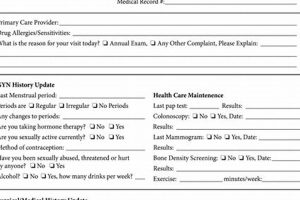
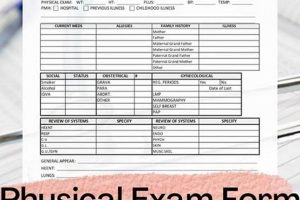
A pre-placement medical evaluation typically involves a standardized document used to record health information relevant to a prospective employee’s ability to perform specific job functions. This documentation often includes a review of medical history, vital signs, physical examination findings, and sometimes specific tests like drug screenings or vision assessments. For example, a candidate for a physically demanding job might undergo strength and endurance testing, while a position involving exposure to hazardous materials may necessitate specific blood tests.
These evaluations serve a crucial role in ensuring workplace safety and mitigating potential health risks. They can help identify pre-existing conditions that might be exacerbated by job duties, allowing employers to make reasonable accommodations or, in some cases, determine if a candidate is medically suited for a particular role. Historically, such assessments have evolved from basic physicals to more specialized examinations reflecting the changing nature of work and growing awareness of occupational health and safety. This evolution underscores the ongoing importance of balancing individual privacy with the need for a safe and productive work environment.
This article will further explore the key components of these assessments, relevant legal considerations, best practices for implementation, and the evolving landscape of workplace health and safety.
Tips for Pre-Placement Medical Evaluations
Navigating pre-placement medical evaluations requires careful consideration from both employers and prospective employees. The following tips offer guidance for a smooth and legally compliant process.
Tip 1: Job-Relatedness: Evaluations should focus solely on health factors directly relevant to essential job functions. Inquiries or examinations unrelated to job duties should be avoided.
Tip 2: Consistency: All candidates for the same position should undergo identical evaluations. Variations can create grounds for discrimination claims.
Tip 3: Confidentiality: Medical information obtained during the evaluation process must be kept strictly confidential and handled in accordance with applicable privacy regulations.
Tip 4: Timing: Medical evaluations should generally occur after a conditional offer of employment has been extended to avoid potential bias in the hiring process.
Tip 5: Documentation: Maintain accurate and complete records of all evaluations, including consent forms, examination findings, and any recommended accommodations.
Tip 6: Communication: Open communication between the employer, candidate, and medical professional is essential to ensure clarity and understanding throughout the process.
Tip 7: Legal Counsel: Consulting with legal counsel is advisable to ensure compliance with relevant disability and discrimination laws.
Adhering to these guidelines promotes fairness, protects individual privacy, and fosters a safe and productive work environment. These proactive measures help establish a strong foundation for a positive and successful employer-employee relationship.
By understanding the key considerations surrounding pre-placement medical evaluations, organizations can create a more inclusive and legally sound hiring process. The following section will conclude this exploration with a brief summary of best practices.
1. Legality
Navigating the legal landscape surrounding pre-placement medical evaluations is crucial for ensuring compliance and protecting the rights of both employers and prospective employees. Legal considerations permeate every aspect of this process, from the design of the evaluation itself to the handling of sensitive medical information.
- Compliance with Disability Laws
Adherence to the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and similar state laws is paramount. These laws prohibit discrimination against qualified individuals with disabilities and mandate reasonable accommodations for applicants and employees who can perform essential job functions with or without such accommodations. For example, requiring a medical examination before a conditional job offer is generally prohibited under the ADA. A medical examination can only be required after a conditional offer of employment has been extended, and it must be required of all entering employees in the same job category. Understanding and complying with these regulations is essential for avoiding legal challenges.
- Privacy and Confidentiality
Maintaining the confidentiality of medical information obtained during pre-placement evaluations is legally and ethically obligated. Laws such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and state privacy laws dictate strict guidelines for handling and storing sensitive health data. Information gleaned from medical evaluations must be kept separate from personnel files and accessible only to authorized personnel on a need-to-know basis. Failure to uphold these standards can result in substantial penalties and legal action.
