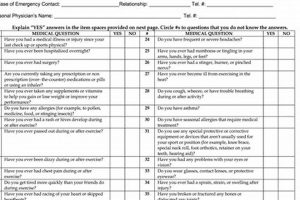
A standardized document typically required for prospective physical therapy students or those seeking specific certifications, serves as a record of time spent observing licensed physical therapists in clinical settings. This documentation usually requires detailed information about the observation site, dates and times of observation, and the supervising therapist’s signature and license information. An example might include a student observing various therapeutic interventions, patient interactions, and administrative tasks within an outpatient clinic.
Accurate and comprehensive completion of this documentation is crucial for demonstrating practical experience and understanding of the profession. It provides evidence of exposure to real-world clinical practice, allowing aspiring therapists to gain insights into patient care, professional conduct, and the overall workings of a physical therapy setting. Historically, the emphasis on practical observation has evolved alongside the development of the profession itself, recognizing the importance of experiential learning in cultivating competent and ethical practitioners. This documentation helps ensure aspiring professionals understand and meet the demands of this patient-centered career.
Further exploration of related topics such as the application process for physical therapy programs, the role of observation in professional development, and the varying requirements across different jurisdictions offers a broader perspective on the importance of practical experience in the field.
Tips for Maximizing Observational Experiences
Maximizing the value of observational experiences requires careful planning and active engagement. The following tips offer guidance for prospective physical therapists to gain the most from their observation hours.
Tip 1: Secure Placement Early: Initiating the process of securing observation sites well in advance is crucial. Popular clinics often have limited availability, and early application allows for greater flexibility in scheduling and potentially more diverse observational opportunities.
Tip 2: Diversify Clinical Settings: Observing in various clinical settings such as hospitals, outpatient clinics, and rehabilitation centers provides exposure to a broader range of patient populations and treatment approaches. This breadth of experience can enhance understanding of the field’s scope.
Tip 3: Active Observation and Note-Taking: Passive observation yields limited benefits. Active engagement, including detailed note-taking on observed procedures, patient interactions, and clinical decision-making, facilitates deeper learning and retention.
Tip 4: Professional Conduct: Maintaining a professional demeanor, adhering to dress codes, and respecting patient privacy are paramount. Professionalism demonstrates respect for the clinical environment and the individuals within it.
Tip 5: Engage Respectfully: While observing, engage respectfully with the supervising therapist by asking clarifying questions. Demonstrating genuine interest and seeking deeper understanding enhances the learning experience.
Tip 6: Reflect and Synthesize: Regular reflection upon observed practices allows for synthesis of information and identification of areas requiring further exploration. This process solidifies learning and facilitates personal growth.
Tip 7: Maintain Accurate Records: Meticulous record-keeping, including dates, times, and supervisor signatures, is essential for accurate documentation. Accurate records ensure compliance with program requirements.
By adhering to these guidelines, aspiring therapists can transform observational experiences into valuable learning opportunities, cultivating a strong foundation for future professional practice.
The insights gained from observational experiences contribute significantly to the development of well-rounded physical therapists.
1. Accurate Documentation
Accurate documentation forms the cornerstone of a verifiable and credible record of observational experience in physical therapy. Its importance lies in providing demonstrable proof of practical exposure, which is often a prerequisite for academic progression and professional certification. Meticulous record-keeping ensures that the documented experience accurately reflects the time spent observing and the activities witnessed.
- Specificity of Activities:
Precise descriptions of observed activities, avoiding vague generalizations, are crucial. Rather than stating “observed patient treatment,” a detailed entry might describe “observed gait training techniques with a post-stroke patient using parallel bars.” This level of detail provides valuable context and demonstrates engagement with the observational process. Specific details strengthen the documented experience, illustrating a commitment to learning.
- Timekeeping Precision:
Accurate recording of dates and times, ideally broken down into specific start and end times for each observation period, is essential. This precision eliminates ambiguity and supports the validity of the documented hours. For example, logging “9:00 AM – 12:00 PM: Observed therapeutic exercises for patients with lower back pain” offers a verifiable record of the observation period.
