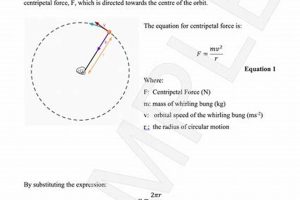
Categorizing Internal Assessment (IA) topics within physics allows for structured exploration of diverse areas such as mechanics, waves, thermodynamics, and fields. For example, an IA exploring the relationship between the tension and frequency of a vibrating string would fall under the category of “waves.” This systematic organization facilitates a focused approach to research and experimentation.
A well-defined classification system offers several advantages. It streamlines the selection process, enabling students to identify topics aligning with their interests and available resources. This structure also benefits educators by providing a framework for guidance and assessment. Historically, the increasing complexity and breadth of physics knowledge have necessitated such categorization for effective pedagogical approaches.
This structured approach to topic selection paves the way for a deeper exploration of specific areas within physics. The subsequent sections will delve into the key categories, providing further examples and guidance for developing robust research questions.
Tips for Categorizing Physics IA Topics
Effective categorization of Internal Assessment (IA) topics is crucial for focused research. The following tips provide guidance for navigating this process.
Tip 1: Align with Personal Interests: Selecting a topic within a preferred branch of physics, such as optics or astrophysics, fosters engagement and motivation.
Tip 2: Consider Resource Availability: Ensure access to necessary equipment and materials before finalizing a topic. An IA on fluid dynamics may require specialized apparatus.
Tip 3: Explore Existing Literature: Reviewing published research papers and scientific journals helps identify potential research gaps and refine the scope of the investigation.
Tip 4: Define a Clear Research Question: Formulate a specific, testable question that guides the experimental design and data analysis. A broad topic like “electricity” should be narrowed down to a specific research question.
Tip 5: Consult with Educators: Discuss potential topics and research questions with teachers or mentors to gain valuable feedback and ensure alignment with assessment criteria.
Tip 6: Ensure Feasibility: Evaluate the practicality of conducting the experiment within the given timeframe and available resources. Complex experiments requiring extensive data collection may prove challenging.
Tip 7: Consider Ethical Implications: Be mindful of any ethical considerations related to the chosen topic, particularly if involving human participants or sensitive data.
Following these guidelines ensures the selection of a well-defined, manageable, and impactful IA topic, laying the groundwork for a successful investigation.
By adhering to these principles, students can embark on a fulfilling research journey, contributing meaningfully to the field of physics.
1. Categorization
Categorization forms the cornerstone of effective physics IA topic selection. A systematic classification framework provides structure and clarity, enabling students to navigate the diverse landscape of potential research areas. This process involves assigning topics to specific categories based on their underlying principles and subject matter. For instance, an investigation into projectile motion falls under classical mechanics, while an exploration of spectral lines belongs to atomic physics. This structured approach ensures focused research, facilitating in-depth exploration within clearly defined boundaries.
The importance of categorization extends beyond mere organization. It plays a crucial role in shaping the research process itself. By classifying a topic, students gain a deeper understanding of its theoretical underpinnings and experimental methodologies. This understanding facilitates the development of focused research questions, the selection of appropriate experimental designs, and the interpretation of experimental findings. Furthermore, categorization aids in identifying relevant resources and existing literature, enabling students to build upon established knowledge and contribute meaningfully to the field. For example, categorizing an IA as related to “thermodynamics” would guide the student towards specific journals, experimental setups, and relevant equations.
In conclusion, categorization is integral to the success of a physics IA. It provides a crucial framework for navigating the complexities of research, ensuring focused inquiry and meaningful contributions to scientific understanding. Challenges may arise in classifying interdisciplinary topics, requiring careful consideration of underlying principles and research goals. However, the benefits of a well-defined categorization system far outweigh these challenges, laying the foundation for impactful and insightful investigations within the realm of physics.
2. Structure
Structure plays a vital role in the classification of physics IA topics. A well-defined structure ensures clarity and coherence, guiding the research process and facilitating meaningful exploration. This structure typically involves categorizing topics based on established branches of physics, such as mechanics, thermodynamics, electromagnetism, and quantum physics. Within each category, further subdivisions can be made based on specific concepts or experimental approaches. For example, within mechanics, one might find subcategories like kinematics, dynamics, and rotational motion. This hierarchical structure provides a framework for organizing and classifying diverse IA topics, enabling a systematic approach to investigation.
