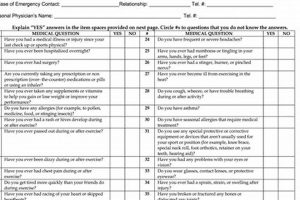
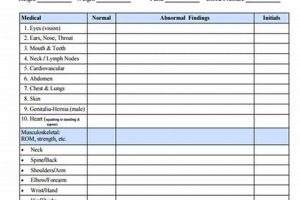
A pre-employment medical evaluation, often required before starting a new job, assesses an individual’s physical capability to perform essential job functions. For example, a position involving heavy lifting might necessitate an evaluation of back strength and overall fitness. This process helps ensure a prospective employee can safely and effectively meet the physical demands of the role.
These evaluations benefit both employers and employees. For employers, they mitigate the risk of workplace injuries and associated costs, while ensuring appropriate job placement. For employees, they offer reassurance of their fitness for the job and identify potential health concerns that could be exacerbated by specific work tasks. Historically, such evaluations have evolved from basic screenings to more comprehensive assessments reflecting the changing nature of work and increased awareness of occupational health and safety.
This understanding of pre-employment medical evaluations provides a foundation for exploring related topics such as legal considerations, specific evaluation components, and the role of occupational health professionals.
Tips for Pre-Employment Medical Evaluations
Preparation for a pre-employment medical evaluation can ensure a smooth and informative process. The following tips offer guidance for navigating this important step.
Tip 1: Be Honest and Transparent: Accurate disclosure of medical history, including previous injuries or conditions, is crucial for a comprehensive assessment. Withholding information can lead to inaccurate evaluations and potential complications later.
Tip 2: Understand the Job Requirements: Reviewing the physical demands of the position beforehand allows for better preparation and informed discussion with the evaluating physician.
Tip 3: Dress Comfortably and Appropriately: Comfortable attire allows for ease of movement during physical assessments. Consider the specific requirements of the evaluation, such as bringing appropriate footwear for a gait assessment.
Tip 4: Follow Instructions Carefully: Listen attentively and adhere to instructions provided by medical professionals during the evaluation process. This ensures accurate and reliable results.
Tip 5: Ask Clarifying Questions: Do not hesitate to seek clarification on any aspect of the evaluation process or the results. Open communication facilitates a clear understanding of one’s physical capabilities and any potential limitations.
Tip 6: Maintain a Professional Demeanor: Approaching the evaluation with a professional attitude demonstrates respect for the process and the medical professionals involved.
Following these guidelines ensures a productive and insightful evaluation, benefiting both the prospective employee and the employer.
These preparatory steps contribute to a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s suitability for a specific role and lay the groundwork for a safe and successful working relationship.
1. Medical History Review
Medical history review forms a cornerstone of pre-employment medical evaluations. It provides crucial context for interpreting physical examination findings and functional capacity assessments. A thorough review encompasses past illnesses, injuries, surgeries, chronic conditions, and current medications. This information helps identify potential risk factors that could impact job performance or be exacerbated by specific work tasks. For example, a history of back problems might influence the assessment of a candidate’s suitability for a physically demanding role. Similarly, knowledge of a pre-existing respiratory condition informs decisions regarding exposure to airborne hazards.
The practical significance of a comprehensive medical history review lies in its ability to facilitate informed decision-making regarding job placement and necessary accommodations. It allows employers to match individuals with roles that align with their physical capabilities, minimizing the risk of workplace injuries and promoting employee well-being. Furthermore, understanding an individual’s medical history allows for the development of appropriate safety measures and preventative strategies. For instance, an employee with a history of allergies might require specific protective equipment or environmental modifications. This proactive approach fosters a safer and healthier work environment for all.
In conclusion, the medical history review, as a key component of pre-employment medical evaluations, plays a vital role in promoting workplace safety and employee well-being. Its ability to inform job placement decisions, guide accommodations, and support the development of preventative strategies underscores its importance in fostering a productive and healthy workforce. Challenges remain in ensuring accurate and comprehensive information gathering while respecting individual privacy. Addressing these challenges through standardized procedures and clear communication protocols is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of medical history reviews.
