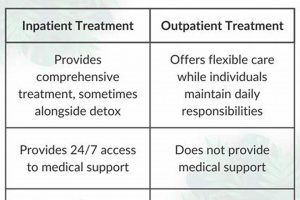
Best-in-class rehabilitative treatment aims to restore and optimize physical function, encompassing a range of evidence-based techniques tailored to individual needs. These interventions address mobility issues, pain management, and injury recovery, often involving exercises, manual therapy, and modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation. For instance, a patient recovering from knee surgery might undergo a personalized program incorporating strengthening exercises, range-of-motion activities, and manual therapy to regain full functionality.
High-quality, individualized rehabilitative care plays a vital role in improving quality of life by promoting physical independence and reducing pain. Historically, such care has evolved significantly, transitioning from rudimentary practices to sophisticated, research-backed interventions. This evolution reflects a growing understanding of the body’s intricate mechanisms and the importance of tailored treatment approaches. Ultimately, the objective is to empower individuals to regain control over their physical well-being and participate fully in daily activities.
The following sections will delve deeper into specific aspects of achieving optimal physical function, exploring various treatment modalities, the role of personalized care plans, and the long-term benefits of proactive rehabilitation.
Tips for Optimal Physical Recovery
Achieving optimal physical function and well-being requires a proactive and informed approach. The following tips offer valuable guidance for maximizing recovery and maintaining long-term physical health.
Tip 1: Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting qualified healthcare professionals is crucial for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. A thorough assessment establishes a foundation for effective rehabilitation.
Tip 2: Adhere to Prescribed Treatment: Consistent adherence to recommended exercises and therapies is essential for progress. Deviation from the prescribed plan can hinder recovery and prolong healing time.
Tip 3: Prioritize Proper Body Mechanics: Maintaining correct posture and movement patterns minimizes strain on the body and reduces the risk of re-injury. Ergonomic adjustments in daily activities can further enhance physical well-being.
Tip 4: Incorporate Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, tailored to individual capabilities, strengthens muscles, improves flexibility, and promotes overall physical health. Gradual progression in exercise intensity is key to sustainable progress.
Tip 5: Listen to the Body: Recognizing and respecting pain signals is essential. Pushing through pain can exacerbate injuries. Rest and recovery are integral components of any rehabilitation program.
Tip 6: Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Proper nutrition, adequate sleep, and stress management contribute significantly to overall health and support the healing process. A holistic approach optimizes physical recovery.
Tip 7: Focus on Long-Term Wellness: Rehabilitation is not merely about recovering from injury; it’s about building a foundation for long-term physical health. Adopting healthy habits promotes sustained well-being and minimizes the risk of future issues.
By embracing these principles, individuals can significantly improve their chances of achieving optimal physical function and enjoying a higher quality of life. These practices empower individuals to take control of their physical well-being and maintain long-term health.
In conclusion, the journey towards optimal physical well-being requires commitment, informed decision-making, and consistent effort. The information provided herein serves as a valuable resource for individuals seeking to maximize their physical potential.
1. Individualized Treatment Plans
Individualized treatment plans constitute a cornerstone of best practice rehabilitation. Generic approaches fail to address the unique circumstances of each individual, potentially leading to suboptimal outcomes. Variability in injury type, severity, pre-existing conditions, and personal goals necessitates a tailored approach. An individualized plan considers these factors to optimize the effectiveness of interventions and maximize functional recovery. For example, a runner with a hamstring strain requires a different rehabilitation protocol than an office worker with the same injury. The runner’s plan will likely emphasize restoring speed and agility, while the office worker’s plan might focus on regaining comfortable sitting and walking. This individualized focus ensures that the chosen therapies effectively address the specific needs and goals of each patient.
The effectiveness of individualized plans is rooted in their ability to address the specific biomechanical and physiological factors contributing to dysfunction. A comprehensive assessment identifies areas requiring intervention, enabling therapists to target specific impairments. This targeted approach maximizes the impact of each treatment session and accelerates the recovery process. Furthermore, individualized plans promote patient engagement by incorporating patient preferences and goals. This collaborative approach fosters motivation and adherence to the prescribed program, ultimately leading to better long-term outcomes. Consider a patient with a fear of certain movements; an individualized plan will progressively address this fear, building confidence and facilitating a complete return to function.
