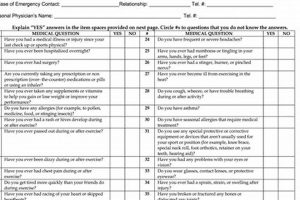
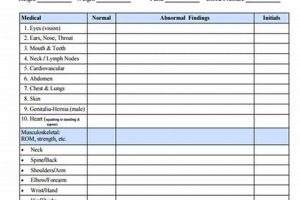
A medical evaluation requested by an employer as a contingency of hiring is a common practice. This assessment typically involves a review of medical history, a physical examination, and sometimes specific tests like drug screenings or vision checks. For example, a transportation company might require a hearing test and assessment of physical strength and stamina, while an office-based role might involve a more general health check. These evaluations ensure prospective employees can safely and effectively perform the essential functions of a specific job.
Such evaluations benefit both employers and prospective employees. Employers can mitigate workplace safety risks, reduce insurance costs, and ensure regulatory compliance. For individuals, these checks can identify potential health concerns early on, allowing for proactive management and potentially preventing future complications. Historically, these practices evolved from broader public health initiatives and a growing awareness of occupational hazards. Over time, they became increasingly standardized and tailored to specific industries and roles.
The following sections delve further into specific components of this process, covering legal considerations, common examination procedures, and best practices for both employers and candidates.
Successfully navigating the medical evaluation process requires preparation and understanding. The following tips offer guidance for both employers and candidates.
Tip 1: Understand Legality and Confidentiality. Employers must adhere to relevant laws and regulations regarding medical inquiries. Information gathered during the process must be kept confidential and used solely for assessing fitness for duty.
Tip 2: Transparency is Key. Employers should clearly communicate the evaluation process and its purpose to candidates. Candidates should likewise be forthcoming about any existing medical conditions or concerns.
Tip 3: Focus on Essential Job Functions. Evaluations should be tailored to assess abilities directly relevant to the job’s physical demands. Unnecessary or overly broad inquiries should be avoided.
Tip 4: Choose Qualified Professionals. Employers should utilize licensed medical professionals experienced in occupational health. These professionals understand the legal framework and can conduct appropriate evaluations.
Tip 5: Respect Candidate Privacy. Evaluations should be conducted in a private and respectful manner. Candidates should feel comfortable asking questions and raising concerns.
Tip 6: Provide Reasonable Accommodations. Employers are obligated to provide reasonable accommodations for individuals with disabilities, provided they can perform the essential functions of the job with such accommodations.
Tip 7: Document the Process. Clear documentation of the evaluation process and its outcomes is crucial for both legal compliance and effective record-keeping.
By adhering to these guidelines, employers and candidates can ensure a fair, legally compliant, and informative evaluation process that contributes to a safe and productive work environment.
These considerations underscore the importance of a well-managed medical evaluation process. The final section offers concluding thoughts and emphasizes the ongoing need for best practices in this area.
1. Legality
Legality forms a cornerstone of the pre-employment medical evaluation process. Navigating this landscape requires strict adherence to relevant laws and regulations, primarily focusing on anti-discrimination and privacy. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the United States, for example, prohibits employers from making disability-related inquiries or requiring medical examinations before a conditional job offer is extended. This prevents discrimination against qualified individuals with disabilities. Premature medical inquiries can inadvertently reveal protected health information, leading to potential legal challenges. A seemingly innocuous question about frequent doctor visits, for instance, could reveal information about a chronic illness or pregnancy, opening the door to potential bias.
Furthermore, any medical information obtained after a conditional offer must be job-related and consistent with business necessity. This means employers must demonstrate a clear connection between the required examination and the essential functions of the job. Requiring a vision test for a truck driver is justifiable, whereas demanding the same test for an office worker who primarily uses a computer might not meet this criterion. Additionally, all medical information obtained during the process must be treated as confidential medical records, stored securely and separately from general personnel files. Failing to maintain this confidentiality can result in legal action and reputational damage. Consider a scenario where an employee’s medical information is inadvertently disclosed, leading to stigmatization or discriminatory treatment within the workplace; such a breach would have serious legal and ethical implications.
