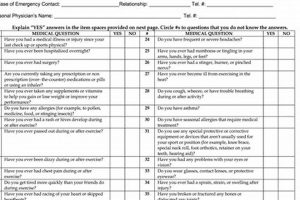
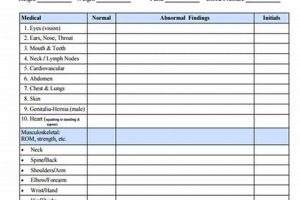
A pre-participation medical evaluation document required by many educational institutions and sports organizations verifies an athlete’s physical fitness for athletic competition. This documentation usually involves a comprehensive medical history review, a physical examination, and may include additional assessments depending on specific requirements. A completed evaluation serves as evidence that a healthcare professional has cleared a student-athlete for safe participation.
Such evaluations are essential for safeguarding student-athletes’ health and well-being. They help identify potential health concerns that could pose risks during strenuous physical activity. Early detection allows for appropriate medical interventions, preventing potential complications or exacerbations of pre-existing conditions. This proactive approach benefits not only individual athletes but also the integrity of sports programs by promoting a culture of safety and responsibility. Historically, these forms have evolved alongside increasing awareness of the importance of sports safety and the potential health risks associated with athletic competition.
This article further explores the components of a typical pre-participation medical evaluation, the procedures involved in completing the evaluation, and the various parties responsible for ensuring compliance. It also discusses the legal and ethical considerations surrounding the use of these medical evaluations.
Tips for Completing Pre-Participation Medical Evaluations
Ensuring a comprehensive and accurate evaluation process is crucial for effective health screening of student-athletes. The following tips offer guidance for navigating the process successfully.
Tip 1: Schedule the evaluation well in advance of the intended sport season. This allows ample time to address any identified health concerns and ensures eligibility for participation from the start.
Tip 2: Gather necessary medical information, including immunization records and details of past injuries or illnesses. Having a complete medical history readily available streamlines the evaluation process.
Tip 3: Be honest and forthcoming with the healthcare provider conducting the evaluation. Accurate information is crucial for a thorough assessment and appropriate medical guidance.
Tip 4: Follow any instructions provided by the healthcare provider regarding further testing or follow-up appointments. Adherence to medical recommendations is essential for addressing potential health issues.
Tip 5: Keep a copy of the completed evaluation for personal records. This documentation serves as a valuable reference for future medical consultations.
Tip 6: Parents or guardians should be actively involved in the evaluation process for minors. Their involvement ensures proper communication and understanding of the athlete’s health status.
Tip 7: Understand the specific requirements and deadlines established by the relevant sports organization or educational institution. Compliance with these policies is essential for participation eligibility.
By following these tips, stakeholders can contribute to a more efficient and effective pre-participation medical evaluation process, promoting athlete health and safety. These steps are essential for minimizing risks and ensuring a safe and enjoyable athletic experience.
This information provides a practical guide for completing the evaluation process. The following section concludes the discussion with a summary of key takeaways and emphasizes the importance of prioritizing student-athlete health and well-being.
1. Medical History
A comprehensive medical history forms the cornerstone of any pre-participation sports physical evaluation, including those mandated by CMS. This detailed record of past health issues provides crucial context for understanding an athlete’s current physical state and potential risks associated with athletic participation. A thorough medical history allows healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding clearance for sports activities.
- Previous Injuries:
Documentation of prior injuries, including fractures, sprains, concussions, and musculoskeletal issues, is essential. For instance, a history of multiple ankle sprains might indicate increased susceptibility to future ankle injuries, requiring preventative measures or modified training regimens. This information informs decisions regarding safe participation levels and necessary precautions within the CMS framework.
- Pre-existing Medical Conditions:
Conditions like asthma, diabetes, epilepsy, or cardiac abnormalities require careful consideration. A student with asthma, for example, might need an emergency action plan in place to manage potential exacerbations during exercise. Accurate reporting of such conditions allows for appropriate management strategies and ensures compliance with CMS guidelines for athlete safety.
- Prior Surgeries and Hospitalizations:
Information about past surgical procedures and hospital stays, including dates, reasons, and outcomes, is critical. A previous knee surgery, for instance, might necessitate specific rehabilitation protocols or activity restrictions. Understanding these historical health events allows for a more targeted and individualized assessment of the athlete’s readiness for sports within the CMS context.