In summary, individualized treatment plans represent an essential component of effective rehabilitation. Their capacity to address unique patient needs, target specific impairments, and foster active patient participation contributes significantly to achieving optimal physical function. While standardized protocols can provide a general framework, the individualized approach ultimately determines the success and sustainability of rehabilitation outcomes. This personalized focus remains paramount in achieving optimal physical restoration and long-term well-being.
2. Evidence-based techniques
Evidence-based techniques form the foundation of achieving optimal physical function. Reliance on proven methodologies ensures treatment efficacy and maximizes the likelihood of positive outcomes. Scientific rigor, through research and clinical trials, validates the effectiveness of these techniques. This data-driven approach distinguishes optimal care from interventions lacking empirical support. For example, utilizing manual therapy techniques supported by research demonstrating positive effects on joint mobility and pain reduction exemplifies evidence-based practice. Conversely, employing unproven methods risks ineffective treatment and potential harm. The commitment to evidence-based practice demonstrates a dedication to providing the highest quality care and achieving optimal results. This approach ensures interventions are grounded in scientific understanding, maximizing patient benefit and minimizing potential risks.
Integrating evidence-based techniques into rehabilitation programs offers numerous practical advantages. Treatment plans rooted in scientific evidence offer a higher probability of success, reducing the need for prolonged interventions or alternative approaches. This efficiency translates to quicker recovery times, minimized discomfort, and a more rapid return to normal activities. Furthermore, evidence-based practice promotes cost-effectiveness by focusing on interventions proven to yield results. Consider the application of therapeutic exercises supported by research demonstrating their effectiveness in strengthening specific muscle groups; this targeted approach maximizes functional gains while avoiding unnecessary interventions. This commitment to evidence-based care underscores a dedication to responsible resource allocation and achieving optimal patient outcomes. The emphasis on proven methodologies contributes to efficient, effective, and cost-conscious care.
In conclusion, adhering to evidence-based techniques is paramount in delivering superior rehabilitative care. Scientific validation provides the basis for informed decision-making and ensures treatments are both safe and effective. This commitment to evidence-based practice represents a dedication to excellence, prioritizing patient well-being and maximizing the potential for optimal physical function. Challenges may arise in staying current with the latest research and integrating new findings into practice, but the ongoing pursuit of evidence-based methodologies remains essential to advancing the field and optimizing patient care. The benefits of this rigorous approach are undeniable, contributing to improved outcomes, enhanced efficiency, and a higher standard of care.
3. Skilled Therapists
Skilled therapists are integral to delivering optimal physical therapy. Their expertise translates theoretical knowledge into effective practical application, bridging the gap between scientific principles and individualized patient care. A therapist’s proficiency in assessment, diagnosis, and treatment planning forms the cornerstone of successful rehabilitation. This expertise enables accurate identification of impairments, development of targeted interventions, and ongoing monitoring of progress. For instance, a skilled therapist can discern subtle biomechanical deviations contributing to a patient’s pain and implement corrective exercises to address the root cause. Without this level of skill, treatment might only address symptoms, leading to incomplete recovery and potential recurrence. The therapist’s ability to tailor interventions to individual needs, informed by a deep understanding of anatomy, physiology, and pathology, distinguishes effective from mediocre care. This proficiency ensures patients receive the precise interventions necessary to maximize their functional potential.
The practical significance of skilled therapists extends beyond technical proficiency. Effective communication, empathy, and the ability to motivate patients contribute significantly to successful outcomes. A therapist who fosters a positive therapeutic relationship empowers patients to actively participate in their recovery. This collaborative approach enhances adherence to treatment plans and promotes long-term self-management. Consider a patient struggling with chronic pain; a skilled therapist provides not only targeted exercises but also emotional support and coping strategies, crucial for managing pain and improving overall quality of life. Furthermore, skilled therapists adapt their approach based on ongoing assessment and patient feedback. This dynamic process ensures the treatment plan remains relevant and effective throughout the rehabilitation journey, maximizing the likelihood of achieving optimal outcomes. The ability to adapt to individual responses and adjust treatment strategies accordingly distinguishes skilled therapists and optimizes patient progress.
In summary, the contribution of skilled therapists to achieving optimal outcomes in physical therapy is paramount. Their expertise, combined with effective communication and patient-centered care, forms the cornerstone of successful rehabilitation. While access to advanced technology and evidence-based protocols plays a crucial role, the human element, embodied by the skilled therapist, remains indispensable. Challenges such as therapist shortages and variations in skill levels underscore the importance of ongoing professional development and robust training programs. Ultimately, investing in the development and retention of skilled therapists represents an investment in optimal patient care and improved health outcomes. Addressing these challenges strengthens the foundation of the profession and ensures access to high-quality physical therapy services for all who require them.
