The required medical evaluation for student-athletes participating in college athletics under the National Collegiate Athletic Association’s jurisdiction ensures their readiness for the demands of competitive sport. This process typically involves a comprehensive review of medical history, a physical examination, and may include additional assessments depending on the specific sport and institutional requirements. A standardized document facilitates this evaluation, capturing essential medical information and clearances.
This pre-participation assessment is critical for protecting student-athlete well-being. It allows medical professionals to identify pre-existing conditions that could pose a risk during athletic activity, enabling appropriate management strategies. Early detection and intervention can prevent serious injuries and long-term health complications. Furthermore, the standardized nature of these evaluations promotes consistency across institutions and helps ensure equitable access to safe participation opportunities. Historically, these requirements have evolved to reflect advancements in sports medicine and a growing understanding of the unique health and safety considerations relevant to collegiate athletes.
The following sections delve deeper into the specific components of the evaluation process, outlining the necessary steps for compliance, and exploring related topics such as institutional policies, medical disqualification waivers, and the role of healthcare providers in supporting student-athlete health and safety.
Successfully completing the required medical evaluation is crucial for participation in NCAA athletics. The following tips provide guidance for navigating this process efficiently and effectively.
Tip 1: Schedule an Appointment Early: Securing an appointment with a qualified medical professional well in advance of pre-season activities is essential. This allows ample time to complete all necessary components of the evaluation, including any follow-up testing or specialist referrals.
Tip 2: Gather Relevant Medical History: Compiling a comprehensive medical history, including prior injuries, illnesses, and current medications, streamlines the evaluation process. Providing accurate and detailed information enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding participation clearance.
Tip 3: Be Prepared for a Physical Examination: The physical examination will assess overall health and fitness for participation. Understanding the scope of this examination can help alleviate any pre-appointment anxieties.
Tip 4: Disclose All Medical Information: Full disclosure of all medical conditions, even seemingly minor ones, is paramount. Withholding information can have serious consequences for both individual health and eligibility.
Tip 5: Follow Up on Recommendations: If further testing or specialist consultations are recommended, adhering to these instructions promptly ensures timely completion of the evaluation process.
Tip 6: Maintain Open Communication: Open communication with coaches, athletic trainers, and medical staff facilitates a collaborative approach to managing any identified health concerns.
Tip 7: Understand Institutional Policies: Familiarizing oneself with specific institutional policies regarding medical evaluations ensures compliance and avoids potential delays in clearance.
Following these tips promotes a smooth and efficient evaluation experience, allowing student-athletes to focus on their athletic pursuits while ensuring their health and well-being.
By prioritizing these recommendations, prospective student-athletes can contribute to a safe and successful collegiate athletic career.
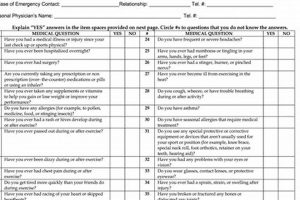
1. Medical History
A comprehensive medical history forms the cornerstone of the NCAA sports physical form, providing crucial insights into an athlete’s health status and informing decisions regarding participation eligibility and safety. Accurate and detailed medical history disclosure is essential for effective pre-participation evaluation.
- Previous Injuries:
Documentation of prior injuries, including concussions, fractures, and sprains, is critical. For example, a history of multiple ankle sprains might indicate a predisposition to future injuries, requiring preventative measures or specialized training regimens. This information allows medical professionals to assess potential risks associated with continued athletic participation.
- Pre-existing Conditions:
Disclosure of pre-existing medical conditions, such as asthma, diabetes, or cardiac conditions, enables appropriate management strategies and facilitates individualized care. For instance, an athlete with asthma might require an emergency action plan and readily available medication during practices and competitions. Understanding these conditions is paramount for safeguarding athlete well-being.
- Prior Surgeries and Hospitalizations:
Information regarding past surgeries and hospitalizations provides valuable context for interpreting current health status. A history of knee surgery, for example, might necessitate additional assessments to ensure complete recovery and functional capacity. This knowledge aids in preventing re-injury and promoting optimal recovery.
- Current Medications and Allergies:
Disclosing current medications and allergies is crucial for avoiding potential adverse reactions or complications. An athlete with a known drug allergy requires careful consideration of prescribed medications and emergency protocols. This information ensures safe and effective medical management.
These facets of medical history, when thoroughly documented and analyzed, provide a holistic view of an athlete’s health trajectory, enabling medical professionals to make informed decisions regarding participation clearance and individualized care within the context of the NCAA sports physical form. This comprehensive approach is vital for promoting athlete safety and well-being throughout their collegiate athletic career.
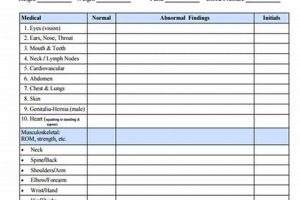
2. Physical Examination
The physical examination constitutes a critical component of the NCAA sports physical form, providing a real-time assessment of an athlete’s current physical condition and informing decisions regarding participation safety and eligibility. This hands-on evaluation complements the information gathered through the medical history, offering a comprehensive overview of the athlete’s health status.