- Family Medical History:
Certain medical conditions, such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or Marfan syndrome, have a genetic component and can significantly impact an athlete’s cardiovascular health. Knowledge of family history allows for early detection and appropriate referrals for specialized cardiac screening, aligning with CMS recommendations for comprehensive cardiovascular evaluation.
By meticulously documenting these elements of medical history, healthcare providers gain a comprehensive understanding of an athlete’s health profile, allowing for informed decisions regarding participation in sports activities. This comprehensive approach, a critical element of the CMS sports physical form, ensures athlete safety and promotes responsible participation in competitive athletics.
2. Physical Examination
The physical examination constitutes a crucial component of the CMS sports physical form, providing objective data that complements the information gathered through the medical history. This hands-on assessment, conducted by a qualified healthcare professional, evaluates various physiological systems to identify potential health concerns that could impact an athlete’s ability to safely participate in sports. The examination’s findings, documented within the CMS form, directly influence the physician’s clearance decision and contribute significantly to the overall assessment of athlete readiness.
Several key areas are typically assessed during the physical examination. Cardiovascular evaluation, including auscultation of the heart and assessment of peripheral pulses, is essential for detecting potential cardiac abnormalities. Pulmonary evaluation assesses respiratory function, critical for athletes engaging in strenuous activities. Musculoskeletal screening evaluates range of motion, strength, and stability, identifying potential vulnerabilities or pre-existing injuries that could be aggravated by sports participation. Vision and hearing assessments ensure that athletes possess the necessary sensory acuity for safe engagement in their chosen sport. For example, an athlete with limited range of motion in the shoulder following a previous dislocation might require specific rehabilitation exercises before receiving clearance for contact sports. Similarly, the detection of a heart murmur during auscultation could necessitate further cardiological evaluation before participation is deemed safe. These practical applications underscore the importance of a thorough physical examination within the CMS sports physical form.
In summary, the physical examination provides essential objective data that informs the overall assessment of an athlete’s fitness for participation in sports. It plays a critical role in identifying potential health concerns, guiding further investigations, and ultimately contributing to the physician’s clearance decision within the CMS framework. The examination’s findings, when combined with the athlete’s medical history, provide a comprehensive picture of their health status, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions that prioritize athlete safety and well-being.
3. Physician Clearance
Physician clearance represents the culmination of the pre-participation medical evaluation process within the CMS sports physical form framework. This critical step signifies that a qualified healthcare professional has reviewed the athlete’s medical history, conducted a thorough physical examination, and deemed the athlete medically fit to participate in their chosen sport. The physician’s clearance, documented within the CMS form, serves as formal authorization for participation and carries significant weight in ensuring athlete safety and compliance with established guidelines.
- Assessment of Medical Fitness:
The physician considers all available information, including the athlete’s medical history and physical examination findings, to determine overall medical fitness. This assessment involves evaluating potential risks associated with pre-existing conditions or previous injuries. For example, an athlete with a history of concussions might require specialized neurological assessment before receiving clearance for contact sports. This individualized approach ensures that participation decisions align with the athlete’s specific health profile and the demands of their chosen sport within the CMS framework.
- Identification of Restrictions or Modifications:
In some cases, full clearance might be granted with specific restrictions or modifications to training or competition. An athlete recovering from a knee injury, for example, might be cleared for non-contact drills but restricted from full-contact scrimmages until further rehabilitation is completed. These tailored recommendations, documented within the CMS form, aim to minimize re-injury risk while allowing for continued participation under safe and controlled conditions.
- Referral for Specialized Evaluation:
If the initial evaluation reveals potential health concerns requiring further investigation, the physician might refer the athlete to a specialist. Detection of a heart murmur, for instance, could necessitate a cardiology consultation and further testing before clearance can be granted. This proactive approach ensures comprehensive assessment of complex medical issues, aligning with CMS guidelines for prioritizing athlete health and safety.