4. Progressive exercises
Progressive exercises constitute a cornerstone of achieving optimal physical function within a rehabilitation framework. These exercises, characterized by a gradual increase in intensity, complexity, or duration, play a vital role in restoring strength, mobility, and overall functional capacity. The progressive nature of these interventions allows the body to adapt and strengthen gradually, minimizing the risk of re-injury and maximizing long-term gains. Consider a patient recovering from a rotator cuff tear; initial exercises might focus on passive range of motion, progressing to active-assisted, and eventually, strengthening exercises with resistance bands. This gradual progression allows the healing tissues to adapt to increasing loads, optimizing recovery and preventing setbacks. Without this progressive approach, the patient risks re-injury or chronic pain, hindering the achievement of optimal physical function.
The practical significance of progressive exercises stems from their ability to target specific impairments and progressively challenge the body’s systems. This targeted approach facilitates efficient and effective rehabilitation, promoting a faster return to normal activities. For instance, a runner recovering from an ankle sprain might begin with balance exercises on a stable surface, progressing to unstable surfaces, and eventually plyometric exercises to restore agility and power. This systematic progression systematically rebuilds the ankle’s stability and prepares it for the demands of running. Furthermore, progressive exercises promote long-term musculoskeletal health by enhancing strength, flexibility, and endurance. This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of future injuries and contributes to overall physical well-being. Consider an individual with chronic low back pain; a progressive core strengthening program not only alleviates current pain but also builds resilience, minimizing the risk of recurrence and improving long-term functional capacity.
In summary, the integration of progressive exercises is essential for optimal physical therapy outcomes. This methodical approach, rooted in sound physiological principles, facilitates safe and effective rehabilitation, promotes long-term musculoskeletal health, and maximizes the likelihood of achieving optimal physical function. Challenges such as accurately assessing individual starting points and adjusting exercise progression based on patient response highlight the need for skilled therapists and ongoing monitoring. However, the benefits of incorporating progressive exercises into rehabilitation programs are undeniable, contributing to improved patient outcomes, enhanced functional capacity, and sustained physical well-being. Overcoming these challenges reinforces the commitment to providing high-quality, patient-centered care and optimizing the potential for long-term physical health.
5. Pain management strategies
Effective pain management constitutes a critical component of achieving optimal physical therapy outcomes. Uncontrolled pain hinders progress by limiting participation in therapeutic exercises and interfering with functional recovery. Addressing pain effectively creates a conducive environment for healing and restoration of physical function. A comprehensive approach to pain management encompasses various strategies tailored to individual needs and the underlying cause of pain. For instance, a patient experiencing acute pain from a recent injury may benefit from modalities like ice, compression, and elevation, while chronic pain may necessitate a multidisciplinary approach incorporating medication, manual therapy, and psychological support. This multifaceted approach underscores the interconnectedness of physical and psychological well-being in optimizing recovery and achieving optimal outcomes.
The integration of pain management strategies into physical therapy programs yields several practical benefits. Reduced pain levels enable patients to engage more fully in therapeutic exercises, maximizing the effectiveness of interventions and accelerating recovery. This active participation strengthens muscles, improves mobility, and promotes functional restoration. Moreover, effective pain management improves patients’ overall quality of life by reducing discomfort and enhancing physical function. Consider a patient with chronic back pain limiting daily activities; successful pain management enables participation in previously avoided activities, improving independence and overall well-being. Furthermore, addressing pain proactively reduces the risk of developing chronic pain syndromes, which can have debilitating long-term consequences. This proactive approach emphasizes the importance of early and effective pain management in optimizing long-term health outcomes.
In conclusion, the importance of incorporating pain management strategies into optimal physical therapy practice cannot be overstated. Effective pain control facilitates active participation in rehabilitation, improves quality of life, and reduces the risk of developing chronic pain. Challenges such as accurately assessing pain levels, individual responses to different modalities, and access to appropriate pain management resources underscore the need for ongoing assessment, individualized treatment plans, and interdisciplinary collaboration. Addressing these challenges optimizes patient outcomes and reinforces the commitment to providing comprehensive and patient-centered care. The integration of pain management strategies remains crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of physical therapy interventions and achieving optimal physical function and overall well-being.