- Cardiovascular Assessment
Evaluation of cardiovascular health, including blood pressure, heart rate, and auscultation for murmurs, is essential for identifying potential risks associated with strenuous athletic activity. For example, detection of an irregular heartbeat might necessitate further cardiological evaluation, including an electrocardiogram (ECG) to rule out underlying conditions. This assessment safeguards athletes from potential cardiac events during competition.
- Musculoskeletal Evaluation
Assessment of musculoskeletal function, including range of motion, joint stability, and palpation for tenderness or abnormalities, is crucial for identifying potential areas of weakness or pre-existing injuries. For instance, limited range of motion in the shoulder joint might suggest a rotator cuff injury, requiring targeted rehabilitation or activity modification. This evaluation helps prevent exacerbation of existing injuries and promotes optimal biomechanics.
- Neurological Screening
Basic neurological screening, including reflexes, balance, and coordination assessments, helps detect any underlying neurological deficits that could impact athletic performance or pose a safety risk. An athlete exhibiting impaired balance might require further neurological evaluation to identify the underlying cause. This screening safeguards athletes with potential neurological conditions.
- General Physical Assessment
A general physical assessment, including height, weight, and body mass index (BMI) measurements, provides baseline data for monitoring an athlete’s overall health and fitness. Significant deviations from expected values might warrant further investigation to address potential underlying health concerns. This assessment provides a comprehensive overview of an athlete’s physical presentation.
These facets of the physical examination, when integrated with the information gleaned from the medical history, paint a comprehensive picture of an athlete’s health status within the context of the NCAA sports physical form. This holistic approach is fundamental to promoting athlete safety and well-being, ensuring informed decisions regarding participation eligibility and facilitating individualized care strategies throughout their collegiate athletic career.
3. Clearance Status
Clearance status represents the culmination of the NCAA sports physical form process, signifying an athlete’s medical eligibility to participate in collegiate athletics. This determination, made by qualified medical professionals, hinges upon a comprehensive review of the athlete’s medical history, physical examination findings, and any additional diagnostic testing deemed necessary. Clearance status directly impacts an athlete’s ability to train, compete, and receive athletic-related medical care.
Several scenarios illustrate the critical role of clearance status. An athlete with a previously undiagnosed heart condition, identified during the evaluation process, might receive clearance contingent upon further specialist evaluation and treatment. Similarly, an athlete recovering from a significant injury might receive conditional clearance, allowing participation in limited activities while undergoing rehabilitation. Conversely, an athlete with a condition posing an unacceptable risk to themselves or others might be denied clearance, safeguarding their well-being and maintaining a safe competitive environment. These examples underscore the practical significance of clearance status as a critical component of the sports physical form. Without proper clearance, participation in NCAA-sanctioned activities is strictly prohibited.
Understanding the implications of clearance status is crucial for all stakeholders involved in collegiate athletics. Coaches rely on clearance status to make informed decisions regarding team composition and athlete participation. Athletic trainers utilize clearance information to develop appropriate training and rehabilitation programs. Athletes themselves benefit from understanding their clearance status, enabling them to make informed decisions about their health and athletic pursuits. The timely and accurate determination of clearance status ensures the integrity of the NCAA sports physical form process, promoting athlete safety and maintaining a fair and equitable competitive landscape.
4. Required Documentation
Required documentation forms the backbone of the NCAA sports physical form process, providing verifiable evidence of an athlete’s medical history, current health status, and compliance with NCAA regulations. Meticulous record-keeping is essential for ensuring eligibility, facilitating appropriate medical care, and protecting athlete well-being. Complete and accurate documentation supports informed decision-making by medical professionals and athletic administrators.
- Completed Sports Physical Form:
The cornerstone of required documentation is the fully completed and signed sports physical form itself. This document serves as a centralized repository of the athlete’s medical information, including medical history, physical examination findings, and clearance status. A missing signature or incomplete section can render the form invalid, delaying participation clearance.
- Supporting Medical Records:
In certain cases, supporting medical records, such as immunization records, specialist evaluations, or imaging reports, might be required to provide a more comprehensive understanding of an athlete’s medical history. For example, an athlete with a history of cardiac issues might need to submit an electrocardiogram (ECG) report. These supplementary documents provide crucial context for medical professionals evaluating the athlete’s eligibility.
- Consent and Release Forms:
Signed consent and release forms authorize medical professionals to access and share relevant medical information, ensuring appropriate communication and coordination of care. These forms also protect the privacy of athlete medical information, adhering to relevant regulations such as HIPAA. Without proper consent, access to critical medical information might be restricted, hindering effective medical management.