- Job-Relatedness and Business Necessity
Medical evaluations must be demonstrably job-related and consistent with business necessity. This principle ensures that inquiries and examinations are narrowly tailored to assess an individual’s ability to perform the essential functions of a specific job. A blanket requirement for extensive medical testing unrelated to job duties could be considered discriminatory. For example, a company requiring all applicants to undergo a psychological evaluation, regardless of the position, would likely face legal scrutiny. Establishing a clear link between the evaluation and the essential job functions is critical.
- Uniform Application of Standards
Consistency in the application of pre-placement medical evaluations is vital. All applicants for the same position should undergo the same evaluation process, regardless of perceived disabilities or other protected characteristics. Deviations from this standard can create the appearance of discriminatory practices and open the door to legal challenges. Maintaining uniform procedures reinforces fairness and helps ensure compliance with anti-discrimination laws.
These legal considerations underscore the complexity of pre-placement medical evaluations. Adherence to these principles not only safeguards legal compliance but also contributes to a fair and equitable hiring process, ultimately fostering a more inclusive and productive work environment.
2. Confidentiality
Confidentiality is paramount in the context of employment physical exam forms. These forms contain sensitive personal health information, requiring stringent safeguards to protect individual privacy. The ethical and legal obligations surrounding confidentiality influence every stage of the process, from the collection and storage of data to its access and dissemination.
Several regulations, including the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), mandate strict confidentiality protocols for medical information. For instance, the ADA requires employers to keep medical information separate from general personnel files, stored in a confidential medical file, accessible only to limited personnel. HIPAA outlines comprehensive privacy and security rules, including restrictions on the use and disclosure of protected health information. Violations of these regulations can lead to significant legal penalties and reputational damage.
Real-world examples illustrate the importance of confidentiality. Imagine a scenario where an applicant discloses a pre-existing condition on a medical exam form. If this information were inadvertently shared with hiring managers, it could lead to discriminatory practices, even if unintentional. Similarly, the unauthorized disclosure of an employee’s medical status could lead to stigmatization or discrimination in the workplace. These examples highlight the potential consequences of confidentiality breaches.
Ensuring confidentiality requires robust policies and procedures. Access to medical information should be limited to personnel with a legitimate need to know, such as occupational health professionals or human resources staff handling accommodations. Clear protocols for data storage, retrieval, and disposal are essential. Regular training for personnel handling sensitive information reinforces best practices and minimizes the risk of inadvertent disclosures. A strong commitment to confidentiality fosters trust between employers and employees and contributes to a respectful and legally compliant workplace environment. Failure to prioritize confidentiality can lead to significant legal and ethical consequences.
3. Job-Relatedness
Job-relatedness serves as a critical legal and ethical cornerstone in the utilization of employment physical exam forms. This principle dictates that all medical inquiries and examinations included within these forms must directly relate to the essential functions of the specific job in question. Establishing a clear nexus between the information sought and the job requirements ensures that evaluations are narrowly tailored, non-discriminatory, and serve a legitimate business purpose. This focus on essential functions helps prevent unnecessary intrusions into an individual’s medical history and upholds their right to privacy. A lack of job-relatedness can lead to legal challenges and create a perception of unfair or discriminatory hiring practices.
Real-world examples illustrate the practical significance of this principle. Consider a position requiring heavy lifting. In this case, a physical assessment evaluating strength and endurance would be deemed job-related. Conversely, inquiring about an applicant’s mental health history for the same position, without a demonstrable connection to the job’s essential functions, would likely be viewed as lacking job-relatedness and potentially discriminatory. Another example involves a position requiring frequent travel. A vision test might be considered job-related, but asking about an applicant’s family medical history would likely not be. These distinctions highlight the importance of careful consideration of job requirements when designing pre-placement medical evaluations.
Understanding the implications of job-relatedness offers practical advantages. Employers can mitigate legal risks by ensuring assessments are tailored to specific job requirements. This practice also strengthens the hiring process by focusing on factors directly relevant to job performance. Furthermore, it promotes a sense of fairness and transparency for applicants. Challenges can arise when determining the precise boundaries of job-relatedness, particularly for roles with complex or evolving responsibilities. Consulting with legal counsel and conducting thorough job analyses can help navigate these complexities. Ultimately, prioritizing job-relatedness in the development and implementation of employment physical exam forms protects both employers and applicants, fostering a legally sound and equitable hiring process.