The importance of structure becomes evident when considering its impact on the research process. A structured approach allows for efficient navigation of complex concepts and facilitates the identification of relevant resources. It enables students to define clear research questions, design appropriate experiments, and analyze data effectively. For instance, a structured approach to an IA on simple harmonic motion would involve classifying it under mechanics, identifying relevant equations of motion, and designing experiments to measure key variables like period and amplitude. Without a clear structure, the research process can become disorganized and inefficient, leading to ambiguity and potentially compromising the validity of the findings.
In summary, structure provides essential scaffolding for classifying and conducting physics IAs. It enables systematic exploration of complex concepts, facilitates efficient research, and enhances the overall quality and impact of scientific investigations. While the specific structure may vary depending on the research area and educational context, its fundamental role in promoting clarity, coherence, and rigor remains crucial for meaningful scientific inquiry.
3. Organization
Organization is fundamental to the effective classification of physics IA topics. A systematic approach to organizing research ensures clarity, efficiency, and coherence throughout the investigation. This involves structuring information, resources, and experimental procedures in a logical manner, facilitating a streamlined research process and enhancing the overall quality of the IA.
- Resource Management
Effective resource management is crucial for organized IA research. This includes compiling relevant literature, procuring necessary equipment, and managing experimental data. For instance, organizing research papers by topic and maintaining a well-structured lab notebook contributes significantly to a streamlined research process. This organized approach ensures easy access to information, minimizes redundancy, and facilitates efficient data analysis. In the context of physics IA classification, organized resource management enables a more focused approach to topic selection and research execution.
- Experimental Design
A well-organized experimental design is essential for conducting rigorous and reliable physics investigations. This involves meticulously planning experimental procedures, defining control variables, and establishing clear data collection protocols. For example, creating a detailed experimental plan outlining the steps, apparatus, and data analysis techniques ensures a systematic approach to data collection and interpretation. This meticulous organization minimizes experimental errors, enhances the reliability of results, and strengthens the overall scientific validity of the IA.
- Data Analysis
Organized data analysis is crucial for extracting meaningful insights from experimental findings. This involves systematically processing and interpreting collected data, employing appropriate statistical methods, and presenting results in a clear and concise manner. For example, organizing data into tables and graphs, performing statistical tests, and documenting the analysis process ensures transparency and facilitates accurate interpretation of results. In the context of physics IA classification, organized data analysis enables a more comprehensive understanding of the investigated topic and strengthens the overall scientific merit of the research.
- Time Management
Effective time management is essential for successful completion of a physics IA. This involves establishing a realistic timeline, allocating sufficient time for each stage of the research process, and adhering to deadlines. For example, creating a project schedule outlining key milestones and deadlines ensures timely progress and prevents delays. This organized approach allows for efficient allocation of resources, minimizes stress, and enhances the overall quality and impact of the IA.
These organizational facets are integral to a successful physics IA. By implementing these strategies, students can effectively classify their chosen topic, conduct rigorous research, and contribute meaningfully to scientific understanding. A lack of organization can lead to inefficiencies, inconsistencies, and compromised research outcomes. Therefore, prioritizing organization throughout the IA process is paramount for achieving research excellence.
4. Systematization
Systematization is integral to classifying physics IA topics effectively. It provides a structured framework for organizing diverse research areas, ensuring clarity, consistency, and coherence in the investigative process. Systematization involves establishing a logical system for categorizing topics based on underlying principles, experimental methodologies, or specific subject matter. This systematic approach facilitates efficient navigation of the complex landscape of physics concepts, enabling students to select appropriate research questions, design robust experiments, and analyze data effectively. For instance, a systematic approach to classifying IA topics might involve categorizing them based on branches of physics (e.g., mechanics, electromagnetism, thermodynamics), further subdivided by specific concepts (e.g., kinematics, optics, heat transfer). This structured framework clarifies the relationships between different topics and guides the research process towards meaningful outcomes. The absence of systematization can lead to fragmented research, ambiguous classifications, and difficulty in drawing meaningful conclusions.
A practical example of systematization in physics IA classification is the use of standardized experimental procedures. By systematizing experimental setups, data collection methods, and analysis techniques, researchers ensure consistency and comparability across different investigations. This systematic approach enhances the reliability of findings and facilitates meaningful comparisons between different studies. Furthermore, systematization aids in identifying potential sources of error and bias, leading to more robust and accurate scientific conclusions. For instance, systematizing the measurement of gravitational acceleration using a pendulum involves standardizing the length of the pendulum, the initial angle of displacement, and the method for timing oscillations. This systematic approach minimizes experimental error and ensures reliable results.