- Supervisor Verification:
Supervisor signatures and license information serve as essential validation of the observation experience. This authentication confirms that the documented activities occurred under the guidance of a qualified professional. A form lacking appropriate signatures and credentials may be deemed incomplete or invalid.
- Adherence to Form Requirements:
Strict adherence to the specific requirements of the designated observation hours form, including correct completion of all required fields, is paramount. Different institutions or regulatory bodies may have unique form requirements, and failing to adhere to these specific guidelines may lead to rejection of the documentation. Attention to detail, including ensuring the correct date format or providing required contact information, demonstrates professionalism and attention to protocol.
These components of accurate documentation collectively contribute to a reliable and comprehensive record of observation, ensuring the validity of the documented experience for both academic and professional purposes. A meticulously completed observation hours form serves as demonstrable evidence of commitment to the field and adherence to professional standards, thus strengthening applications for further education and career advancement within physical therapy.
2. Supervisor Verification
Supervisor verification constitutes a critical component of the physical therapy observation hours form, directly impacting its validity and acceptance. This verification, typically achieved through the supervisor’s signature and license information, serves as irrefutable proof that the documented observation hours were completed under the guidance of a qualified professional. This process establishes accountability and ensures adherence to professional standards. For instance, a student completing observation hours in a sports rehabilitation clinic requires verification from the licensed physical therapist overseeing their experience. This signature validates the student’s presence and participation in the specified activities within the clinic, ensuring the documented hours are genuine and meet required standards.
The absence of supervisor verification renders the observation hours form incomplete and potentially invalid. It undermines the credibility of the documented experience, raising questions about the authenticity of the claimed hours and the oversight provided. Consider a scenario where an applicant submits a form detailing observation hours in a neurological rehabilitation setting. Without the supervising therapist’s signature, the claimed experience lacks validation. This omission may lead to rejection of the application, highlighting the crucial role verification plays in substantiating the documented observation hours. The importance of this validation underscores the need for meticulous record-keeping throughout the observation period.
Supervisor verification, therefore, functions as an essential safeguard, ensuring accountability, upholding professional standards, and validating the veracity of documented observation hours. Its presence on the physical therapy observation hours form strengthens the applicant’s credibility and ensures compliance with established requirements. This understanding underscores the integral connection between supervised experience and the formal documentation process within the physical therapy profession. This rigorous documentation process ensures the quality and legitimacy of practical training, contributing to the development of competent and ethical practitioners.
3. Specified Timeframe
A specified timeframe forms an integral component of a physical therapy observation hours form, defining the precise period during which observation occurred. This defined period, typically documented with specific start and end dates, serves as a crucial parameter for quantifying the observation experience. The timeframe not only denotes the duration of observation but also contextualizes the documented activities within a specific period. For instance, an entry indicating “January 10, 2024 – March 15, 2024: Observation of outpatient orthopedic rehabilitation” clearly demarcates the observation period, allowing for accurate assessment of the documented hours and correlation with other experiences. This precise timeframe contributes significantly to the form’s overall validity and allows for objective evaluation of the documented experience.
Accurate delineation of the timeframe allows for verification of compliance with program-specific requirements for observation hours. Many physical therapy programs stipulate a minimum number of observation hours within designated clinical settings. A clearly defined timeframe enables reviewers to assess whether the documented experience fulfills these prerequisites. Consider an instance where a program mandates 100 hours of observation. A form with detailed entries and precise timeframes enables reviewers to quickly and accurately calculate the total hours, streamlining the evaluation process and confirming adherence to program guidelines. Lack of a specified timeframe may necessitate further clarification or potentially lead to rejection of the documentation.
The specified timeframe, therefore, functions as a crucial organizational and validation element within the physical therapy observation hours form. It establishes the boundaries of the documented experience, enables accurate quantification of observation hours, and facilitates compliance verification. Precise documentation of the timeframe strengthens the integrity of the record and contributes to a more robust and credible documentation of the observational experience. This precision reinforces the professional standards expected within the field and facilitates the development of competent practitioners through verifiable practical experience.
