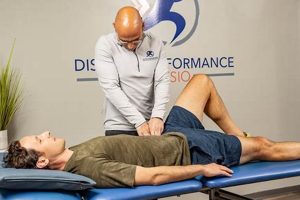
Rehabilitative treatment provided in a municipality known for its historical connection to the hat-making industry offers residents access to specialized care for restoring physical function and mobility. For example, such treatment can address injuries, chronic conditions, or post-surgical recovery needs.
Access to quality rehabilitative services is crucial for community well-being. Restoring physical function improves quality of life, reduces pain, and promotes independence. Understanding the historical context of a region often provides valuable insights into the development of its healthcare infrastructure and the specific needs of its population.
The following sections will explore specific treatment modalities, the role of qualified practitioners, and the impact of community-based rehabilitation programs within this unique setting.
Tips for Optimizing Physical Well-being
These practical strategies can support individuals in managing pain, improving mobility, and enhancing overall physical function. Consistent application of these principles contributes significantly to long-term health and wellness.
Tip 1: Maintain Proper Posture: Correct posture aligns the body, reducing strain on joints and muscles. Whether standing, sitting, or lifting, mindful attention to posture minimizes the risk of injury and promotes efficient movement.
Tip 2: Incorporate Regular Exercise: Engaging in appropriate physical activity strengthens muscles, improves flexibility, and enhances cardiovascular health. A balanced exercise program tailored to individual needs is essential for maintaining physical well-being.
Tip 3: Prioritize Proper Lifting Techniques: Lifting heavy objects incorrectly can strain the back and other vulnerable areas. Adhering to proper lifting techniques protects against injury and promotes safe movement.
Tip 4: Listen to Your Body: Recognizing pain signals and respecting physical limitations is crucial. Pushing through pain can exacerbate existing conditions and lead to further injury. Rest and recovery are integral components of a healthy lifestyle.
Tip 5: Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting qualified healthcare practitioners provides personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to individual needs. Professional guidance ensures appropriate care and facilitates optimal recovery.
Tip 6: Manage Stress Effectively: Stress can manifest physically, exacerbating pain and tension. Implementing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness or relaxation exercises, supports overall well-being.
Tip 7: Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight places additional strain on joints and muscles. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the body and improves overall function.
Tip 8: Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports joint lubrication and overall bodily function. Consistent fluid intake is essential for maintaining physical health.
By incorporating these tips into daily routines, individuals can proactively manage their physical well-being and optimize their quality of life. Consistent effort and attention to these principles contribute significantly to long-term health and wellness.
This foundation of practical strategies leads to a discussion on the importance of seeking professional care and accessing specialized treatment within a community setting.
1. Specialized Treatment
Within the context of rehabilitation services provided in a location historically linked to the hat-making industry, specialized treatment takes on particular significance. This approach recognizes that effective care must address the unique physical demands and potential health risks associated with specific occupations and regional history. Understanding these connections is fundamental to providing comprehensive and relevant rehabilitation programs.
- Ergonomic Assessments and Interventions
Ergonomic assessments tailored to the physical demands of historical and contemporary occupations within the community are crucial. These assessments may identify repetitive strain injuries related to hat-making or other local industries, informing targeted interventions. For example, a therapist might develop exercises to address specific muscle imbalances resulting from repetitive hand movements or prolonged standing, common in hat manufacturing. This specialization ensures interventions directly address the community’s unique needs.
- Environmental Adaptations
Specialized treatment considers environmental factors that may impact physical health. In a “hat city,” this might involve analyzing historical workplace layouts or current community spaces to identify potential hazards or barriers to accessibility. Recommendations for modifications, such as improved lighting or adaptive equipment, can then be made to promote safety and functional independence within these environments. This consideration of environmental context enhances the effectiveness of interventions.
- Manual Therapy Techniques
Skilled manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilization and soft tissue manipulation, play a vital role in addressing specific musculoskeletal issues. Therapists with specialized training can apply these techniques to alleviate pain, improve range of motion, and restore function in areas commonly affected by occupational activities or environmental factors prevalent in the community. This expertise ensures targeted and effective treatment.
