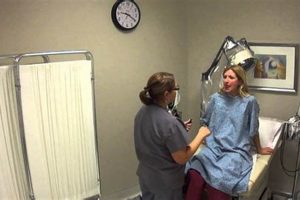
A periodic health evaluation for women often focuses on reproductive and gynecological health, including screenings for cervical cancer and sexually transmitted infections, as well as counseling on family planning and other women’s health concerns. A broader yearly health assessment encompasses a wider range of health aspects, including cardiovascular health, respiratory function, and other preventative screenings based on individual risk factors like age and family history. While the former may be a component of the latter, they are not synonymous and offer distinct scopes.
Regular health assessments offer crucial preventative care, enabling early detection and management of potential health issues. For women, specialized screenings can identify and address conditions specific to their biology and reproductive health. Comprehensive annual evaluations provide a holistic overview of overall wellness, facilitating timely interventions and promoting long-term health maintenance. This proactive approach has become a cornerstone of modern healthcare, contributing significantly to improved health outcomes and increased lifespans.
The following sections will delve deeper into the specific components of both types of examinations, highlighting their differences and respective benefits in greater detail. This exploration aims to provide clarity and empower individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Tips for Optimizing Healthcare
Proactive engagement with healthcare contributes significantly to overall well-being. The following tips offer guidance on maximizing the benefits of routine health assessments.
Tip 1: Schedule periodic gynecological check-ups. Regular visits with a gynecologist allow for preventative screenings, such as Pap smears and STI testing, which are vital for early detection and management of potential health issues.
Tip 2: Understand the scope of annual physical examinations. These comprehensive evaluations encompass a broad range of health factors beyond reproductive health, including cardiovascular and respiratory function. They provide a holistic overview of individual well-being.
Tip 3: Maintain open communication with healthcare providers. Clearly articulating health concerns and discussing family history enables providers to tailor examinations and screenings based on individual risk factors.
Tip 4: Recognize the distinct roles of each type of examination. Gynecological check-ups focus specifically on reproductive health, while annual physicals offer a broader assessment of overall wellness. Both contribute to preventative care and should be incorporated into routine healthcare.
Tip 5: Be aware of recommended screening guidelines. Consult with healthcare providers to determine the frequency and types of screenings appropriate for individual age, family history, and lifestyle.
Tip 6: Prioritize preventative care. Regular health assessments empower individuals to take proactive steps towards maintaining long-term health and well-being.
By incorporating these tips into healthcare routines, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their health status and work collaboratively with providers to optimize well-being.
The following section concludes this discussion by summarizing key takeaways and reinforcing the importance of regular health assessments.
1. Scope
Understanding the scope of medical examinations is fundamental to differentiating between a well-woman exam and an annual physical. Scope defines the breadth and limits of each examination, influencing the areas assessed and the information gathered. Clarifying these parameters provides a framework for informed decision-making regarding healthcare.
- Gynecological Health
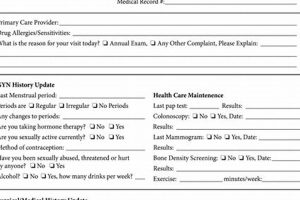
Well-woman exams prioritize reproductive and gynecological health. This includes pelvic exams, Pap smears for cervical cancer screening, and STI testing. These components fall within the specific scope of a well-woman exam, reflecting its core focus on female reproductive well-being. An annual physical may address gynecological concerns, but typically not with the same depth.
- General Physical Health
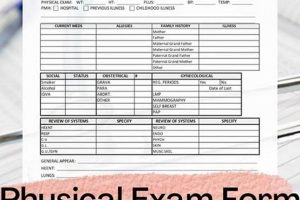
Annual physicals encompass a broader scope, evaluating overall physical health. This may include cardiovascular health assessments (blood pressure, cholesterol), respiratory function tests, and general physical examinations. While a well-woman exam might briefly touch upon some of these areas, they are not its primary focus. The broader scope of the annual physical positions it as a comprehensive health assessment.
- Preventative Screenings
Both exam types incorporate preventative screenings, but the specific screenings within their scope differ. Well-woman exams often include screenings related to reproductive health (e.g., mammograms), while annual physicals may include screenings based on age and risk factors (e.g., colonoscopies). Scope dictates the types of preventative measures offered in each context.
- Counseling and Education
The scope of a well-woman exam often includes counseling on family planning, contraception, and other women’s health topics. Annual physicals may also provide health counseling, but with a broader focus on overall wellness and disease prevention. The specific counseling provided reflects the respective scopes of each examination.
The distinct scopes of well-woman exams and annual physicals underscore their complementary roles in women’s healthcare. While the well-woman exam provides focused attention on reproductive and gynecological health, the annual physical offers a broader assessment of overall well-being. Recognizing these differences empowers individuals to make informed choices about their healthcare needs and ensures comprehensive preventative care.