2. Physical Examination
The physical examination constitutes a critical component of the pre-employment medical evaluation, directly informing the completion of the basic work physical form. This examination provides objective data regarding an individual’s physical health and functional capacity, enabling a comprehensive assessment of their suitability for specific job demands.
- Cardiovascular Assessment
Evaluation of cardiovascular health, including blood pressure, heart rate, and auscultation, helps determine an individual’s capacity for physically demanding tasks. For roles involving strenuous activity, such as construction or firefighting, a healthy cardiovascular system is essential. Abnormal findings might necessitate further investigation or indicate limitations in performing certain job functions.
- Musculoskeletal Evaluation
Assessment of range of motion, strength, and stability in joints and muscles is crucial for roles involving lifting, carrying, or repetitive movements. For example, evaluating back strength and flexibility is vital for jobs requiring manual material handling. This assessment helps identify potential musculoskeletal issues that could be aggravated by specific work activities.
- Neurological Examination
Neurological assessments, including reflexes, coordination, and sensory function, provide insights into an individual’s overall neurological health. This is particularly important for roles requiring fine motor skills, quick reaction times, or complex cognitive functions. Impaired neurological function could pose safety risks in certain occupational settings.
- Respiratory Evaluation
Assessment of respiratory function, including lung capacity and breathing patterns, is essential for roles involving exposure to dust, fumes, or other airborne hazards. Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma, might require specific precautions or accommodations to perform safely in such environments. This evaluation contributes to informed decision-making regarding appropriate job placement and necessary safety measures.
These facets of the physical examination, documented within the basic work physical form, provide a comprehensive overview of an individual’s physical capabilities and limitations. This information, considered alongside the medical history and other evaluation components, enables informed decisions regarding job suitability and the implementation of appropriate safety measures to mitigate potential risks and promote a healthy and productive workforce. Further, the results can inform recommendations for workplace accommodations, helping employers fulfill their legal obligations and create a more inclusive work environment.
3. Functional Capacity Testing
Functional capacity testing (FCT) plays a crucial role within the basic work physical form, providing objective data regarding an individual’s physical abilities to perform work-related tasks. This testing goes beyond a standard physical examination by assessing an individual’s capacity for specific activities, such as lifting, carrying, pushing, pulling, and other movements integral to various job roles. FCT establishes a baseline measurement of an individual’s functional abilities, informing decisions about job suitability and potential accommodations. For example, a warehouse worker might undergo FCT to evaluate their ability to safely lift and carry heavy boxes, while a nurse might be assessed on their capacity to assist patients with mobility.
FCT serves as a vital tool in preventing work-related injuries. By objectively measuring an individual’s functional capacity, employers can ensure appropriate job placement, minimizing the risk of placing individuals in roles that exceed their physical capabilities. This proactive approach contributes to a safer work environment and reduces the likelihood of injuries resulting from overexertion or repetitive strain. Moreover, FCT can help determine appropriate return-to-work strategies following an injury. By assessing an individual’s recovery progress, healthcare professionals and employers can collaborate to develop a safe and effective return-to-work plan, minimizing the risk of re-injury and facilitating a successful transition back into the workplace. This data-driven approach benefits both employees and employers by promoting a safe and timely return to full productivity.
In summary, FCT provides essential information within the context of a basic work physical form, facilitating informed decisions regarding job placement, injury prevention, and return-to-work strategies. Its ability to objectively measure functional capacity strengthens the overall pre-employment evaluation process, promoting workplace safety and fostering a healthier, more productive workforce. While FCT offers substantial benefits, challenges remain in standardizing testing protocols and ensuring consistent interpretation of results across various occupational settings. Addressing these challenges through ongoing research and collaboration among healthcare professionals, employers, and regulatory bodies will further enhance the value and effectiveness of FCT in promoting occupational health and safety.