- Patient Education and Self-Management Strategies
Empowering individuals with knowledge and skills to manage their conditions independently is a crucial aspect of specialized treatment. Educating patients about proper body mechanics, injury prevention techniques, and self-care strategies specific to their needs fosters long-term health and well-being. In a “hat city,” this education might include information on preventing repetitive strain injuries common in the historical hat-making industry or adapting tasks to accommodate existing limitations. This focus on self-management promotes sustainable health outcomes.
These specialized approaches, when integrated within a community-focused rehabilitation program, demonstrate a commitment to addressing the unique needs of the population. By considering the historical context, occupational demands, and environmental factors relevant to a “hat city,” physical therapists can deliver highly effective and relevant care that promotes lasting health and well-being within the community.
2. Community Focus
Effective rehabilitation requires a deep understanding of the community it serves. In the context of a location known for its hat-making heritage, this community focus takes on a unique dimension. Integrating local knowledge, historical context, and specific community needs enhances the relevance and effectiveness of provided services.
- Local Partnerships
Collaborations with local organizations, businesses, and community leaders are essential for understanding the specific needs and resources available within a “hat city.” Partnering with historical societies or museums can provide insights into the physical demands of the hat-making industry, informing the development of targeted rehabilitation programs. For example, collaborations with local businesses could lead to injury prevention workshops tailored to current occupational demands within the community. These partnerships foster a shared responsibility for community health and well-being.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity
Ensuring accessible services for all members of the community is paramount. This requires considering factors such as transportation, language barriers, and cultural sensitivities. In a “hat city,” understanding the demographics and historical context of the population allows for tailored outreach programs and accessible facilities. For instance, providing transportation assistance or offering multilingual services can significantly improve access to care for underserved populations. This commitment to inclusivity strengthens community health outcomes.
- Community Health Initiatives
Participating in community health initiatives strengthens the connection between rehabilitation services and the broader health needs of the “hat city.” This involvement might include offering educational workshops on injury prevention, promoting healthy lifestyles, or supporting local health screenings. By actively engaging in community health initiatives, rehabilitation providers contribute to a culture of wellness and empower residents to prioritize their health. This proactive approach strengthens the overall health infrastructure of the community.
- Tailored Programming
Developing rehabilitation programs that address the specific needs and interests of the “hat city” community enhances engagement and effectiveness. This might involve incorporating activities relevant to local history, culture, or occupational demands. For example, a program might include exercises designed to mimic movements used in hat-making or incorporate local landmarks into therapeutic activities. This tailored approach increases patient motivation and reinforces the connection between rehabilitation and community identity.
By prioritizing community focus, rehabilitation services become deeply integrated within the fabric of a “hat city.” This integration strengthens the relevance, effectiveness, and overall impact of care, promoting lasting health and well-being for all community members.
3. Local Expertise
Local expertise forms a cornerstone of effective physical therapy within a community known for its hat-making history. This specialized knowledge base encompasses an understanding of the unique physical demands associated with the industry, prevalent health concerns within the population, and the historical context shaping community health. The cause-and-effect relationship between local expertise and positive patient outcomes is significant. Therapists possessing this nuanced understanding can develop targeted treatment plans addressing specific needs stemming from occupational hazards, environmental factors, and historical health trends within the hat city. For instance, a therapist familiar with the repetitive hand motions involved in traditional hat-making can effectively address resulting carpal tunnel syndrome or other repetitive strain injuries in contemporary patients. Without this localized knowledge, treatment plans may lack the specificity necessary for optimal outcomes.
The importance of local expertise as a component of “hat city” physical therapy extends beyond addressing historical occupational hazards. It also encompasses an understanding of the community’s current demographics, socioeconomic factors, and access to healthcare resources. This broader perspective informs the development of community health initiatives, outreach programs, and strategies to overcome barriers to care. For example, therapists with local expertise can adapt treatment plans to accommodate the specific needs of older adults who may have worked in the hat industry decades earlier and now experience age-related mobility challenges compounded by previous occupational strain. This integration of historical and contemporary understanding is critical for providing comprehensive and relevant care.