In conclusion, systematization is essential for effective classification and execution of physics IAs. It provides a structured framework for organizing research, enhancing clarity, consistency, and reliability. While challenges may arise in classifying interdisciplinary topics or adapting standardized procedures to novel research questions, the benefits of systematization in terms of research quality and scientific rigor are undeniable. A systematic approach to classification lays the foundation for meaningful contributions to scientific understanding and fosters a deeper appreciation of the interconnectedness of physical phenomena.
5. Arrangement
Arrangement plays a crucial role in the effective classification of physics IA topics. A logical arrangement facilitates clear navigation through diverse research areas, enabling efficient exploration and analysis. This involves structuring topics based on inherent relationships, connecting theoretical underpinnings with experimental methodologies. A well-defined arrangement ensures coherence, enabling a systematic approach to investigating complex phenomena. For instance, arranging IA topics by increasing complexity, starting with classical mechanics and progressing to quantum physics, provides a structured learning pathway. This logical flow enhances understanding and facilitates the development of robust research questions. Conversely, a disorganized arrangement can lead to fragmented research, hindering effective analysis and limiting the potential for meaningful scientific contributions. Arranging topics by energy scales, for example, connects macroscopic phenomena in thermodynamics with microscopic interactions in particle physics, offering a cohesive perspective.
The practical significance of a well-considered arrangement extends to experimental design and data analysis. A structured arrangement guides the selection of appropriate experimental techniques and ensures data is collected and analyzed systematically. For instance, in an IA exploring the relationship between pressure and volume of a gas, arranging the experimental procedure to control temperature ensures data accuracy and facilitates analysis using the ideal gas law. Furthermore, arranging experimental data in tables and graphs, ordered by independent variables, enhances visual representation and aids in identifying trends and drawing valid conclusions. A clear arrangement also facilitates communication of scientific findings, enabling effective dissemination of knowledge and fostering further research.
In summary, a systematic arrangement is integral to the effective classification and execution of physics IAs. It fosters coherence, enhances understanding, and facilitates rigorous scientific investigation. While challenges may arise in arranging interdisciplinary topics or accommodating diverse experimental approaches, the benefits of a well-defined arrangement in terms of research clarity, efficiency, and impact are paramount. A logical arrangement lays the foundation for robust scientific inquiry and contributes significantly to the advancement of physics knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common queries regarding the classification of physics Internal Assessment (IA) topics, providing clarity and guidance for successful research endeavors.
Question 1: How does topic classification influence the scope of a physics IA?
Classification defines the boundaries of research, ensuring a focused investigation. A clearly classified topic prevents scope creep and facilitates in-depth exploration within a specific area of physics.
Question 2: What are the primary categories typically used for classifying physics IA topics?
Common categories include classical mechanics, thermodynamics, electromagnetism, waves and optics, atomic and nuclear physics, and astrophysics. Further subcategories may exist within each branch.
Question 3: How does one choose an appropriate IA category based on available resources?
Consider available equipment, materials, and expertise when selecting a category. Resource limitations may restrict the feasibility of certain experimental investigations.
Question 4: Can a physics IA topic span multiple categories?
Interdisciplinary investigations are possible, but require careful consideration of the connections between categories and a clearly defined research focus. This approach often necessitates a more complex experimental design and data analysis process.
Question 5: How does topic classification relate to the assessment criteria for physics IAs?
Classification ensures alignment with assessment criteria by defining the scope and focus of the research. A well-classified topic facilitates a structured approach to addressing assessment requirements.
Question 6: What are the consequences of misclassifying a physics IA topic?
Misclassification can lead to an unfocused investigation, difficulty in meeting assessment criteria, and a compromised research outcome. It can also make it challenging to find relevant background information and appropriate experimental methodologies.
Careful consideration of these frequently asked questions ensures a clear understanding of the importance and implications of physics IA topic classification. A systematic approach to classification lays the groundwork for a successful and impactful research endeavor.
The following section will provide practical examples of classified physics IA topics, demonstrating the application of these principles in real-world research scenarios.
Conclusion
Effective classification of Internal Assessment topics within physics provides a crucial framework for structured research. Systematic categorization, coupled with logical arrangement, facilitates efficient exploration of diverse areas such as mechanics, waves, and fields. A well-defined structure, coupled with meticulous organization, ensures clarity and coherence throughout the research process, from topic selection to data analysis. Systematization enhances rigor and reliability, while a thoughtful arrangement strengthens the connection between theoretical understanding and experimental design.
Precise categorization of IA topics is essential for meaningful contributions to the field of physics. This structured approach empowers students to conduct impactful research, fostering a deeper understanding of physical phenomena and cultivating essential scientific skills. The meticulous classification of research within physics ultimately contributes to a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the universe.