4. Standardization
Standardization plays a vital role in the implementation of employment physical exam forms, ensuring fairness, consistency, and legal defensibility throughout the evaluation process. Standardized forms and procedures help mitigate bias, promote equitable treatment of applicants, and contribute to a more objective assessment of an individual’s suitability for a specific job. A lack of standardization can introduce inconsistencies, create vulnerabilities to legal challenges, and undermine the integrity of the hiring process.
- Consistent Evaluation Criteria
Standardization ensures all applicants for the same position are evaluated against identical criteria. This consistency helps eliminate potential bias and promotes equitable treatment. For example, if all candidates for a physically demanding role undergo the same standardized physical assessment, comparisons of their abilities become more objective and less susceptible to subjective interpretations. This uniformity strengthens the validity and defensibility of hiring decisions.
- Streamlined Processes
Standardized forms and procedures streamline the evaluation process, improving efficiency and reducing administrative burden. Utilizing a consistent template for medical history questionnaires and physical examinations simplifies data collection and analysis. For instance, a standardized form ensures all necessary information is gathered consistently from each applicant, minimizing the need for follow-up inquiries and reducing the time required to complete the evaluation process.
- Enhanced Legal Compliance
Standardization strengthens legal compliance by promoting consistent application of evaluation criteria across all applicants. This uniformity helps demonstrate that hiring decisions are based on objective, job-related factors, mitigating the risk of discrimination claims. For example, using a standardized form for documenting medical evaluations ensures consistent record-keeping practices, which can be crucial in defending against potential legal challenges.
- Improved Data Analysis and Interpretation
Standardized data collection facilitates more effective analysis and interpretation of results. When information is gathered in a consistent format, it becomes easier to identify trends, compare applicants, and make informed hiring decisions based on objective data. This consistency is particularly valuable when evaluating large applicant pools or comparing candidates across multiple locations.
These interconnected facets of standardization underscore its significance in the context of employment physical exam forms. By promoting fairness, efficiency, and legal compliance, standardization strengthens the integrity of the hiring process and contributes to a more equitable and legally sound approach to pre-employment medical evaluations. A commitment to standardization demonstrates a commitment to best practices in hiring and a respect for the rights of all applicants.
5. Documentation
Meticulous documentation forms an integral part of the employment physical exam form process. Complete and accurate records serve multiple crucial functions, ranging from legal compliance and risk mitigation to ensuring continuity of care and facilitating informed decision-making. Proper documentation provides a verifiable audit trail, supports data analysis, and safeguards both employers and employees.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Maintaining comprehensive documentation is essential for demonstrating adherence to legal and regulatory requirements. Laws such as the ADA and HIPAA mandate specific record-keeping practices for medical information. Documented compliance protects organizations from potential legal challenges and penalties. For example, maintaining records of job-relatedness assessments and accommodation requests demonstrates good-faith efforts to comply with disability laws.
- Risk Management and Liability Mitigation
Thorough documentation serves as a critical risk management tool. Accurate records can protect employers from liability in cases involving workplace injuries or illnesses. For instance, if an employee experiences a work-related injury, documentation of pre-employment physical evaluations can help determine if the injury was pre-existing or work-related, influencing workers’ compensation claims. Detailed records also facilitate investigations into potential safety hazards or incidents.
- Continuity of Care and Informed Decision-Making
Complete medical records provide valuable information for healthcare professionals involved in an employee’s care. This information helps ensure continuity of care and facilitates informed decision-making regarding treatment and accommodations. For example, if an employee requires modified duties due to a medical condition, documentation of their pre-employment physical evaluation can help inform the development of an appropriate accommodation plan. This continuity is particularly crucial for employees with chronic health conditions.
- Data Analysis and Process Improvement
Documentation supports data analysis and continuous improvement of the pre-employment medical evaluation process. Analyzing aggregated data can reveal trends, identify potential areas for improvement, and inform the development of more effective evaluation protocols. For example, tracking the types of accommodations requested can reveal patterns that suggest modifications to job descriptions or workplace environments. This data-driven approach strengthens the overall effectiveness and fairness of the hiring process.