- Documentation and Communication:
The physician’s clearance, along with any associated restrictions or recommendations, is clearly documented within the CMS sports physical form. This formal record serves as evidence of medical suitability for participation and informs coaches, athletic trainers, and other relevant personnel about the athlete’s health status. Effective communication ensures that all stakeholders are aware of potential health considerations and can implement appropriate safety measures. Proper documentation also facilitates tracking of athlete health over time and compliance with CMS requirements.
These facets of physician clearance highlight its integral role within the CMS sports physical form process. By carefully considering medical history, physical examination findings, and potential need for specialized evaluation, physicians provide informed decisions that prioritize athlete safety and well-being. The resulting clearance, documented within the CMS form, serves as the final authorization for participation, ensuring compliance with established guidelines and promoting a safe and healthy athletic environment. This final step emphasizes the collaborative nature of the process, involving healthcare professionals, athletes, and relevant stakeholders in promoting responsible and informed participation in sports within the CMS framework.
4. Immunization Records
Immunization records constitute a critical component of the CMS sports physical form, serving as verification of compliance with mandated vaccination protocols. Maintaining updated immunization records is essential for safeguarding athlete health and preventing the spread of communicable diseases within the athletic community. This documentation provides evidence of immunity against vaccine-preventable illnesses, contributing to a safer and healthier environment for all participants.
- Verification of Immunity:
Immunization records provide documented proof of immunity against vaccine-preventable diseases such as measles, mumps, rubella, and tetanus. These records typically include dates of vaccination and specific vaccine administered. For instance, a student’s record might show they received the MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine on two separate occasions, fulfilling the requirement for documented immunity. This verification process aligns with CMS guidelines for promoting public health within the athletic community.
- Disease Prevention and Control:
Requiring updated immunization records helps prevent outbreaks of communicable diseases within sports teams and educational institutions. By ensuring a high level of immunity within the athletic population, the spread of these diseases is significantly reduced. This proactive approach safeguards not only individual athletes but also the broader community, minimizing disruptions to training schedules and competitions due to outbreaks. This contributes to the overall health and well-being of the athletic environment.
- Compliance with Regulations:
Many states and educational institutions have specific immunization requirements for student participation in sports and extracurricular activities. Submission of immunization records demonstrates compliance with these mandates, ensuring eligibility for participation. For instance, a state might require proof of meningococcal vaccination for all incoming college students participating in sports. Adherence to these regulations is essential for maintaining a safe and compliant athletic program within the CMS framework.
- Exemptions and Waivers:
In certain situations, individuals might be exempt from specific immunization requirements due to medical or religious reasons. These exemptions typically require supporting documentation and adherence to specific protocols. A student with a documented allergy to a vaccine component, for example, might require a medical exemption. Understanding and managing these exemptions ensures compliance with CMS guidelines while respecting individual circumstances.
In conclusion, maintaining accurate and updated immunization records plays a vital role within the CMS sports physical form framework. By verifying immunity, preventing disease outbreaks, ensuring compliance with regulations, and managing exemptions appropriately, immunization records contribute significantly to the health and safety of the athletic community. This documentation, a key element of the CMS form, reinforces the importance of preventative healthcare and responsible participation in sports.
5. Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular health assumes paramount importance within the context of the CMS sports physical form. Rigorous physical activity inherent in competitive sports places significant demands on the cardiovascular system. Therefore, assessing cardiovascular health is crucial for identifying potential risks and ensuring safe participation. A thorough evaluation helps mitigate the risk of adverse cardiac events during strenuous exertion and contributes significantly to the overall health and well-being of student-athletes.
- Family History of Cardiac Conditions:
A family history of sudden cardiac death, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, or other inherited cardiac conditions significantly increases an athlete’s risk. For instance, a family history of sudden cardiac death in a young relative warrants further investigation, potentially including an electrocardiogram (ECG) or echocardiogram. Documenting this information within the CMS sports physical form allows for appropriate referrals and preventive measures.
- Personal History of Cardiac Symptoms:
Experiences such as chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or syncope during exercise raise concerns about underlying cardiac issues. An athlete reporting frequent episodes of shortness of breath during training, for example, might require further cardiopulmonary evaluation. Accurate reporting of these symptoms within the CMS form facilitates timely intervention and appropriate management.