2. Focus
The distinct focuses of well-woman exams and annual physicals contribute significantly to their differing roles in healthcare. A well-woman exam centers primarily on reproductive and gynecological health. This encompasses areas such as cervical health (Pap smears, HPV testing), breast health (clinical breast exams, mammogram referrals), and screening and treatment for sexually transmitted infections. Family planning, contraceptive counseling, and discussions regarding menopausal health also fall within this focused approach. Conversely, an annual physical maintains a broader focus encompassing overall health and wellness. This includes assessments of cardiovascular health (blood pressure, cholesterol levels), respiratory function, and other preventative screenings based on individual risk factors such as age, family history, and lifestyle. While an annual physical may briefly touch upon aspects of reproductive health, it does not delve into the specific detail characteristic of a well-woman exam. For instance, a Pap smear would typically be performed during a well-woman exam, not a standard annual physical.
This difference in focus stems from the specialized nature of each examination. The well-woman exam provides targeted care addressing the unique health concerns of women, whereas the annual physical offers a more holistic but less specialized evaluation. Understanding this distinction enables appropriate utilization of each type of examination. A woman experiencing irregular menstrual cycles would benefit from the focused attention of a well-woman exam, while someone concerned about potential cardiovascular issues would find a broader annual physical more appropriate. Utilizing each examination according to its focus maximizes the effectiveness of preventative care and ensures that specific health concerns are adequately addressed.
In summary, the distinct focuses of well-woman exams and annual physicals play a critical role in their complementary contributions to womens healthcare. The specialized focus of the well-woman exam addresses specific reproductive and gynecological health concerns, while the broader focus of the annual physical provides a comprehensive overview of overall wellness. Recognizing this distinction allows individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare needs and optimize preventative care strategies.
3. Preventative Care
Preventative care forms a cornerstone of both well-woman exams and annual physicals, although the specific preventative measures differ based on the scope of each examination. Well-woman exams prioritize preventative care related to reproductive and gynecological health. This includes screenings for cervical cancer (Pap smears, HPV tests), sexually transmitted infections (STI testing), and breast cancer (clinical breast exams, mammogram referrals). These screenings aim to detect potential issues early, improving treatment outcomes and overall prognosis. Annual physicals, on the other hand, incorporate broader preventative care measures. These might include screenings for cardiovascular disease (blood pressure, cholesterol checks), colorectal cancer (colonoscopies), and other conditions based on individual risk factors like age and family history. Vaccinations, such as influenza and pneumonia, are also often addressed during annual physicals. The inclusion of such preventative measures underscores the role of these examinations in maintaining overall health and well-being.
The practical significance of understanding the role of preventative care in both types of examinations is substantial. For instance, regular Pap smears during well-woman exams have significantly reduced cervical cancer mortality rates. Similarly, early detection of high blood pressure during annual physicals can lead to timely interventions, preventing or mitigating the development of cardiovascular complications. These examples demonstrate the tangible impact of preventative care on individual health outcomes. While both examination types contribute to preventative care, their distinct focuses ensure comprehensive coverage of different health aspects. Attending both well-woman exams and annual physicals maximizes the benefits of preventative care, fostering early detection, timely interventions, and improved long-term health outcomes.
In conclusion, preventative care represents a crucial component of both well-woman exams and annual physicals. While the specific preventative measures implemented differ based on the focus of each examination, both contribute significantly to early detection and management of potential health issues. Understanding the distinct yet complementary roles of these examinations in preventative care empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare and actively participate in maintaining long-term well-being. The practical impact of this understanding is evident in the improved health outcomes observed through consistent engagement with preventative care strategies.
4. Frequency
Frequency of medical examinations plays a crucial role in preventative healthcare, and understanding the recommended frequency for both well-woman exams and annual physicals is essential for optimizing health outcomes. While both contribute to preventative care, their recommended frequencies may differ based on individual circumstances and risk factors. Exploring the frequency of these examinations provides valuable insights into effective healthcare management.
- Well-Woman Exam Frequency
The recommended frequency of well-woman exams can vary based on age, sexual activity, and individual risk factors. Generally, annual visits are recommended for most women, particularly those of reproductive age. However, specific circumstances may necessitate more frequent visits. For example, women with a history of abnormal Pap smears or other gynecological concerns may require more frequent monitoring. Adhering to recommended frequencies facilitates early detection and management of potential reproductive health issues.
- Annual Physical Exam Frequency
Annual physical exams are generally recommended for adults regardless of gender. These yearly check-ups provide comprehensive assessments of overall health, enabling early detection of potential health concerns. While annual frequency is typical, individual circumstances, such as chronic health conditions or specific risk factors, may necessitate more frequent visits. Consistent adherence to the recommended frequency supports preventative care and facilitates timely interventions.
- Factors Influencing Frequency
Several factors influence the recommended frequency of both types of examinations. Age plays a significant role, as certain health risks increase with age. Family history of specific conditions can also influence screening frequency. Lifestyle factors, such as smoking and diet, may necessitate more frequent monitoring for certain health concerns. Individual medical history and pre-existing conditions also contribute to determining the appropriate frequency of examinations. Understanding these factors empowers individuals to engage in informed discussions with healthcare providers regarding personalized screening schedules.