These interconnected facets of documentation underscore its pivotal role in the responsible and effective use of employment physical exam forms. Comprehensive, accurate, and readily accessible documentation protects the interests of both employers and employees, ensuring legal compliance, mitigating risk, and promoting a safe and healthy work environment. A robust approach to documentation contributes to a more transparent, equitable, and legally sound approach to pre-employment medical evaluations.
6. Accessibility
Accessibility in the context of employment physical exam forms refers to the ease with which authorized personnel can obtain, review, and utilize the information contained within these documents. Appropriate accessibility is crucial for efficient workflow, informed decision-making, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements regarding medical information management. Balancing accessibility with stringent confidentiality protocols is essential for responsible and ethical handling of sensitive health data. This balance ensures relevant information is readily available to those who require it while safeguarding individual privacy.
- Secure Storage and Retrieval
Secure storage and retrieval systems are fundamental to accessibility. These systems must allow authorized personnel, such as human resources professionals or occupational health providers, to readily access necessary information while simultaneously preventing unauthorized access. Examples include password-protected electronic health record systems or secure, locked physical filing cabinets. Efficient retrieval processes minimize delays in decision-making related to accommodations or return-to-work clearances. A robust system balances the need for prompt access with stringent security measures, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and preventing data breaches.
- Clear and Concise Documentation
Clear and concise documentation within the forms themselves contributes significantly to accessibility. Information should be presented in a logical, easy-to-understand format, minimizing ambiguity and facilitating efficient review. Using standardized templates, clearly labeled sections, and concise language enhances readability and reduces the risk of misinterpretation. For example, a well-designed form might group relevant information, such as cardiovascular health metrics, within a dedicated section, making it easier for reviewers to quickly locate and interpret specific data points. This clarity is particularly important when multiple individuals, potentially with different medical expertise, need to access and understand the information.
- Appropriate Data Sharing Mechanisms
Appropriate data sharing mechanisms facilitate secure and efficient communication of relevant information among authorized parties. These mechanisms might include secure electronic platforms for transmitting medical records or established protocols for sharing information with healthcare providers involved in an employee’s care. For example, if an employee requires an accommodation due to a medical condition, secure data sharing ensures the appropriate individuals within the organization receive the necessary information to implement the accommodation effectively. These mechanisms must adhere to strict confidentiality guidelines to prevent unauthorized disclosures.
- Accommodation for Individuals with Disabilities
Accessibility considerations extend to ensuring individuals with disabilities have equal access to the information contained within their own employment physical exam forms. This might involve providing documents in alternative formats, such as large print or Braille, or offering interpretation services for individuals with hearing impairments. This inclusivity is essential for upholding legal and ethical obligations related to equal access to information and supports informed decision-making for all individuals. Failure to provide accessible formats can create barriers to employment and perpetuate discriminatory practices.
These interconnected aspects of accessibility underscore its critical role in the effective and ethical use of employment physical exam forms. By implementing secure systems, clear documentation practices, appropriate data sharing mechanisms, and inclusive accommodations, organizations can ensure relevant information is readily available to authorized personnel while simultaneously safeguarding individual privacy and upholding legal and ethical obligations. A well-designed and implemented accessibility framework contributes to a more efficient, equitable, and legally compliant approach to pre-employment medical evaluations.
7. Accuracy
Accuracy in employment physical exam forms is paramount for several critical reasons. Inaccurate information can lead to flawed hiring decisions, misdiagnosis of health conditions, inappropriate accommodations, and potential legal liabilities. The effects of inaccurate data can range from minor inconveniences to significant adverse impacts on both the individual and the organization. For instance, an inaccurate recording of blood pressure could lead to a misdiagnosis of hypertension, potentially disqualifying a qualified candidate or necessitating unnecessary medical interventions. Conversely, failing to accurately document a pre-existing condition could result in an individual being placed in a role that exacerbates their condition, leading to safety risks and potential legal challenges. Accuracy is not merely a desirable attribute; it is a fundamental requirement for ethical and legally sound pre-employment medical evaluations. The forms themselves must be designed to facilitate accurate data capture, incorporating clear instructions, unambiguous language, and appropriate response formats.
