of life. Assessing the functional limitations imposed by endocrine disorders allows for a more patient-centered approach to treatment planning.
- Symptom Triggers and Relievers
Inquiring about factors that exacerbate or alleviate symptoms can provide additional diagnostic clues. For example, certain foods might trigger gastrointestinal discomfort in patients with thyroid disorders. Identifying these triggers and relievers allows for personalized management strategies aimed at minimizing symptom burden and improving overall well-being.
The information gathered through detailed symptom discussion during the endocrinologist physical exam plays a crucial role in directing subsequent diagnostic testing and shaping treatment plans. Correlating subjective symptom reports with objective physical findings and laboratory results allows for a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the patient’s endocrine health, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes. This interactive process emphasizes the importance of patient-physician communication in the diagnostic journey and highlights the value of the patient’s lived experience in navigating complex endocrine conditions. A patient’s detailed account of experiencing increased anxiety and heart palpitations, coupled with observations of a slight tremor during the physical exam, could guide further investigations towards confirming or ruling out hyperthyroidism. Integrating all aspects of the examination, from visual inspection and palpation to vital signs and symptom discussion, ultimately facilitates a more accurate and individualized approach to endocrine care.
6. Targeted Physical Maneuvers
Targeted physical maneuvers represent a crucial component of the endocrinologist physical exam, extending beyond basic observation and palpation to provide specific insights into neurological and musculoskeletal function, often subtly affected by endocrine disorders. These maneuvers, tailored to assess specific hormonal imbalances, enhance diagnostic accuracy and contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s condition. For example, assessing deep tendon reflexes can reveal delayed relaxation phase characteristic of hypothyroidism. Evaluating for proximal muscle weakness may indicate Cushing’s syndrome. Careful observation of gait and balance can uncover neurological manifestations associated with various endocrine disorders. These targeted assessments provide valuable information not readily apparent through routine examination techniques.
The practical significance of incorporating targeted physical maneuvers lies in their ability to detect subtle signs of endocrine dysfunction, which might otherwise be overlooked. The assessment of carpal tunnel syndrome, for instance, can be relevant in patients with hypothyroidism due to fluid accumulation in the tissues surrounding the median nerve. Similarly, assessing for signs of acromegaly, such as enlarged hands and feet, requires specific measurements and observations beyond general inspection. These targeted maneuvers bridge the gap between systemic hormonal imbalances and their localized manifestations, enabling the endocrinologist to connect seemingly disparate findings and arrive at a more accurate diagnosis. Early detection of these subtle signs facilitates timely intervention and can significantly improve long-term patient outcomes.
Integrating targeted physical maneuvers into the broader context of the endocrinologist physical exam enhances diagnostic precision and improves patient care. Challenges may arise in interpreting findings in patients with pre-existing neurological or musculoskeletal conditions. Therefore, careful consideration of the patient’s medical history and other examination findings is paramount. Targeted physical maneuvers, while often subtle in their execution, provide valuable information that contributes significantly to the comprehensive assessment and management of complex endocrine disorders, ultimately leading to a more nuanced understanding of the interplay between hormonal imbalances and their impact on the human body.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding consultations with hormonal specialists, aiming to provide clarity and dispel misconceptions.
Question 1: What should one expect during a consultation with a hormonal specialist?
A typical consultation involves a comprehensive review of medical history, discussion of symptoms, physical examination, and potentially, blood tests or imaging studies to assess hormonal function. The specialist will evaluate for signs and symptoms of hormonal imbalances and recommend appropriate management strategies.
Question 2: How frequently should individuals undergo hormonal evaluations?
The frequency of hormonal evaluations depends on individual circumstances, such as the presence of underlying endocrine disorders, family history, and specific risk factors. Regular check-ups are crucial for individuals with diagnosed hormonal conditions. For others, the frequency may vary based on age, gender, and overall health status.
Question 3: Are there specific preparations required before a hormonal assessment?
Certain assessments may necessitate fasting or specific dietary restrictions. Following any pre-appointment instructions provided by the specialist’s office ensures accurate test results.
Question 4: What distinguishes a hormonal specialist consultation from a regular physician visit?
Hormonal specialists possess in-depth knowledge and expertise in diagnosing and managing complex endocrine disorders. They offer specialized assessments and targeted treatment strategies for hormonal imbalances.
Question 5: What role does lifestyle play in hormonal health?
Lifestyle factors, including diet, exercise, stress management, and sleep quality, significantly influence hormonal balance. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall endocrine health and mitigate the risk of hormonal disorders.
Question 6: When should one consider seeking consultation with a hormonal specialist?
Individuals experiencing persistent symptoms suggestive of hormonal imbalance, such as unexplained weight changes, fatigue, mood swings, or changes in sleep patterns, should consider consulting a hormonal specialist for further evaluation.
Open communication with healthcare providers is crucial for addressing hormonal health concerns effectively. Consulting with a specialist ensures accurate diagnosis and personalized management of endocrine disorders.
Further exploration of this topic can involve a more in-depth look at specific hormonal conditions and their respective diagnostic procedures.
Conclusion
A comprehensive endocrinologist physical exam, encompassing visual inspection, palpation, vital sign assessment, thorough medical history review, detailed symptom discussion, and targeted physical maneuvers, provides a crucial foundation for understanding and managing hormonal health. This multifaceted approach allows for the detection of subtle signs often indicative of underlying endocrine disorders. The integration of these components facilitates accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies, emphasizing the importance of a holistic approach to endocrine care.
Prioritizing endocrine health through regular evaluations and open communication with healthcare providers empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards maintaining overall well-being. Early detection and intervention remain paramount in mitigating the potential long-term consequences of hormonal imbalances, underscoring the significance of the endocrinologist physical exam in promoting optimal health outcomes. Continued advancements in diagnostic techniques and therapeutic interventions promise further refinements in the assessment and management of endocrine disorders, offering hope for improved quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.