6. Functional Restoration
Functional restoration represents a core objective within best-practice physical therapy. It emphasizes regaining the ability to perform essential daily tasks and participate fully in life activities. This outcome-oriented approach moves beyond simply alleviating symptoms, focusing on restoring practical function and improving overall quality of life. Understanding the components of functional restoration clarifies its pivotal role in achieving optimal physical well-being.
- Task-Specific Training:
This involves practicing specific movements or activities relevant to a patient’s daily life or occupational demands. For example, a carpenter recovering from a shoulder injury might practice hammering or sawing motions under the guidance of a therapist. This tailored approach ensures the rehabilitation program directly addresses the functional demands placed on the individual, maximizing the likelihood of a successful return to work or other essential activities. The focus on task-specific training aligns directly with the overarching goal of functional restoration.
- Adaptation and Compensation:
When full restoration of pre-injury function is not feasible, adaptation and compensatory strategies become crucial. This might involve modifying activities, using assistive devices, or adopting alternative movement patterns to accomplish tasks. For example, an individual with persistent knee pain might learn modified lifting techniques or use a reacher to avoid excessive bending. These strategies empower individuals to maintain independence and participate in meaningful activities despite limitations, reflecting the core principle of maximizing functional capacity.
- Graded Exposure:
This involves gradually increasing the demands placed on the body during functional activities. It allows for safe and controlled progression, promoting adaptation and minimizing the risk of re-injury. For instance, an athlete recovering from a hamstring strain might start with walking, progress to jogging, and eventually return to sprinting, with each stage carefully monitored and adjusted based on their response. This controlled progression mirrors the principles of progressive exercises, further emphasizing the interconnectedness of various rehabilitation components.
- Objective Measurement:
Utilizing standardized assessments and outcome measures provides objective data to track progress and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. These measures might include range of motion, strength testing, functional questionnaires, or performance-based tests. Objective data allows therapists to monitor progress, modify treatment plans as needed, and demonstrate the tangible benefits of rehabilitation. This data-driven approach underscores the commitment to evidence-based practice and achieving optimal outcomes.
These facets of functional restoration work synergistically to optimize physical therapy outcomes. By focusing on practical, real-world applications and utilizing objective measurement, functional restoration ensures that rehabilitation efforts translate into meaningful improvements in patients’ lives. This focus aligns perfectly with the core principles of optimal physical therapy, emphasizing the importance of individualized treatment plans, evidence-based techniques, and skilled therapists in achieving lasting functional gains. Ultimately, functional restoration bridges the gap between therapeutic interventions and the ability to live a full and active life.
7. Long-Term Wellness
Long-term wellness represents the ultimate goal of optimus physical therapy, extending beyond immediate rehabilitation to encompass sustained physical health and well-being. It acknowledges that physical therapy is not merely a reactive process for addressing injuries but a proactive approach to cultivating lifelong health. Exploring the multifaceted connection between long-term wellness and optimus physical therapy reveals its profound implications for overall quality of life.
- Preventive Strategies:
Optimus physical therapy equips individuals with the knowledge and tools to prevent future injuries and manage chronic conditions. This proactive approach emphasizes ergonomic awareness, proper body mechanics, and individualized exercise programs designed to maintain strength, flexibility, and balance. For example, an individual with a history of back pain might learn specific exercises and postural adjustments to minimize strain and prevent recurrence. These preventive strategies empower individuals to take control of their physical health and reduce the likelihood of future impairments. This aligns directly with the long-term wellness objective of minimizing health risks and promoting sustained physical well-being.
- Self-Management:
Optimus physical therapy empowers individuals to become active participants in their own health management. Patients gain a deeper understanding of their bodies, including how to recognize warning signs, manage pain, and adapt activities to minimize strain. For instance, an individual recovering from a knee injury learns self-mobilization techniques, stretching exercises, and activity modification strategies to manage discomfort and prevent re-injury. This emphasis on self-management equips individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to maintain long-term physical health and minimize reliance on healthcare interventions. It fosters independence and promotes a proactive approach to health management, essential components of long-term wellness.
