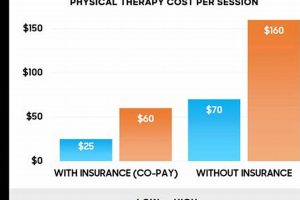
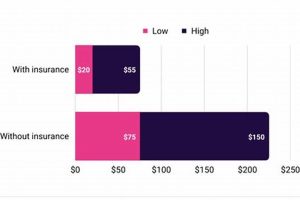
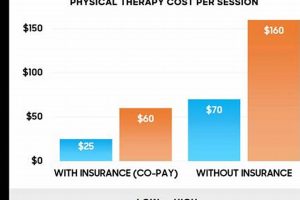
Rehabilitative care provided to naval personnel addresses a range of musculoskeletal injuries and conditions, from acute trauma sustained in training or operational settings to chronic overuse syndromes. This specialized care often incorporates advanced techniques and modalities tailored to the unique physical demands placed on sailors, marines, and other maritime service members. For example, a sailor might receive targeted interventions for a rotator cuff injury sustained during repetitive lifting, while a marine could undergo a rehabilitation program for a lower extremity injury incurred during a field exercise.
Maintaining optimal physical readiness is paramount for a robust and effective naval force. Restoring function, mitigating pain, and preventing re-injury are crucial aspects of maintaining operational effectiveness. Historically, the focus has evolved from basic injury management to a comprehensive, proactive approach encompassing injury prevention, performance optimization, and lifelong health and wellness for service members. This evolution reflects the growing recognition of the vital role specialized rehabilitation plays in maintaining a fit and deployable force.
Further exploration of this topic will cover specific treatment approaches, technological advancements in rehabilitation, and the role of specialized practitioners in ensuring the health and readiness of naval personnel.
Tips for Maintaining Optimal Physical Readiness
Preserving peak physical condition is essential for individuals engaged in demanding physical activities. These recommendations can assist in minimizing injury risk and promoting long-term musculoskeletal health.
Tip 1: Prioritize Proper Warm-up: Adequate warm-up prepares the body for strenuous activity by increasing blood flow to muscles and enhancing joint mobility. Incorporating dynamic stretches, such as arm circles and leg swings, is recommended.
Tip 2: Employ Correct Lifting Techniques: Lifting heavy objects improperly can strain the back and other muscle groups. Maintaining a neutral spine and engaging core muscles is crucial during lifting activities.
Tip 3: Incorporate Regular Strength Training: A well-rounded strength training program strengthens muscles and connective tissues, reducing the risk of injuries. Focusing on compound exercises that engage multiple muscle groups is advisable.
Tip 4: Integrate Flexibility Exercises: Maintaining flexibility improves range of motion and reduces muscle tightness, promoting optimal movement patterns and injury prevention. Regular stretching, including static and dynamic stretches, is beneficial.
Tip 5: Ensure Adequate Rest and Recovery: Sufficient rest allows the body to repair and rebuild muscle tissue, reducing the risk of overuse injuries. Incorporating rest days into training schedules is essential.
Tip 6: Maintain Proper Hydration: Hydration plays a vital role in muscle function and overall physical performance. Consuming adequate fluids throughout the day is crucial, especially during periods of intense physical activity.
Tip 7: Listen to Your Body: Recognizing and responding to pain signals is crucial for preventing minor aches from developing into significant injuries. Seeking professional medical advice when necessary is essential.
Adhering to these recommendations can significantly contribute to injury prevention and the maintenance of optimal physical function, promoting long-term health and well-being.
By understanding and implementing these strategies, individuals can proactively address potential musculoskeletal issues and maintain a high level of physical readiness.
1. Injury Prevention
Injury prevention forms a cornerstone of naval physical therapy, aiming to minimize the incidence and severity of musculoskeletal problems within the naval force. Proactive strategies are essential for maintaining operational readiness and reducing the burden of long-term health issues. This approach emphasizes identifying risk factors and implementing interventions to mitigate potential harm.
- Biomechanical Analysis and Correction:
Evaluating movement patterns and posture identifies biomechanical deficiencies that increase injury susceptibility. For example, analyzing a sailor’s lifting technique can reveal improper form that strains the lower back. Corrective exercises and ergonomic adjustments mitigate these risks, improving movement efficiency and reducing injury potential.
- Targeted Exercise Programs:
Specific exercises address strength imbalances and enhance neuromuscular control, crucial for injury prevention. A program designed to strengthen a marine’s core musculature can stabilize the spine and protect against injuries during demanding physical tasks. These programs are tailored to the specific demands of different roles within the navy.
- Education and Training:
Empowering personnel with knowledge regarding proper body mechanics, safe lifting techniques, and appropriate exercise form promotes a culture of injury prevention. Workshops on proper posture during prolonged periods of sitting or standing can reduce the risk of back pain among personnel working in office environments. This education extends beyond physical practices to encompass lifestyle factors that influence musculoskeletal health.
- Protective Equipment and Ergonomic Considerations:
Utilizing appropriate protective equipment and implementing ergonomic principles in workspaces minimize injury risk. Ensuring sailors wear proper footwear during strenuous activities can prevent ankle and foot injuries. Similarly, ergonomic assessments of workstations can reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries among personnel performing computer-based tasks.