In summary, local expertise provides the foundation for effective and culturally sensitive physical therapy services within a “hat city” context. This specialized knowledge base enhances treatment efficacy, informs community health initiatives, and ensures that care is tailored to the unique needs of the population. Recognizing the value of local expertise and investing in its development strengthens the overall health infrastructure and promotes positive health outcomes within the community. This understanding is crucial for stakeholders involved in healthcare planning, resource allocation, and community development within locations possessing a distinct industrial heritage like “hat cities.”
4. Accessible Care
Accessible care is a critical component of effective healthcare delivery, particularly within communities with distinct historical and socioeconomic contexts, such as locations known for their hat-making heritage. Ensuring equitable access to physical therapy services requires careful consideration of various factors that may create barriers to care and implementing strategies to overcome these challenges. This focus on accessibility strengthens community health outcomes and promotes inclusivity.
- Transportation
Transportation presents a significant barrier to accessing healthcare for many individuals. In a “hat city,” addressing transportation needs might involve partnering with local transport services, providing shuttle options to and from appointments, or offering telehealth consultations when appropriate. These strategies reduce the burden of travel and make physical therapy services more accessible to individuals with limited mobility or residing in remote areas. Consider the impact on an elderly resident relying on public transport to access essential rehabilitation services; accessible transport options become crucial for consistent care.
- Affordability
Financial constraints often limit access to healthcare services. Implementing strategies to address affordability, such as sliding-scale payment options, partnerships with community organizations providing financial assistance, or exploring insurance coverage options, improves access to necessary care. Imagine a single parent working in a contemporary industry within the “hat city” struggling to afford physical therapy after a work-related injury; affordable options become essential for their recovery and ability to return to work, supporting both individual and community well-being.
- Cultural Sensitivity
Culturally sensitive care recognizes and respects the diverse backgrounds and beliefs of community members. In a “hat city” with a potentially rich history of immigration and cultural exchange, providing multilingual services, employing culturally competent staff, and incorporating culturally relevant practices into treatment plans enhances patient comfort and engagement. Consider a recent immigrant navigating the healthcare system in a new language and culture; culturally sensitive care ensures they feel understood and supported throughout their rehabilitation journey.
- Physical Accessibility
Ensuring physical accessibility to facilities is paramount. This involves providing ramps, accessible restrooms, appropriate equipment, and a welcoming environment for individuals with disabilities. Imagine a “hat city” resident using a wheelchair needing access to rehabilitation services after an accident; a physically accessible clinic becomes essential for their ability to receive necessary care. This consideration extends to digital accessibility, ensuring websites and online resources are accessible to individuals with visual or auditory impairments.
By prioritizing accessible care, “hat city” physical therapy services become genuinely inclusive, benefiting all community members. Removing barriers related to transportation, affordability, cultural sensitivity, and physical accessibility strengthens community health and promotes equitable access to essential rehabilitation services. This commitment to accessibility reinforces the vital role physical therapy plays in fostering overall well-being and empowering individuals to achieve optimal physical function within their community.
5. Historical Context
Understanding the historical context of a “hat city” provides crucial insights into the specific needs and challenges faced by individuals seeking physical therapy services. The city’s industrial past, particularly its focus on hat manufacturing, often involved repetitive motions, prolonged standing, and exposure to specific materials, potentially leading to distinct patterns of musculoskeletal injuries and occupational hazards. This historical context directly informs contemporary physical therapy practice. For instance, a therapist aware of the prevalence of repetitive strain injuries among former hat-makers can develop specialized treatment plans incorporating ergonomic principles and targeted exercises to address these specific conditions. Ignoring this historical context risks overlooking crucial factors influencing patient health and limits the effectiveness of interventions. Consider the case of a patient presenting with chronic wrist pain; understanding their past employment in the hat industry allows the therapist to connect their current condition to historical occupational demands, leading to a more accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment approach.