Practical implications of prioritizing accuracy extend throughout the entire evaluation process. Training personnel involved in administering and interpreting these forms is crucial. This training should cover proper techniques for collecting data, recognizing potential sources of error, and understanding the significance of accurate documentation. Regular quality control checks, such as reviewing completed forms for completeness and consistency, can help identify and rectify inaccuracies. Furthermore, establishing clear protocols for correcting errors, including maintaining an audit trail of corrections made, is essential for maintaining the integrity of the data. For example, if an error is discovered in a candidate’s medical history, a clear process should be in place for correcting the record and documenting the correction, ensuring transparency and accountability. Technology can also play a crucial role, with electronic forms incorporating validation checks and automated data entry processes to minimize human error. Investing in these strategies not only improves accuracy but also demonstrates a commitment to responsible data management practices.
In conclusion, accuracy represents a non-negotiable element of employment physical exam forms. Its importance stems from its direct impact on individual health, safety, and employment opportunities, as well as organizational compliance and risk management. Prioritizing accuracy requires a multifaceted approach encompassing form design, personnel training, quality control procedures, and appropriate utilization of technology. Challenges may include maintaining accuracy when dealing with complex medical information or balancing the need for detailed data with the imperative for concise documentation. Addressing these challenges proactively through continuous improvement efforts strengthens the integrity and ethical foundation of pre-employment medical evaluations, ultimately contributing to a fairer, safer, and more legally sound hiring process.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding pre-placement medical evaluations, providing clarity on key aspects of the process.
Question 1: When in the hiring process can a medical examination be requested?
Medical examinations can generally be requested only after a conditional offer of employment has been extended. Requesting an examination prior to a conditional offer is generally prohibited under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and similar state regulations.
Question 2: What information can be requested on a medical history form?
Inquiries must be job-related and consistent with business necessity. Questions should focus on whether an applicant can perform the essential functions of the job with or without reasonable accommodation. Inquiries about genetic information or family medical history are generally disallowed.
Question 3: Who can access the information collected during a pre-placement medical evaluation?
Access should be restricted to individuals with a legitimate need to know, such as occupational health professionals, human resources staff handling accommodations, and supervisors who need to be aware of work restrictions. Information must be handled and stored in accordance with applicable privacy regulations.
Question 4: What if an applicant refuses to complete the medical examination?
If an applicant refuses a job-related and legally compliant medical examination after a conditional offer of employment, the employer may generally withdraw the offer. However, engaging in an interactive process to explore potential accommodations before making a final decision is often advisable.
Question 5: How are pre-placement medical evaluations different for existing employees?
Medical examinations for existing employees are generally permissible only if job-related and consistent with business necessity. Examples include fitness-for-duty examinations after an extended absence or periodic medical surveillance for employees exposed to specific workplace hazards. Such examinations must be applied uniformly to all employees in similar situations.
Question 6: What constitutes a “reasonable accommodation” under disability laws?
A reasonable accommodation is a modification or adjustment to the job, work environment, or hiring process that enables a qualified individual with a disability to perform the essential functions of a job. Examples include modified work schedules, assistive technologies, or adjustments to physical workspaces. The accommodation must not impose an undue hardship on the employer.
Understanding these key points helps ensure a legally compliant and ethically sound pre-placement medical evaluation process. Consulting with legal counsel is always recommended to navigate specific situations and ensure compliance with applicable regulations.
For further information on best practices and legal considerations, the following resources may be helpful…
Conclusion
Pre-placement medical evaluations, documented through standardized forms, serve as a crucial component of a responsible and legally compliant hiring process. This exploration has highlighted the multifaceted nature of these evaluations, emphasizing the importance of job-relatedness, standardization, confidentiality, documentation, accessibility, and accuracy. Each aspect contributes to a process that balances the need for a safe and productive work environment with the protection of individual rights and privacy. Navigating these complexities requires careful consideration of applicable regulations, including the ADA and relevant privacy laws, along with a commitment to ethical and transparent practices.
Organizations must prioritize ongoing review and refinement of pre-placement medical evaluation procedures. This proactive approach, informed by legal developments and evolving best practices, strengthens the integrity of the hiring process, fosters a culture of workplace safety, and promotes equitable opportunities for all candidates. The careful and judicious use of these evaluations contributes significantly to a healthy, productive, and legally compliant workforce.