- Auscultation for Murmurs and Irregular Rhythms:
Careful auscultation of the heart during the physical examination allows healthcare professionals to detect heart murmurs or irregular rhythms. A newly discovered murmur, for example, might necessitate an echocardiogram to assess heart valve function and structure. These findings, documented within the CMS form, contribute to a comprehensive cardiovascular assessment.
- Blood Pressure Evaluation:
Monitoring blood pressure helps identify hypertension, a risk factor for various cardiovascular complications. Elevated blood pressure readings during the evaluation might require follow-up monitoring and lifestyle modifications. This information, recorded within the CMS sports physical form, contributes to a comprehensive health profile and informs recommendations for ongoing health management.
These facets of cardiovascular health assessment within the CMS sports physical form collectively contribute to a comprehensive evaluation of an athlete’s cardiac risk. This information informs the physician’s clearance decision and guides recommendations for further evaluation, management, or activity modifications. Thorough attention to cardiovascular health is paramount for promoting safe participation in sports and mitigating the risk of adverse cardiac events. This emphasis on cardiovascular well-being underscores the importance of the CMS form in prioritizing athlete health and safety within the context of competitive athletics.
6. Orthopedic Assessment
Orthopedic assessment within the CMS sports physical form framework focuses on evaluating the musculoskeletal system’s integrity and functionality. This assessment plays a critical role in identifying pre-existing injuries, assessing joint stability and range of motion, and determining an athlete’s readiness for the physical demands of their chosen sport. A comprehensive orthopedic evaluation helps prevent exacerbations of prior injuries and promotes safe participation by addressing potential musculoskeletal vulnerabilities.
- Joint Stability and Range of Motion:
Evaluating joint stability and range of motion is essential for identifying limitations or instability that could predispose an athlete to injury. For instance, an athlete with decreased shoulder range of motion following a prior dislocation might be at increased risk of re-injury. Assessing these factors allows for targeted interventions, such as specific exercises to improve flexibility and stability, promoting safe participation within the CMS framework.
- Previous Injury Evaluation:
A history of previous injuries, such as fractures, sprains, or dislocations, requires careful consideration during the orthopedic assessment. An athlete with a history of ankle sprains, for example, might require ankle bracing or specific exercises to improve stability and prevent recurrence. Thorough documentation of previous injuries within the CMS sports physical form guides appropriate management strategies.
- Assessment of Strength and Flexibility:
Evaluating muscle strength and flexibility helps identify imbalances or weaknesses that could increase injury risk. An athlete with significant quadriceps-hamstring strength imbalance, for instance, might be more susceptible to hamstring strains. Addressing these imbalances through targeted training programs contributes to improved musculoskeletal function and injury prevention within the CMS context.
- Postural Assessment:
Postural abnormalities can contribute to musculoskeletal imbalances and increase the risk of certain injuries. For example, an athlete with excessive forward head posture might be more prone to neck pain and headaches. Identifying and addressing postural issues through corrective exercises or other interventions promotes optimal biomechanics and reduces injury risk, aligning with the CMS emphasis on preventative care.
These components of the orthopedic assessment, documented within the CMS sports physical form, collectively contribute to a comprehensive evaluation of the athlete’s musculoskeletal system. This information informs the physician’s clearance decision, guides recommendations for activity modifications or further evaluation, and promotes safe participation in sports. A thorough orthopedic assessment is essential for identifying potential vulnerabilities, preventing re-injury, and ensuring that athletes can participate in their chosen sport with minimal risk within the CMS framework.
7. Consent and Signatures
The “Consent and Signatures” section of the CMS sports physical form represents a critical legal and ethical component, formalizing the agreement between all parties involved in the athlete’s participation in sports. This section ensures informed consent for the evaluation process itself, acknowledges the risks inherent in athletic participation, and authorizes the release of necessary medical information. Properly executed consent and signatures protect both the athlete and the healthcare providers involved, establishing a framework of shared responsibility for the athlete’s health and safety.
- Acknowledgement of Risks:
This component requires the athlete or their legal guardian to acknowledge the inherent risks associated with participating in the specified sport. This includes risks ranging from minor injuries like sprains and strains to more severe outcomes like concussions or fractures. Acknowledging these risks ensures informed participation and underscores the importance of adhering to safety guidelines. This facet of the consent process aligns with the CMS framework’s focus on athlete safety and risk management.