In conclusion, navigating the legal aspects of pre-employment medical evaluations requires careful consideration of anti-discrimination laws, privacy regulations, and the principle of job relevance. Employers must establish clear policies and procedures that comply with these legal frameworks. Understanding and adhering to these principles not only mitigates legal risks but also fosters a fair and equitable hiring process. This rigorous approach contributes to a more inclusive and respectful work environment for all individuals. The legal framework surrounding these evaluations continues to evolve, necessitating ongoing review and adaptation to ensure best practices are maintained.
2. Confidentiality
Maintaining confidentiality is paramount throughout the pre-employment medical evaluation process. This principle safeguards sensitive personal information and ensures compliance with ethical and legal standards. Protecting candidate privacy builds trust and fosters a respectful hiring environment. The following facets illuminate the crucial role of confidentiality within this context.
- Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Stringent legal and regulatory frameworks govern the confidentiality of medical information. Regulations like the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe mandate strict protocols for handling sensitive personal data. These regulations dictate how medical information is collected, stored, accessed, and used. Non-compliance can lead to substantial legal penalties and reputational damage. For instance, unauthorized disclosure of an applicant’s medical condition could result in legal action and erode public trust in the organization.
- Data Security Measures
Robust data security measures are essential for safeguarding confidential medical information. Employers must implement secure storage systems, access controls, and encryption protocols to protect against unauthorized access or breaches. This includes physical security measures like locked filing cabinets and digital safeguards like password protection and firewalls. A data breach involving medical records can have severe consequences, including identity theft, financial loss, and emotional distress for affected individuals. Investing in robust security measures demonstrates a commitment to protecting candidate privacy and mitigating potential risks.
- Need-to-Know Access
Adhering to the principle of “need-to-know” access is crucial for maintaining confidentiality. Only authorized personnel directly involved in the hiring process and with a legitimate need for the information should have access to medical records. This restricts access to individuals such as hiring managers, occupational health professionals, and designated human resources staff. Limiting access minimizes the risk of inadvertent disclosures or misuse of information. For example, sharing an applicant’s medical history with colleagues who are not involved in the hiring decision would violate this principle and could have legal ramifications.
- Transparency and Consent
Transparency and informed consent are fundamental to maintaining confidentiality. Candidates should be fully informed about how their medical information will be collected, used, and protected. They should be provided with clear and concise privacy policies and consent forms that outline their rights and the organization’s responsibilities. This fosters trust and empowers candidates to make informed decisions about sharing their medical information. For example, candidates should be explicitly informed about the types of medical examinations required, the purpose of these examinations, and who will have access to the results.
These facets of confidentiality underscore the importance of ethical and legal handling of medical information throughout the pre-employment process. By prioritizing data security, adhering to legal frameworks, and respecting candidate privacy, organizations can create a fair and trustworthy hiring experience. Breaches in confidentiality can not only lead to legal repercussions but also damage an organization’s reputation and erode trust among potential candidates. Maintaining robust confidentiality protocols is therefore not merely a legal obligation but a cornerstone of ethical and responsible hiring practices.
3. Job Relevance
Job relevance serves as a critical filter in pre-employment medical evaluations, ensuring assessments focus solely on an individual’s ability to safely and effectively perform essential job functions. This principle aligns evaluations with business necessity and prevents unnecessary intrusions into personal medical information. A direct correlation must exist between the required examination and the specific physical demands or potential health risks associated with the role. For instance, requiring a lifting assessment for a warehouse position involving heavy lifting is justifiable due to the inherent physical demands of the job. However, imposing the same assessment on a data entry clerk who performs primarily sedentary work lacks job relevance and could be considered discriminatory.