4. Drug Screening
Drug screening constitutes a critical component of the basic work physical form, serving as a preventative measure to ensure workplace safety and mitigate potential risks associated with substance abuse. Its inclusion in pre-employment evaluations reflects a growing awareness of the impact of substance use on job performance, safety, and overall workplace productivity. This process helps employers maintain a drug-free work environment, protecting both employees and the organization as a whole.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations
Drug screening procedures must adhere to legal and ethical guidelines, respecting employee privacy while fulfilling the employer’s responsibility to maintain a safe workplace. Legal frameworks vary by jurisdiction, dictating permissible testing methods, notification requirements, and handling of test results. Ethical considerations involve informed consent, confidentiality, and non-discrimination. Balancing these legal and ethical imperatives ensures a fair and respectful process for all parties involved.
- Types of Drug Tests
Various drug testing methods exist, each with specific advantages and limitations. Urine tests are common due to their cost-effectiveness and ability to detect a range of substances. Hair follicle testing provides a longer detection window, while blood tests offer greater accuracy for recent drug use. The choice of testing method depends on factors such as cost, detection window, and specific job requirements. For example, safety-sensitive positions, such as transportation or heavy machinery operation, might necessitate more stringent testing protocols.
- Interpretation of Results
Accurate interpretation of drug test results requires expertise and adherence to established protocols. Positive results should be confirmed through a secondary testing method to minimize the risk of false positives. Furthermore, employers must consider the possibility of legitimate medication use that might trigger a positive result. Open communication with the candidate or employee and appropriate medical consultation are essential to ensure fair and accurate assessment of the findings.
- Impact on Employment Decisions
Drug screening results, in conjunction with other components of the basic work physical form, inform employment decisions. A positive drug test does not automatically disqualify a candidate. Employers must consider relevant legal and ethical guidelines, job requirements, and company policies when making employment decisions based on drug screening results. In some cases, conditional employment offers might be contingent upon successful completion of a substance abuse treatment program.
In conclusion, drug screening, as a key element of the basic work physical form, contributes significantly to workplace safety and productivity. By adhering to legal and ethical standards, employing appropriate testing methods, and accurately interpreting results, employers can effectively manage the risks associated with substance abuse in the workplace. This, in turn, fosters a safer and healthier work environment for all employees, ultimately contributing to organizational success. However, continuous review and adaptation of drug screening policies and practices are essential to keep pace with evolving legal landscapes, scientific advancements in testing methodologies, and changing societal attitudes towards substance use.
5. Vision and Hearing Tests
Vision and hearing tests represent integral components of the basic work physical form, providing crucial insights into an individual’s sensory capabilities and their potential impact on job performance. These tests assess the adequacy of sensory function for specific job demands, contributing to informed decisions regarding job suitability, safety measures, and potential accommodations. Impairments in vision or hearing can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform certain tasks safely and effectively, underscoring the importance of these assessments in promoting workplace safety and productivity.
- Visual Acuity
Visual acuity tests measure the clarity of vision at various distances. This assessment is essential for roles requiring sharp vision, such as operating machinery, driving, or performing detailed work. For example, a pilot requires excellent visual acuity to safely navigate an aircraft. Impaired visual acuity can pose significant safety risks in certain occupational settings and might necessitate corrective measures or job modifications.
- Color Perception
Color perception tests assess an individual’s ability to distinguish between different colors. This is crucial for roles involving color-coding, such as electrical work or laboratory analysis. Deficiencies in color perception can lead to errors in tasks requiring accurate color identification, potentially impacting safety and productivity. Accommodations, such as modified lighting or alternative labeling systems, can mitigate the impact of color vision deficiencies in the workplace.
- Auditory Threshold
Auditory threshold tests measure the quietest sound an individual can hear at various frequencies. This assessment is crucial for roles requiring effective communication, such as emergency response dispatchers or customer service representatives. Hearing loss can impede communication and compromise safety in noisy environments. Hearing protection devices or assistive listening technologies can help mitigate the impact of hearing loss in the workplace.
- Speech Discrimination
Speech discrimination tests assess an individual’s ability to understand spoken words in both quiet and noisy environments. This is essential for roles involving verbal communication, such as teaching or healthcare. Difficulties in speech discrimination can hinder effective communication, potentially impacting job performance and patient safety. Strategies such as clear enunciation, minimizing background noise, and utilizing assistive listening devices can improve communication effectiveness.