4. Clinical Setting Details
Clinical setting details constitute a crucial component of a physical therapy observation hours form, providing essential context for the documented experience. Detailed descriptions of the clinical environment, including the type of facility (e.g., hospital, outpatient clinic, rehabilitation center), its specialization (e.g., orthopedics, neurology, pediatrics), and the patient population served, enrich the record and offer valuable insights into the observer’s exposure. For example, an entry specifying “Observation at a university-affiliated hospital specializing in acute care for traumatic brain injuries” provides significantly more context than simply stating “Hospital observation.” This level of detail clarifies the specific nature of the observational experience and the types of patient cases encountered, enabling a more comprehensive assessment of the acquired knowledge and skills. The inclusion of such detail illuminates the practical relevance of the observation hours and demonstrates a commitment to understanding specific aspects of physical therapy practice.
The specificity of clinical setting details allows for a more nuanced understanding of the observer’s practical experience. Observation within a pediatric clinic, for instance, exposes an individual to developmental milestones, age-appropriate interventions, and family-centered care, contrasting significantly with the experience gained in a geriatric rehabilitation setting focused on balance and mobility training for older adults. Furthermore, detailing specific equipment or technologies utilized within the setting, such as gait analysis systems or specialized exercise equipment, further enriches the record. Such details underscore the observer’s exposure to diverse treatment modalities and enhance the credibility of the documented experience. These specifics allow reviewers to gauge the breadth and depth of the observation and its alignment with specific career interests or academic goals.
In summary, clinical setting details within the physical therapy observation hours form offer crucial context, allowing for a more comprehensive evaluation of the observer’s practical experience. Detailed descriptions of the clinical environment, patient population, and specialized equipment contribute to a more robust and informative record. This precise information not only enhances the credibility of the documented hours but also provides valuable insights into the observer’s exposure to diverse aspects of the physical therapy profession, ultimately contributing to a more thorough understanding of the field and its various applications. This understanding serves as a critical foundation for future professional development and specialization within physical therapy.
5. Patient Interaction Types
Patient interaction types documented within a physical therapy observation hours form provide crucial insights into the range and depth of an observer’s exposure to real-world clinical practice. Documenting diverse interaction types, such as initial evaluations, progress assessments, therapeutic exercise instruction, and patient education sessions, demonstrates a broader understanding of patient care beyond basic treatment procedures. For instance, observing a therapist conduct an initial evaluation, including history taking, physical examination, and diagnosis formulation, provides valuable insight into the clinical reasoning process. Conversely, observing patient education sessions on pain management strategies or home exercise programs highlights the importance of communication and patient empowerment within the therapeutic relationship. These varied interactions offer a more holistic view of patient management and underscore the multifaceted nature of physical therapy practice. Accurately recording these different interaction types strengthens the documented experience, transforming observation into a comprehensive learning opportunity. This comprehensive record demonstrates engagement beyond passive observation and highlights active learning from various patient care scenarios.
The documented patient interaction types also serve as valuable data points for evaluating the comprehensiveness of the observation experience. A form reflecting exposure to diverse interactions, spanning initial consultations to discharge planning, suggests a more well-rounded observational experience compared to one solely focused on therapeutic exercises. Consider an observation period encompassing interactions with patients across the lifespan, including pediatric patients undergoing developmental therapy, athletes undergoing post-surgical rehabilitation, and geriatric patients managing chronic conditions. This breadth of experience demonstrates exposure to diverse patient populations and their unique needs, enriching the observer’s understanding of physical therapy’s wide-ranging applications. Such varied exposure fosters adaptability and prepares aspiring therapists for the diverse challenges encountered in clinical practice.