Understanding the practical significance of job relevance requires considering the potential impact on individuals and the overall hiring process. Evaluations lacking job relevance can inadvertently disadvantage qualified candidates with underlying health conditions that do not impede their ability to perform the essential functions of the role. Consider a scenario where a candidate with a well-managed chronic illness is excluded from consideration due to an irrelevant medical examination. This not only harms the individual but also deprives the employer of a potentially valuable employee. Moreover, focusing solely on job-relevant criteria streamlines the hiring process, reduces unnecessary costs, and minimizes potential legal challenges. Unnecessary medical inquiries can prolong the hiring process, increase administrative burdens, and potentially expose employers to legal risks associated with discrimination and privacy violations.
Maintaining job relevance as a central component of pre-employment medical evaluations necessitates careful job analysis and consultation with occupational health professionals. A comprehensive job analysis identifies the essential physical requirements and potential health risks associated with each role. This information informs the design of tailored medical evaluations that focus specifically on relevant criteria. Occupational health professionals provide expert guidance in developing appropriate assessments that comply with legal and ethical standards. This collaborative approach ensures evaluations remain focused on job-related factors, promoting a fair and equitable hiring process while safeguarding candidate privacy. Challenges can arise in determining the precise boundaries of job relevance, particularly in roles with complex or evolving physical demands. Ongoing review and adaptation of evaluation protocols are crucial for maintaining alignment with changing job requirements and ensuring continued compliance with legal and ethical standards.
4. Qualified Professionals
The integrity and effectiveness of pre-employment medical evaluations hinge on the involvement of qualified professionals. These individuals possess the necessary medical expertise, legal awareness, and ethical understanding to conduct assessments that are both legally compliant and relevant to the specific job requirements. Utilizing qualified professionals ensures evaluations are conducted according to established medical standards, minimizing the risk of inaccurate or biased assessments. Their expertise allows for accurate interpretation of medical findings and appropriate recommendations based on the individual’s health status and the demands of the role. For example, a physician specializing in occupational medicine can discern the difference between a minor health issue and a significant impediment to job performance, ensuring recommendations are proportionate to the specific situation.
Furthermore, qualified professionals understand the legal framework surrounding pre-employment medical evaluations, including anti-discrimination laws and privacy regulations. This knowledge ensures compliance with legal mandates, protecting both the employer and the candidate. They can differentiate between permissible and impermissible inquiries, ensuring the evaluation process remains within legal boundaries. For instance, a qualified professional would understand the limitations of inquiries related to genetic information or family medical history, avoiding questions that could violate legal protections. Moreover, their ethical commitment to patient confidentiality safeguards sensitive medical information and maintains the integrity of the evaluation process. This ethical framework promotes trust between the candidate, the employer, and the evaluating professional, fostering a respectful and transparent hiring experience.
In conclusion, the involvement of qualified professionals is not merely a best practice but a fundamental requirement for legally sound and ethically conducted pre-employment medical evaluations. Their expertise ensures accurate assessments, legal compliance, and the protection of candidate privacy. Failing to engage qualified professionals can undermine the integrity of the evaluation process, potentially leading to discriminatory practices, legal challenges, and inaccurate assessments of a candidate’s fitness for duty. The ongoing evolution of employment law and medical practices necessitates continuous professional development for those conducting these evaluations, ensuring their expertise remains current and aligned with best practices.
5. Candidate Experience
Candidate experience during the pre-employment medical evaluation significantly impacts overall perceptions of the hiring organization and the process itself. A positive experience fosters trust, reinforces professionalism, and contributes to a smoother onboarding process. Conversely, a negative experience can deter qualified candidates and damage an organization’s reputation. The following facets highlight key components of candidate experience within this context.
- Respect and Dignity
Treating candidates with respect and dignity throughout the evaluation process is paramount. This includes maintaining privacy during examinations, using appropriate language, and addressing any concerns or questions with sensitivity. A respectful environment reduces anxiety and ensures candidates feel comfortable sharing relevant medical information. For example, providing private changing areas and ensuring clear communication about the examination procedures contribute to a positive experience.
- Transparency and Communication
Clear and consistent communication about the evaluation process is essential. Candidates should be informed about the purpose of the examination, the types of tests involved, and how the results will be used. Transparency builds trust and reduces potential apprehension. Providing clear instructions beforehand, explaining the timeline for receiving results, and offering a point of contact for questions fosters a sense of clarity and control for the candidate.