- Institutional Requirements:
Individual institutions may have additional documentation requirements specific to their policies and procedures. These might include proof of insurance, emergency contact information, or waivers for specific medical conditions. Adherence to institutional requirements ensures seamless integration into the athletic program and facilitates timely access to necessary resources and support.
These documentation components, when compiled meticulously, form a comprehensive record of an athlete’s medical profile within the context of the NCAA sports physical form. This rigorous documentation process ensures compliance with NCAA regulations, safeguards athlete well-being, and facilitates informed decision-making regarding participation eligibility and appropriate medical care. Maintaining accurate and up-to-date documentation is a shared responsibility among athletes, medical professionals, and athletic administrators, reflecting a commitment to upholding the highest standards of athlete health and safety within the collegiate athletic environment.
5. Institutional Policies
Institutional policies play a crucial role in the implementation and interpretation of NCAA sports physical form requirements. While the NCAA provides overarching guidelines, individual institutions retain autonomy in establishing specific procedures and protocols related to pre-participation medical evaluations. This interplay between national guidelines and institutional policies ensures adherence to core health and safety principles while accommodating the unique circumstances of each institution. For instance, an institution located in a region with a high prevalence of a particular medical condition might implement additional screening measures beyond the minimum NCAA requirements. Similarly, institutions may adopt specific protocols for managing medical disqualification waivers or handling sensitive medical information. These institutional policies provide a framework for consistent and equitable application of the NCAA sports physical form requirements across the athletic department.
Understanding the nuances of institutional policies is essential for all stakeholders. Coaches must be aware of their institution’s specific procedures for submitting completed physical forms and managing athlete medical information. Athletic trainers need to understand institutional protocols for handling medical emergencies and communicating with team physicians. Athletes benefit from familiarity with institutional policies regarding medical disqualification waivers and access to medical care. For example, an athlete with a pre-existing condition needs to understand the institution’s process for obtaining necessary accommodations or waivers. Discrepancies between institutional policies and NCAA guidelines can create confusion and potential compliance issues, highlighting the practical significance of this understanding.
Effective management of the sports physical form process requires clear communication and collaboration between institutional stakeholders. Regularly reviewing and updating institutional policies ensures alignment with evolving NCAA guidelines and best practices in sports medicine. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of non-compliance, protects athlete well-being, and maintains the integrity of the collegiate athletic environment. Furthermore, transparent communication of institutional policies fosters a culture of shared responsibility for athlete health and safety. By recognizing the critical role of institutional policies, athletic departments can effectively navigate the complexities of the NCAA sports physical form process and create a supportive environment for student-athlete success.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the NCAA sports physical form, providing clarity on key aspects of the process.
Question 1: What is the purpose of the NCAA sports physical form?
The form ensures student-athlete readiness for collegiate athletics by assessing pre-existing conditions and current health status, mitigating health risks and promoting safe participation.
Question 2: Who is required to complete the NCAA sports physical form?
All prospective student-athletes wishing to participate in NCAA-sanctioned sports at the collegiate level are required to complete the form.
Question 3: Where can one obtain the NCAA sports physical form?
Typically, the form is available through the institution’s athletic department website or directly from the athletic training staff. It’s essential to utilize the official form provided by the institution.
Question 4: What if a medical condition is discovered during the evaluation process?
Discovered medical conditions are addressed by qualified medical professionals. Depending on the nature of the condition, further evaluation, treatment, or activity modifications might be recommended to ensure safe participation.
Question 5: What is a medical disqualification waiver, and when might it be necessary?
A medical disqualification waiver might be required for student-athletes with specific medical conditions that could pose a risk to themselves or others during athletic participation. The waiver process involves a thorough review by medical professionals and the NCAA to determine eligibility.
Question 6: How often is the NCAA sports physical form required?
The frequency varies by institution but typically involves an initial evaluation upon entering the athletic program, with periodic updates or re-evaluations as determined by institutional policy and NCAA guidelines.
Understanding these aspects of the NCAA sports physical form process ensures a smooth transition into collegiate athletics. Consulting with institutional athletic staff and medical professionals addresses individual circumstances effectively.
For further information, consult the NCAA website or contact the athletic department of the institution.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of collegiate athletics requires a comprehensive understanding of pre-participation medical evaluations. This exploration has highlighted the multifaceted nature of these assessments, emphasizing the critical interplay between medical history disclosure, thorough physical examinations, accurate documentation, and adherence to institutional policies. Each component contributes to a holistic evaluation of student-athlete health and safety, ensuring informed decisions regarding participation eligibility and appropriate medical care.
Prioritizing comprehensive pre-participation evaluations reflects a commitment to student-athlete well-being. These evaluations safeguard athletes from potential health risks, facilitate early intervention for identified medical conditions, and promote a safe and equitable competitive environment. Continued adherence to evolving best practices in sports medicine, coupled with open communication among stakeholders, ensures that these crucial processes remain effective in protecting the health and safety of collegiate athletes.