The results of vision and hearing tests, documented within the basic work physical form, contribute significantly to a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s suitability for specific job roles. These findings inform decisions regarding job placement, necessary accommodations, and the implementation of safety protocols. By addressing potential sensory limitations proactively, employers can create a safer and more inclusive work environment, promoting both employee well-being and organizational productivity. Further research and development of standardized testing protocols and assistive technologies will continue to enhance the effectiveness of these assessments in promoting occupational health and safety.
6. Job-Specific Assessments
Job-specific assessments represent a crucial component of the basic work physical form, tailoring the evaluation process to the unique demands of particular roles. These assessments move beyond generalized physical evaluations to focus on the specific physical capabilities required for a given job. This targeted approach ensures that individuals possess the necessary physical attributes to safely and effectively perform the essential functions of their roles. The relationship between job-specific assessments and the basic work physical form is one of granular detail informing a broader understanding of an individual’s suitability for employment. For example, a firefighter candidate might undergo a stair climb test while wearing full gear to simulate the physical demands of fire suppression activities. Similarly, a construction worker might be assessed on their ability to lift and carry specific construction materials.
The practical significance of incorporating job-specific assessments into the basic work physical form lies in its ability to enhance workplace safety and predict successful job performance. By accurately assessing an individual’s capacity for the specific physical demands of a role, employers can minimize the risk of work-related injuries and ensure appropriate job placement. This, in turn, leads to increased productivity and reduced workers’ compensation claims. Furthermore, job-specific assessments can inform the development of tailored training programs and identify potential areas where accommodations might be necessary. For instance, if a candidate demonstrates difficulty with a specific lifting task during the assessment, targeted training or assistive devices can be provided to enhance their performance and minimize the risk of injury. This proactive approach fosters a more inclusive and supportive work environment, benefiting both employees and the organization.
In conclusion, job-specific assessments contribute significantly to the effectiveness of the basic work physical form by providing a targeted evaluation of an individual’s physical capabilities in relation to specific job demands. This focused approach enhances workplace safety, improves job placement decisions, and informs the development of tailored training programs and accommodations. Challenges remain in developing standardized job-specific assessment protocols and ensuring consistent implementation across various industries. Addressing these challenges through ongoing research and collaboration among occupational health professionals, employers, and regulatory bodies will further enhance the value of job-specific assessments in promoting occupational health and safety.
7. Review and Recommendations
The “Review and Recommendations” section of the basic work physical form represents the culmination of the evaluation process, synthesizing all gathered information into a concise summary and actionable recommendations. This section bridges the gap between assessment findings and practical application, guiding decisions regarding job placement, necessary accommodations, and further medical follow-up. Its importance lies in its ability to translate complex medical data into clear, actionable insights that directly impact employment decisions and workplace safety.
- Summary of Findings
This component provides a concise overview of key findings from all preceding sections of the basic work physical form, including medical history, physical examination, functional capacity testing, and any specialized assessments. The summary highlights relevant medical conditions, functional limitations, and any other factors that might influence job performance or safety. For instance, the summary might note a history of back pain, limitations in lifting capacity, or successful completion of all job-specific physical demands. This concise summary allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the essential aspects of the evaluation.
- Job Suitability Determination
Based on the summarized findings, this section provides a clear determination regarding the individual’s suitability for the intended job role. The determination might categorize the individual as fit for duty, fit for duty with restrictions, or not fit for duty. For example, an individual might be deemed fit for duty with a restriction on heavy lifting, reflecting limitations identified during the functional capacity testing. This clear determination guides employment decisions and ensures appropriate job placement.
- Recommendations for Accommodations
Where limitations are identified, this section outlines specific recommendations for reasonable accommodations to enable the individual to perform essential job functions. These recommendations might include modifications to the work environment, assistive devices, or adjusted work schedules. For example, an individual with limited mobility might require an ergonomic workstation or assistive lifting equipment. These recommendations ensure compliance with disability rights legislation and promote an inclusive work environment.