- Efficiency and Timeliness
Streamlining the evaluation process and minimizing delays demonstrates respect for candidates’ time. Efficient scheduling, prompt communication of results, and a clear timeline for next steps contribute to a positive experience. Unnecessary delays or a lack of communication can create frustration and uncertainty, potentially leading candidates to pursue other opportunities.
- Accommodation and Accessibility
Providing reasonable accommodations for candidates with disabilities ensures equal access to the evaluation process. This may include offering alternative testing formats, providing assistive devices, or adjusting scheduling to accommodate individual needs. Demonstrating a commitment to accessibility reinforces an organization’s commitment to inclusivity and diversity. For example, offering a sign language interpreter for a candidate with a hearing impairment or providing extended time for a candidate with a learning disability ensures equitable access to the evaluation process.
These facets of candidate experience underscore the importance of a well-managed and empathetic approach to pre-employment medical evaluations. Prioritizing respect, transparency, efficiency, and accessibility contributes to a positive candidate experience, fostering a strong employer brand and attracting top talent. A negative experience, on the other hand, can damage an organization’s reputation and deter qualified candidates from pursuing employment opportunities. Ultimately, a positive candidate experience during the pre-employment medical evaluation is an investment in both the individual and the organization’s long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding pre-employment medical evaluations, providing clarity on key aspects of the process.
Question 1: What is the typical scope of a pre-employment medical evaluation?
Scope varies depending on job requirements but often includes a review of medical history, a physical examination, and sometimes specific tests like drug screenings or vision checks. Evaluations focus on determining an individual’s ability to safely perform essential job functions.
Question 2: When in the hiring process does a medical evaluation typically occur?
Evaluations typically occur after a conditional job offer is extended. This practice aligns with legal guidelines regarding disability-related inquiries and protects against potential discrimination.
Question 3: Are there legal limitations on the types of medical inquiries employers can make?
Stringent regulations govern permissible medical inquiries. Inquiries must be job-related and consistent with business necessity. Disability-related inquiries or medical examinations before a conditional job offer are generally prohibited.
Question 4: How is the confidentiality of medical information maintained during this process?
Confidentiality is paramount. Medical information is treated as confidential medical records, stored securely and separately from general personnel files. Access is restricted to authorized personnel with a legitimate need for the information.
Question 5: What role do qualified professionals play in pre-employment medical evaluations?
Qualified professionals, such as occupational health physicians, ensure evaluations are conducted according to medical and legal standards. Their expertise ensures accurate assessments, appropriate recommendations, and adherence to ethical guidelines.
Question 6: What rights do candidates have during the evaluation process?
Candidates have the right to be informed about the purpose and scope of the evaluation, to have their medical information treated confidentially, and to request reasonable accommodations for disabilities during the process.
Understanding these frequently asked questions promotes a transparent and informed approach to pre-employment medical evaluations, benefiting both employers and candidates. Open communication and adherence to legal and ethical guidelines are essential for a successful and equitable process.
The subsequent section provides concluding remarks and emphasizes the ongoing importance of best practices in pre-employment medical evaluations.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of medical evaluations associated with prospective employment requires careful consideration of legal, ethical, and practical implications. This exploration has highlighted the importance of job relevance, the necessity of qualified professionals, and the significance of a positive candidate experience. Strict adherence to confidentiality protocols and legal frameworks ensures evaluations remain non-discriminatory and protect sensitive personal information. Understanding the interplay of these elements contributes to a robust and equitable hiring process.
As workplaces evolve and legal landscapes shift, continuous review and refinement of evaluation practices remain essential. Prioritizing fairness, transparency, and respect for individual rights ensures these evaluations serve as valuable tools for promoting workplace safety and supporting a healthy and productive workforce. Ongoing dialogue and collaboration among stakeholdersemployers, candidates, and healthcare professionalswill further enhance the effectiveness and ethical integrity of these crucial pre-employment procedures.