- Lifestyle Integration:
Optimus physical therapy promotes the integration of healthy habits into daily routines. This holistic approach emphasizes the importance of regular exercise, proper nutrition, stress management, and adequate sleep in supporting long-term physical health. For example, an individual recovering from a stroke might incorporate regular walking, a balanced diet, and stress reduction techniques into their daily routine to optimize recovery and promote overall well-being. This integration of healthy practices fosters sustainable lifestyle changes, contributing to long-term wellness beyond the immediate rehabilitation phase. It establishes a foundation for ongoing health maintenance and reduces the risk of future health issues.
- Ongoing Optimization:
Long-term wellness within the context of optimus physical therapy recognizes the dynamic nature of health and the need for ongoing adaptation. It emphasizes regular check-ups, periodic reassessments, and ongoing communication with healthcare providers to monitor progress, address emerging issues, and adjust strategies as needed. For instance, an athlete might consult with a physical therapist periodically to address training-related imbalances, optimize performance, and prevent injuries. This proactive and ongoing approach ensures that individuals continue to receive the support and guidance necessary to maintain optimal physical function and adapt to changing needs throughout their lives. This adaptability is crucial for preserving long-term wellness and maximizing physical potential across the lifespan.
These interconnected facets of long-term wellness underscore the holistic and proactive nature of optimus physical therapy. By shifting the focus from solely addressing immediate impairments to cultivating lifelong health, optimus physical therapy empowers individuals to achieve and maintain optimal physical function, minimizing the risk of future health issues and maximizing overall well-being. This integrated approach recognizes the intricate interplay between physical health, lifestyle choices, and proactive self-management, ultimately contributing to a higher quality of life and sustained physical well-being across the lifespan.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding achieving optimal physical function through specialized rehabilitation.
Question 1: What distinguishes optimal physical therapy from standard rehabilitation programs?
Optimal physical therapy emphasizes individualized treatment plans tailored to specific needs and goals, utilizing evidence-based techniques and skilled therapists to maximize functional outcomes and long-term wellness. Standard programs may adhere to more generalized protocols, potentially overlooking individual nuances crucial for optimal recovery.
Question 2: How can one determine the most suitable physical therapy approach for a specific condition?
Consulting with a qualified healthcare professional specializing in musculoskeletal conditions is essential. A thorough assessment considering individual medical history, current functional limitations, and personal goals informs the selection of the most appropriate treatment approach.
Question 3: How frequently are physical therapy sessions typically required?
Treatment frequency depends on individual needs and the nature of the condition. While some individuals may benefit from daily sessions, others may require less frequent visits. A qualified therapist develops a personalized treatment plan outlining the recommended frequency and duration of sessions to optimize outcomes.
Question 4: What role does patient commitment play in achieving optimal physical therapy outcomes?
Active patient participation is crucial. Adherence to prescribed exercises, consistent attendance at therapy sessions, and open communication with the therapist contribute significantly to successful outcomes and long-term physical well-being.
Question 5: How long does it typically take to achieve optimal physical function through rehabilitation?
Recovery timelines vary based on individual factors such as the nature and severity of the condition, overall health status, and adherence to the treatment plan. Realistic expectations, established in consultation with the therapist, facilitate a positive and productive rehabilitation experience.
Question 6: What strategies can one employ to maintain optimal physical function following the completion of a formal rehabilitation program?
Integrating healthy habits into daily life, including regular exercise, proper nutrition, and ergonomic awareness, contributes to sustained physical well-being and minimizes the risk of future impairments. Ongoing communication with healthcare providers facilitates proactive management of any emerging issues.
Understanding the nuances of optimal physical therapy empowers informed decision-making and fosters a proactive approach to achieving and maintaining optimal physical well-being.
For further information or to schedule a consultation, please proceed to the contact section.
Conclusion
This exploration of best-practice rehabilitative care has highlighted the multifaceted nature of achieving and maintaining optimal physical function. Emphasis has been placed on the importance of individualized treatment plans, evidence-based techniques, and the expertise of skilled therapists in maximizing patient outcomes. Furthermore, the significance of progressive exercises, effective pain management strategies, and a focus on functional restoration has been underscored as crucial components of comprehensive rehabilitation. Finally, the integration of long-term wellness principles has been presented as essential for sustained physical health and well-being beyond the immediate rehabilitation phase.
Optimal physical function represents an achievable goal for individuals seeking to improve their physical health and overall quality of life. Embracing a proactive approach to rehabilitation, informed by evidence-based practices and delivered by skilled professionals, empowers individuals to reach their full physical potential. The pursuit of optimal physical function signifies a commitment to lifelong well-being and represents an investment in a healthier, more fulfilling future.