The practical significance of understanding the historical context extends beyond individual patient care. It informs community health initiatives, prevention programs, and resource allocation strategies. For example, recognizing the historical prevalence of respiratory issues related to felt processing in hat manufacturing might lead to community-wide health screenings for early detection and intervention. Furthermore, this historical awareness allows for the development of educational programs targeting specific health risks associated with the city’s industrial past, promoting long-term community well-being. This proactive approach, rooted in historical understanding, demonstrates the crucial link between past industrial practices and current community health needs.
In conclusion, integrating historical context into “hat city” physical therapy is essential for providing effective, relevant, and culturally sensitive care. This understanding informs individualized treatment plans, shapes community health initiatives, and fosters a deeper appreciation of the factors influencing community health. Recognizing the enduring impact of the city’s industrial heritage on the health and well-being of its residents strengthens the overall effectiveness of physical therapy services and contributes to a more comprehensive approach to community health management. Addressing this historical connection ensures that the unique needs of a “hat city” population are met with informed and targeted interventions.
6. Patient-Centered Approach
A patient-centered approach is paramount within “hat city” physical therapy. This approach prioritizes individual needs, preferences, and values in all aspects of care. Recognizing the unique circumstances of each patient, particularly within a community shaped by a distinct industrial heritage, is crucial for effective treatment and positive outcomes. The cause-and-effect relationship between a patient-centered approach and successful rehabilitation is well-established. When patients feel heard, understood, and actively involved in their care, they are more likely to adhere to treatment plans, experience improved functional outcomes, and report higher satisfaction with their care. Consider a patient in a “hat city” experiencing hand pain potentially related to past occupational demands in the hat-making industry. A patient-centered approach involves actively listening to their account of symptoms, understanding their work history, and considering their individual preferences when developing a treatment plan. This tailored approach, recognizing the interplay between historical context and individual experience, enhances treatment effectiveness and fosters a strong therapeutic alliance.
The practical significance of a patient-centered approach within “hat city” physical therapy extends beyond individualized treatment plans. It informs communication strategies, goal setting, and the overall therapeutic relationship. For instance, understanding a patient’s cultural background or health literacy level within the context of the “hat city’s” diverse population enables therapists to tailor communication styles and educational materials, ensuring clarity and promoting understanding. Furthermore, involving patients actively in goal setting ensures that treatment aligns with their individual priorities and values, increasing motivation and promoting self-efficacy. Imagine a patient whose primary goal is to regain the ability to participate in a cherished community activity; incorporating this goal into the treatment plan reinforces the patient’s connection to their community and enhances their commitment to rehabilitation.
In conclusion, a patient-centered approach is integral to high-quality, effective physical therapy within a “hat city” context. By prioritizing individual needs, preferences, and values, and recognizing the influence of the community’s historical and cultural context, therapists can foster strong therapeutic relationships, enhance patient engagement, and promote positive, sustainable health outcomes. This approach underscores the importance of recognizing each patient as an individual with a unique story and specific goals within the broader “hat city” community.
7. Restorative Practices
Restorative practices within “hat city” physical therapy emphasize restoring functional capacity and overall well-being, considering the community’s unique context. These practices recognize the impact of historical occupational demands, environmental factors, and individual health histories on current physical function. A cause-and-effect relationship exists between restorative practices and long-term health outcomes. By focusing on restoring strength, mobility, and overall physical function, these practices aim to reduce pain, improve quality of life, and promote independence. For example, a “hat city” resident experiencing limited hand mobility due to past repetitive work in hat manufacturing might benefit from restorative exercises targeting specific muscle groups and joints affected by their previous occupation. This targeted approach, informed by the community’s historical context, directly addresses the root causes of functional limitations, promoting sustainable recovery and preventing future complications.