In summary, meticulous documentation of patient interaction types within the physical therapy observation hours form elevates the value of the documented experience. Detailed recording of these interactions demonstrates not only exposure to various patient care scenarios but also a deeper understanding of the patient-therapist relationship and the comprehensive nature of physical therapy practice. This emphasis on interaction types transforms the observation hours form from a simple record of time spent into a rich tapestry of practical learning, ultimately benefiting both aspiring therapists and the patients they will eventually serve. This comprehensive approach to documenting observation hours contributes to the development of well-rounded and patient-centered practitioners.
6. Treatment Procedures Observed
Documentation of observed treatment procedures forms a cornerstone of the physical therapy observation hours form, providing concrete evidence of exposure to practical applications of therapeutic interventions. Detailed descriptions of these procedures, moving beyond simple observation to critical analysis, demonstrate an active engagement with the learning process and a deeper understanding of the clinical reasoning behind therapeutic choices. This detailed record transforms the observation hours form from a passive log of time into an active portfolio of practical knowledge, enriching the observer’s understanding of the field.
- Therapeutic Exercise Modalities:
Observing a range of therapeutic exercise modalities, from manual therapy techniques like joint mobilization and soft tissue massage to therapeutic exercises using resistance bands, weights, or specialized equipment, provides valuable insights into evidence-based practice. For example, documenting observation of a therapist implementing the Mulligan technique for shoulder mobilization or demonstrating proper form for squats with a patient post-knee surgery clarifies specific interventions and their intended therapeutic effects. This detailed record strengthens the observer’s understanding of various treatment modalities and their applications in diverse clinical scenarios. It lays a foundation for evidence-based practice and fosters critical thinking regarding therapeutic choices.
- Electrotherapeutic and Physical Modalities:
Observation of electrotherapeutic and physical modalities, such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, heat therapy, or cryotherapy, expands the observer’s understanding of the diverse tools utilized in physical therapy. Documenting the parameters used for ultrasound application or the type of electrical stimulation employed, along with observed patient responses, further enhances the record. For example, noting the frequency and intensity of ultrasound used for treating a hamstring strain or the placement of electrodes for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for pain management provides valuable context and demonstrates attention to detail. This level of documentation enhances the value of the observation hours, providing a practical understanding of these modalities.
- Assistive Devices and Adaptive Equipment:
Experiences involving assistive devices and adaptive equipment offer insights into patient-centered care and functional restoration. Observing patient training with crutches, walkers, or wheelchairs, or noting modifications made to accommodate individual needs, demonstrates awareness of functional limitations and adaptive strategies. Documenting the specific type of assistive device used, the patient’s progress in its utilization, and any challenges encountered enriches the observer’s understanding of how these devices facilitate independence and improve quality of life. For instance, observing a therapist fit a patient with a custom orthotic or provide training on proper wheelchair propulsion techniques exemplifies the practical application of adaptive strategies. These observations illustrate the importance of patient-centered care and the role of assistive technology in optimizing functional outcomes.
- Patient Education and Home Exercise Programs:
Observation of patient education and home exercise program development highlights the crucial role of communication and patient empowerment in successful rehabilitation. Documenting the clarity and effectiveness of patient education techniques, the tailoring of home exercise programs to individual needs, and patient engagement with the prescribed program deepens the observer’s understanding of patient-centered care and the importance of self-management. Noting the specific instructions provided for a home exercise program, including frequency, duration, and precautions, and observing the therapist’s communication style when explaining these instructions offer valuable learning opportunities. These observations underscore the importance of effective communication and patient adherence in achieving therapeutic goals.
Comprehensive documentation of observed treatment procedures within the physical therapy observation hours form transforms a passive record of time into an active demonstration of practical knowledge and clinical reasoning. This detailed record enhances the value of the observation experience, providing aspiring therapists with valuable insights into the diverse interventions employed in physical therapy practice and the rationale behind their application. This detailed understanding lays a strong foundation for future clinical practice and underscores the importance of continuous learning within the field.
7. Adherence to Guidelines
Adherence to established guidelines forms the bedrock of a valid and accepted physical therapy observation hours form. Strict compliance with these guidelines, often stipulated by academic institutions or professional regulatory bodies, ensures the documented experience meets recognized standards and serves its intended purpose. Deviation from these guidelines can invalidate the documented hours, jeopardizing academic progression or professional certification. Understanding and adhering to these guidelines is paramount for ensuring the observation experience translates into demonstrable and accepted practical experience.