- Recommendations for Further Evaluation
In some cases, further medical evaluation might be necessary to clarify ambiguous findings or address specific health concerns. This section outlines recommendations for specialist consultations, additional testing, or ongoing medical management. For instance, an individual with abnormal lung function test results might be referred to a pulmonologist for further evaluation. This ensures that potential health issues are addressed proactively, promoting employee well-being and minimizing the risk of future complications.
In conclusion, the “Review and Recommendations” section serves as the cornerstone of the basic work physical form, translating assessment data into actionable insights. Its concise summaries, clear suitability determinations, and targeted recommendations guide employment decisions, inform accommodation strategies, and promote a safe and healthy work environment. The effectiveness of this section depends on clear communication between healthcare professionals, employers, and employees, fostering a collaborative approach to workplace health and safety. Ongoing evaluation and refinement of review and recommendation processes are essential to ensure alignment with evolving best practices in occupational medicine and disability rights legislation.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding pre-employment medical evaluations, providing clarity on the process and its implications.
Question 1: What is the purpose of a pre-employment medical evaluation?
Pre-employment medical evaluations assess an individual’s physical and, sometimes, mental suitability for a specific job. They aim to ensure candidates can safely perform essential job functions while minimizing the risk of work-related injuries.
Question 2: Are pre-employment medical evaluations mandatory?
Legality varies by jurisdiction and job type. Some industries, such as transportation or heavy machinery operation, often mandate pre-employment medical evaluations due to inherent safety risks. Other roles might require evaluations only after a conditional job offer.
Question 3: What information is typically requested during a pre-employment medical evaluation?
Evaluations typically involve a review of medical history, a physical examination, and potentially specialized tests related to specific job demands. Information gathered might include past illnesses, injuries, current medications, and functional capabilities.
Question 4: Are medical evaluations confidential?
Medical information obtained during pre-employment evaluations is subject to strict confidentiality regulations. Employers must adhere to relevant privacy laws and ensure information is accessed only by authorized personnel for legitimate purposes.
Question 5: Can an employer reject a candidate based solely on the medical evaluation results?
Employment decisions must adhere to legal and ethical guidelines. While medical evaluations inform decisions, employers cannot discriminate based on disability. Rejection must be based on a demonstrable inability to perform essential job functions, even with reasonable accommodations.
Question 6: What if one disagrees with the medical evaluation’s findings?
Individuals have the right to seek a second medical opinion if they disagree with the initial evaluation’s findings. Open communication with the employer and appropriate medical professionals is crucial to address concerns and ensure a fair and accurate assessment.
Understanding these key aspects of pre-employment medical evaluations empowers both employers and candidates to navigate the process effectively, ensuring informed decisions and promoting workplace safety.
For further information, consult legal counsel specializing in employment law or relevant occupational health and safety resources.
Conclusion
Pre-employment medical evaluations, often documented through a basic work physical form, serve as a critical tool for promoting workplace safety, ensuring appropriate job placement, and fostering a healthy and productive workforce. These evaluations provide a comprehensive assessment of an individual’s physical capabilities in relation to specific job demands, informing decisions regarding suitability for employment and the potential need for accommodations. Key components such as medical history review, physical examination, functional capacity testing, and job-specific assessments contribute to a thorough understanding of an individual’s physical capacity. Adherence to legal and ethical guidelines throughout the evaluation process is paramount to ensure fairness, respect for individual privacy, and compliance with relevant regulations. Accurate interpretation of evaluation findings and clear communication between healthcare professionals, employers, and candidates are essential for effective decision-making and implementation of appropriate safety measures.
The evolving nature of work and increasing emphasis on preventative healthcare underscore the ongoing importance of pre-employment medical evaluations. Continuous refinement of evaluation protocols, incorporating advancements in medical technology and best practices in occupational health, will further enhance the effectiveness of these assessments in mitigating workplace risks and promoting employee well-being. Commitment to comprehensive pre-employment evaluations contributes significantly to a safer, healthier, and more productive work environment for all.