These facets of injury prevention contribute significantly to the overall effectiveness of naval physical therapy. By proactively addressing potential risks, these strategies enhance operational readiness, reduce healthcare costs, and promote the long-term health and well-being of naval personnel. This focus on prevention is a vital investment in maintaining a robust and deployable naval force.
2. Performance Optimization
Performance optimization within naval physical therapy goes beyond injury rehabilitation; it focuses on enhancing physical capabilities to meet the rigorous demands of naval service. This proactive approach recognizes the direct link between optimized physical function and mission success. Strength, endurance, flexibility, and agility are key components targeted through specialized training programs. Enhancing these attributes contributes to improved operational effectiveness, reduces injury susceptibility, and promotes overall readiness.
Consider a Special Warfare Operator requiring peak physical conditioning for demanding missions. Tailored programs might incorporate high-intensity interval training to improve cardiovascular fitness, advanced strength training to enhance load-bearing capacity, and specialized flexibility exercises to maximize range of motion crucial for navigating confined spaces. For a naval aviator, programs might emphasize neck strength and endurance to withstand G-forces, along with core stability training to maintain optimal posture during flight. These examples illustrate how performance optimization programs are individualized to address specific job requirements within the navy.
The practical significance of performance optimization lies in its contribution to a more effective and resilient naval force. Optimized physical capabilities translate to improved performance in a range of operational scenarios, from combat operations to disaster relief efforts. Furthermore, by pushing physical limits in a controlled environment, these programs can identify potential weaknesses and implement preventative measures to reduce future injury risk. This proactive approach not only enhances current operational capabilities but also invests in the long-term health and readiness of naval personnel.
3. Functional Restoration
Functional restoration represents a critical component of naval physical therapy, emphasizing the return to full operational capacity following injury or illness. This process focuses on restoring lost function, improving mobility, reducing pain, and ultimately enabling individuals to resume their duties effectively. Cause and effect play a significant role in this process, with therapists identifying the root cause of functional limitations and tailoring interventions to address specific impairments. For instance, a sailor suffering from limited shoulder mobility due to a rotator cuff tear would undergo targeted exercises and manual therapy techniques aimed at restoring strength, range of motion, and pain-free movement. Similarly, a marine experiencing balance deficits after a lower extremity injury would engage in a balance training program to regain stability and prevent falls. These examples highlight the individualized nature of functional restoration within naval physical therapy.
The importance of functional restoration stems from its direct impact on operational readiness. Returning personnel to full duty as quickly and safely as possible is paramount for maintaining a robust naval force. Functional restoration programs employ evidence-based interventions, including therapeutic exercises, manual therapy, and modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation, to accelerate recovery and maximize functional outcomes. Consider a scenario where a naval engineer sustains a hand injury impacting fine motor skills crucial for their role. Functional restoration would involve specialized exercises to improve dexterity, grip strength, and coordination, enabling the engineer to resume their duties effectively. The practical significance of this understanding lies in the enhanced operational effectiveness and reduced time lost due to injury or illness.
Successful functional restoration requires a comprehensive approach addressing not only the physical impairments but also the psychological and social factors impacting recovery. Challenges may include pre-existing conditions, the severity of the injury, and individual variations in healing rates. Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration among medical professionals, therapists, and the individual, with a shared goal of achieving optimal functional outcomes and facilitating a seamless return to duty. Ultimately, functional restoration plays a pivotal role in maintaining a healthy and deployable naval force capable of meeting the demands of its mission.
4. Pain Management
Pain management constitutes a critical aspect of naval physical therapy, significantly impacting operational effectiveness and the overall well-being of naval personnel. Addressing pain effectively allows individuals to participate actively in rehabilitation programs, accelerating recovery and facilitating a timely return to duty. Furthermore, effective pain management strategies improve quality of life, reduce reliance on medication, and minimize the potential for chronic pain development. A multi-faceted approach employing various modalities and techniques achieves comprehensive pain control. For instance, a sailor experiencing acute back pain might benefit from a combination of manual therapy techniques, such as spinal mobilization, and therapeutic modalities like ultrasound to reduce inflammation and muscle spasm. Similarly, a marine with chronic knee pain could utilize a combination of targeted exercises, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), and education on pain management strategies for long-term relief.
The significance of pain management within naval physical therapy stems from its direct influence on functional restoration and operational readiness. Untreated or poorly managed pain can hinder progress in rehabilitation, delaying recovery and potentially leading to chronic pain syndromes. Consider a scenario where a navy diver experiences persistent shoulder pain following a diving accident. Effective pain management, through modalities like cryotherapy and therapeutic exercises, facilitates participation in rehabilitation, promoting faster healing and restoring full range of motion necessary for diving duties. Furthermore, a proactive approach to pain management can prevent acute pain from transitioning into chronic pain, a debilitating condition impacting long-term health and career longevity. The practical application of these strategies ensures personnel can perform duties effectively without physical limitations imposed by pain.