- Authorization for Treatment:
This authorization allows designated medical personnel to provide necessary medical care to the athlete in the event of an injury or illness during sports activities. This includes immediate first aid, emergency treatment, and subsequent follow-up care. This provision is crucial for ensuring timely and appropriate medical intervention when needed. This element of the consent form reinforces the importance of prompt medical attention within the CMS framework, contributing to athlete safety and well-being.
- Release of Medical Information:
This component authorizes the release of pertinent medical information to relevant parties, such as coaches, athletic trainers, and school officials, as needed. This ensures effective communication regarding the athlete’s health status and facilitates appropriate management of any health concerns. Sharing relevant information allows for collaborative care and informed decision-making regarding participation, aligning with CMS guidelines for comprehensive health management.
- Signature of Athlete/Guardian and Physician:
The signatures of the athlete (or their legal guardian if a minor) and the examining physician formalize the agreement and attest to the accuracy and completeness of the information provided within the CMS sports physical form. These signatures signify informed consent, shared responsibility, and adherence to established protocols. This final step ensures legal validity and reinforces the importance of accurate documentation within the CMS framework.
These distinct elements of the “Consent and Signatures” section work together to ensure legal compliance, promote ethical practices, and establish a framework of shared responsibility for athlete health and safety within the CMS sports physical form process. This comprehensive approach to consent reinforces the CMS commitment to athlete well-being and emphasizes the importance of informed participation in sports activities. By addressing key legal and ethical considerations, the “Consent and Signatures” section plays a crucial role in facilitating a safe and responsible athletic environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding pre-participation medical evaluations, providing clarity on essential aspects of the process.
Question 1: How often is a pre-participation medical evaluation required?
Typically, a new evaluation is required annually or before each sport season, depending on the specific requirements of the governing sports organization or educational institution.
Question 2: Who can conduct a pre-participation medical evaluation?
Licensed physicians, physician assistants, or nurse practitioners are generally authorized to conduct these evaluations. Specific requirements may vary by state or organization.
Question 3: What happens if a medical concern is identified during the evaluation?
If a potential health concern is discovered, the healthcare provider may recommend further evaluation by a specialist, suggest modifications to training or competition, or, in some cases, restrict participation until the issue is resolved.
Question 4: Are there specific medical conditions that automatically disqualify an athlete from participation?
While certain conditions may require careful consideration and individualized assessment, automatic disqualification is rare. Decisions regarding participation are made on a case-by-case basis, considering the specific condition, its management, and the demands of the chosen sport.
Question 5: Can an athlete participate in sports with a pre-existing medical condition?
Many athletes with pre-existing medical conditions participate successfully in sports. Proper management of the condition, open communication with healthcare providers, and appropriate modifications to training or competition, if necessary, are essential.
Question 6: What is the purpose of the consent and signature section of the form?
This section ensures informed consent for the evaluation, acknowledges inherent risks associated with sports participation, and authorizes the release of necessary medical information. It establishes a legal agreement and shared understanding between all parties involved.
Understanding these key aspects of pre-participation medical evaluations ensures a smoother process and contributes to a safe and healthy athletic experience for all participants.
The subsequent section will explore best practices for completing the evaluation process efficiently and effectively.
CMS Sports Physical Form
This exploration of the CMS sports physical form has underscored its crucial role in safeguarding student-athlete well-being. From comprehensive medical histories and thorough physical examinations to stringent cardiovascular assessments and orthopedic evaluations, each component contributes to a holistic understanding of an individual’s fitness for participation. The importance of accurate immunization records and the legal and ethical implications of informed consent further highlight the form’s comprehensive nature. This meticulous process facilitates early identification of potential health concerns, enabling appropriate interventions and promoting responsible participation in competitive athletics.
Prioritizing athlete health and safety requires ongoing vigilance and a commitment to best practices. The CMS sports physical form serves as a critical tool in this endeavor, providing a framework for informed decision-making and proactive health management. Continued adherence to these established guidelines, coupled with open communication among healthcare providers, athletes, and relevant stakeholders, will further enhance the safety and well-being of student-athletes engaged in competitive sports. This proactive approach safeguards not only individual athletes but also strengthens the integrity of athletic programs by fostering a culture of safety and responsibility.