The practical significance of restorative practices within “hat city” physical therapy extends beyond addressing physical impairments. These practices often incorporate strategies for managing chronic conditions, promoting healthy lifestyles, and preventing future injuries. This broader perspective recognizes the interconnectedness of physical, mental, and social well-being. For instance, a restorative program might include education on proper body mechanics, ergonomic principles for daily activities, and stress management techniques. Consider a “hat city” resident experiencing back pain related to prolonged standing in their current occupation. Restorative practices might involve exercises to strengthen core muscles, improve posture, and promote flexibility, combined with education on ergonomic workstation setup and stress reduction techniques. This comprehensive approach addresses both the physical symptoms and underlying contributing factors, maximizing the effectiveness of interventions and promoting long-term health and well-being.
In summary, restorative practices form a vital component of “hat city” physical therapy, contributing significantly to positive patient outcomes and overall community health. By focusing on restoring function, managing chronic conditions, and promoting healthy lifestyles, these practices address the unique needs of individuals within a community shaped by its industrial heritage. Integrating restorative principles into physical therapy services enhances the quality of care, empowers individuals to manage their health proactively, and contributes to a healthier, more resilient community. This approach acknowledges the lasting impact of historical context on present-day health and emphasizes the importance of restoring not only physical function but also overall well-being within the “hat city” community.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding rehabilitative services within a community historically associated with the hat-making industry. Clear and concise information is provided to promote understanding and address potential concerns.
Question 1: How can physical therapy address the specific needs of individuals affected by occupational hazards related to the hat-making industry?
Physical therapists specializing in occupational health can assess and treat conditions resulting from repetitive motions, prolonged standing, or exposure to specific materials common in hat manufacturing. Interventions may include ergonomic assessments, targeted exercises, manual therapy, and patient education.
Question 2: What role does historical context play in contemporary physical therapy practice within a “hat city”?
Understanding the historical demands of hat-making informs current practice by enabling therapists to recognize patterns of injury, develop preventative strategies, and tailor treatment plans to address the long-term effects of occupational hazards prevalent in the community’s past.
Question 3: How does community engagement enhance the effectiveness of physical therapy services in this setting?
Collaborations with local organizations, businesses, and community leaders provide valuable insights into community-specific needs, facilitate access to resources, and enable the development of targeted health initiatives addressing local health concerns.
Question 4: What strategies can improve access to physical therapy services for all community members, including those facing socioeconomic or cultural barriers?
Strategies include providing transportation assistance, offering sliding-scale payment options, delivering multilingual services, ensuring physical accessibility of facilities, and incorporating culturally sensitive practices into care.
Question 5: How can individuals incorporate preventative measures to mitigate the risk of developing musculoskeletal issues related to occupational or lifestyle factors within a “hat city” context?
Preventative measures include maintaining proper posture, incorporating regular exercise, adhering to proper lifting techniques, managing stress effectively, and seeking ergonomic assessments of workspaces or daily activity patterns.
Question 6: What are the long-term benefits of engaging in restorative physical therapy practices within a community with a history of industry-specific physical demands?
Long-term benefits include improved physical function, reduced pain, increased independence, enhanced quality of life, and a reduced risk of developing chronic conditions or experiencing future injuries. Restorative practices contribute to overall community well-being by empowering individuals to manage their health proactively.
Access to specialized rehabilitative services is crucial for community well-being. Understanding the historical context of a region and addressing local needs enhances the effectiveness of care.
Further exploration of specific treatment modalities and community-based programs is provided in the following sections.
Conclusion
This exploration of rehabilitative services within a municipality known for its historical connection to the hat-making industry underscores the importance of integrating historical context, community focus, and specialized treatment approaches. Access to quality, patient-centered care, delivered with an understanding of local needs and occupational demands, is essential for promoting individual and community well-being. Restorative practices, informed by local expertise and accessible to all community members, contribute significantly to positive, sustainable health outcomes.
Sustained investment in accessible, community-based rehabilitation programs is crucial for fostering a healthier, more resilient population. By acknowledging the interplay between historical context, contemporary challenges, and individual needs, rehabilitative care within such communities can empower residents to achieve optimal physical function and contribute to a thriving community. The future of healthcare within these unique settings relies on continued dedication to providing specialized, accessible, and patient-centered care that honors both the past and the present.