Challenges in pain management within the naval context may include accessing specialized pain management services in remote locations or during deployments, managing pain associated with complex injuries or combat-related trauma, and addressing individual variations in pain perception and response to treatment. Overcoming these challenges requires a collaborative approach involving medical professionals, physical therapists, and psychologists, ensuring comprehensive pain assessment and individualized treatment plans. Integrating pain management strategies into all phases of rehabilitation optimizes outcomes, promotes long-term well-being, and contributes significantly to the overall health and readiness of the naval force.
5. Operational Readiness
Operational readiness represents the culmination of naval physical therapy efforts, signifying the ability of personnel to perform their duties effectively in any operational environment. This critical aspect hinges on the successful integration of injury prevention, performance optimization, functional restoration, and pain management strategies. A direct causal relationship exists between these components and operational readiness. Effective injury prevention programs reduce the incidence of musculoskeletal problems, minimizing time lost due to injury and maximizing the availability of personnel for deployment. Performance optimization programs enhance physical capabilities, ensuring personnel can meet the rigorous demands of their respective roles. Functional restoration returns injured personnel to full duty swiftly and safely, while effective pain management strategies enable individuals to perform their duties without physical limitations imposed by pain. These interconnected elements contribute synergistically to maintaining a highly capable and deployable naval force.
Consider a scenario where a ship is deployed for an extended mission. A sailor sustains a back injury during a heavy lifting operation. The ship’s physical therapist implements a comprehensive treatment plan encompassing pain management, functional restoration exercises, and ergonomic adjustments to the sailor’s work environment. This intervention enables the sailor to return to duty quickly, minimizing the impact on the ship’s operational capacity. In another instance, a marine preparing for a demanding deployment undergoes a performance optimization program focusing on strength and endurance training. This proactive approach enhances the marine’s physical resilience, reducing their susceptibility to injury during the deployment and ensuring they can perform optimally under challenging conditions. These practical examples demonstrate the tangible impact of naval physical therapy on operational readiness.
Maintaining optimal operational readiness presents unique challenges within the naval context. These include providing access to specialized physical therapy services in remote locations or during deployments, managing complex injuries sustained in combat or training environments, and addressing the psychological impact of injury on operational performance. Overcoming these challenges necessitates a robust and adaptable physical therapy infrastructure, equipped to deliver comprehensive care across a spectrum of operational settings. Furthermore, fostering a culture of injury prevention and proactive health management within the naval force is crucial for sustaining long-term operational readiness. Ultimately, the practical significance of understanding the connection between naval physical therapy and operational readiness lies in its contribution to a more effective, resilient, and deployable naval force capable of fulfilling its mission in any environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding rehabilitation services provided to naval personnel.
Question 1: What types of injuries are commonly treated?
Musculoskeletal injuries, ranging from acute trauma like fractures and sprains to overuse injuries such as tendonitis and stress fractures, are frequently addressed. Rehabilitative care also encompasses post-surgical recovery and management of chronic conditions like arthritis and back pain.
Question 2: How does rehabilitation contribute to operational readiness?
Restoring functional capacity after injury or illness is crucial for maintaining a deployable force. Rehabilitation programs focus on returning personnel to full duty as quickly and safely as possible, minimizing time lost due to medical limitations.
Question 3: What specialized equipment or techniques are employed?
Advanced modalities such as therapeutic ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and laser therapy may be utilized. Treatment plans often incorporate manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercise, and functional training tailored to the specific demands of naval occupations.
Question 4: How does prevention factor into the overall approach?
Injury prevention is paramount. Programs emphasizing proper body mechanics, ergonomic assessments, and targeted exercise regimens aim to minimize injury risk and promote long-term musculoskeletal health within the naval force.
Question 5: Are services available during deployments?
Access to rehabilitative care is prioritized even in deployed settings. Medical personnel and embedded physical therapists provide necessary services to maintain operational readiness and manage injuries sustained in the field.
Question 6: What is the long-term impact of these services?
Effective rehabilitation contributes not only to immediate operational readiness but also to the long-term health and well-being of naval personnel. Promoting healthy lifestyles, preventing chronic pain, and optimizing physical function support career longevity and enhance overall quality of life.
Understanding these aspects provides a comprehensive overview of the importance of rehabilitation in maintaining a healthy and effective naval force.
Further exploration of this topic will delve into specific case studies, highlight advancements in rehabilitation techniques, and discuss the future direction of care for naval personnel.
Conclusion
Naval physical therapy demonstrably contributes to maintaining a highly effective and deployable naval force. From injury prevention and performance optimization to functional restoration and pain management, the multifaceted nature of this specialized field directly impacts operational readiness. The comprehensive approach, encompassing advanced techniques and tailored programs, addresses the unique physical demands placed upon naval personnel across various roles and operational environments. Investing in these services safeguards the health and well-being of service members while ensuring a robust and prepared naval force.
The continued evolution of naval physical therapy, incorporating advancements in technology and research, promises further enhancements in injury prevention, treatment efficacy, and performance optimization. Prioritizing these services remains essential for maintaining a naval force capable of meeting present and future challenges, safeguarding national security interests and promoting the long-term health and readiness of those who serve.