- Importance of Regularity
Regularity in health examinations, regardless of specific frequency recommendations, is crucial for effective preventative care. Consistent examinations allow healthcare providers to monitor health trends, identify potential issues early, and implement timely interventions. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of complications and promotes long-term well-being. Maintaining regular examinations, aligned with individual needs and recommendations, forms a cornerstone of preventative healthcare and contributes significantly to improved health outcomes.
The frequency of well-woman exams and annual physicals is a critical aspect of preventative healthcare. While annual frequencies are generally recommended for both, individual needs and risk factors can influence these recommendations. Understanding these factors and maintaining consistent examination schedules, in consultation with healthcare providers, optimizes the benefits of preventative care and promotes long-term health and well-being. The distinct frequencies associated with each examination type reflect their specialized focuses and contribute to comprehensive healthcare management.
5. Target Audience
Target audience considerations are paramount when differentiating between well-woman exams and annual physicals. Well-woman exams specifically target women, addressing their unique reproductive and gynecological health needs. This specialized focus includes screenings for cervical cancer (Pap smears), sexually transmitted infections, and other conditions specific to female reproductive health. Annual physicals, conversely, target a broader audience encompassing adults of all genders. While these examinations also contribute to preventative care, their scope extends beyond reproductive health, encompassing cardiovascular health, respiratory function, and other general health assessments. Understanding the distinct target audiences clarifies the differing purposes and scopes of these examinations.
The practical implications of this distinction are significant. A young woman seeking contraceptive counseling would find a well-woman exam more appropriate, whereas an older adult concerned about potential cardiovascular issues would benefit from a broader annual physical. Consider a woman experiencing irregular menstrual cycles; a well-woman exam, with its focus on reproductive health, provides the appropriate platform for addressing this concern. Conversely, an individual with a family history of heart disease would benefit from the comprehensive cardiovascular assessment offered within an annual physical. These examples highlight the practical importance of considering the target audience when selecting the appropriate type of examination.
In conclusion, target audience considerations are fundamental to distinguishing between well-woman exams and annual physicals. Well-woman exams address the specific health needs of women, particularly regarding reproductive and gynecological health, while annual physicals offer broader health assessments applicable to adults of all genders. This distinction guides individuals toward the most appropriate examination type based on their specific needs and demographics. Effective utilization of these examinations, guided by target audience considerations, optimizes preventative care strategies and promotes informed healthcare decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the distinction between well-woman exams and annual physicals, providing clarity on their respective roles in preventative healthcare.
Question 1: What is the primary difference between a well-woman exam and an annual physical?
A well-woman exam focuses specifically on reproductive and gynecological health, while an annual physical encompasses a broader range of health aspects, including cardiovascular, respiratory, and other preventative screenings.
Question 2: Does a well-woman exam replace the need for an annual physical?
No. These examinations serve distinct yet complementary purposes. While a well-woman exam addresses specific women’s health needs, an annual physical provides a more comprehensive overview of overall health and wellness.
Question 3: What specific services are typically included in a well-woman exam?
Services typically include a pelvic exam, Pap smear, clinical breast exam, and screenings for sexually transmitted infections. Counseling on family planning and other reproductive health topics may also be provided.
Question 4: What is the recommended frequency for each type of examination?
Annual visits are generally recommended for both well-woman exams and annual physicals. However, individual circumstances and risk factors may influence specific frequency recommendations.
Question 5: If one is experiencing specific gynecological concerns, which examination is more appropriate?
A well-woman exam is the more appropriate choice for addressing specific gynecological concerns, given its specialized focus on reproductive health.
Question 6: How do these examinations contribute to preventative healthcare?
Both examinations provide crucial preventative screenings and counseling, facilitating early detection and management of potential health issues, thus contributing significantly to long-term well-being.
Understanding the distinct yet complementary roles of well-woman exams and annual physicals empowers informed decision-making and proactive healthcare management.
The subsequent section offers concluding thoughts on the importance of incorporating both types of examinations into routine healthcare practices.
Conclusion
Distinguishing between a well-woman exam and an annual physical remains crucial for comprehensive healthcare. While both contribute significantly to preventative care and overall well-being, they offer distinct focuses and scopes. Well-woman exams prioritize reproductive and gynecological health, encompassing screenings for cervical cancer, sexually transmitted infections, and other women-specific concerns. Annual physicals, conversely, provide a broader assessment of overall health, including cardiovascular health, respiratory function, and other preventative screenings based on individual risk factors. Understanding these differences allows for informed decision-making regarding healthcare utilization and ensures that specific health needs are adequately addressed.
Prioritizing both well-woman exams and annual physicals, according to recommended frequencies and individual needs, represents a proactive approach to healthcare management. This combined approach ensures comprehensive preventative care, maximizing opportunities for early detection and intervention. The long-term benefits of this proactive strategy extend beyond immediate health outcomes, contributing to enhanced quality of life and overall well-being. Continued education and open communication with healthcare providers further empower informed decision-making and facilitate optimal health outcomes.