- Specificity of Required Information:
Guidelines often dictate specific information required within the observation hours form. This may include precise details regarding the observation site, supervisor credentials, patient demographics (while maintaining privacy), and specific treatment procedures observed. For example, some guidelines may require documentation of specific patient diagnoses or the precise duration of each treatment modality observed. Failure to provide this required information renders the form incomplete and potentially unacceptable, highlighting the importance of meticulous attention to detail and strict adherence to specified requirements.
- Format and Submission Procedures:
Adherence to prescribed formats and submission procedures is crucial for acceptance of the observation hours form. Guidelines may stipulate specific document formats (e.g., PDF, Word), signature requirements (e.g., electronic, handwritten), or submission methods (e.g., online portal, mail). Deviation from these procedures may lead to rejection of the form, regardless of the quality of the observation experience itself. For instance, submitting a handwritten form when an electronic submission is required, or failing to obtain required signatures, can invalidate the documentation. Strict adherence to these seemingly administrative details underscores professionalism and respect for established processes.
- Timeframe and Deadline Adherence:
Guidelines typically establish specific timeframes for completion and submission of observation hours forms. These timeframes may align with academic semesters, application deadlines, or certification requirements. Failure to submit the form within the stipulated timeframe can lead to its rejection, impacting academic progression or professional qualifications. For instance, submitting observation hours accumulated during a previous academic year when the current application cycle requires recent experience may render the documentation invalid. Timely submission demonstrates organizational skills and adherence to established deadlines.
- Ethical Considerations and Professional Conduct:
Guidelines often incorporate ethical considerations and professional conduct expectations. These may include maintaining patient confidentiality, respecting professional boundaries, and adhering to dress code requirements within the clinical setting. Documenting adherence to these ethical guidelines underscores professionalism and commitment to patient well-being. For example, ensuring patient names or identifying information are not included within the observation hours form demonstrates respect for privacy and adherence to ethical guidelines. This commitment to ethical conduct strengthens the credibility of the documented experience.
Adherence to these guidelines ensures the physical therapy observation hours form serves as a valid and reliable record of practical experience. Meticulous attention to detail, strict compliance with specified requirements, and a commitment to ethical conduct collectively contribute to a credible documentation of observation hours, ultimately benefiting aspiring therapists and strengthening the integrity of the physical therapy profession. This rigorous approach to documentation safeguards the quality of practical training and ensures the development of competent and ethical practitioners.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding documentation of observation hours in physical therapy, providing clarity on frequently encountered questions and potential misconceptions.
Question 1: What constitutes a valid observation site for physical therapy observation hours?
Valid observation sites typically include licensed physical therapy clinics, hospitals, rehabilitation centers, and other healthcare facilities where licensed physical therapists provide direct patient care. Sites must offer opportunities to observe genuine patient interactions and therapeutic interventions. Verification of site validity may be required through program-specific guidelines.
Question 2: How are observation hours formally documented?
Formal documentation typically involves completing a standardized observation hours form. This form requires detailed information about the observation site, dates and times of observation, specific activities observed, and supervisor verification through signature and license information. Strict adherence to program-specific guidelines regarding form completion and submission is crucial.
Question 3: Can observation hours be completed prior to applying to a physical therapy program?
Completing observation hours prior to application strengthens an application and demonstrates proactive engagement with the profession. However, program-specific prerequisites regarding the timing of observation hours vary. Some programs may require observation within a specific timeframe preceding application. Adherence to individual program guidelines is essential.
Question 4: Is there a limit to the number of observation hours that can be completed at a single site?
While accumulating a significant number of hours at a single site demonstrates commitment, diversifying observation experiences across different clinical settings is often encouraged. Exposure to various patient populations, treatment approaches, and clinical environments provides a broader understanding of the field. Program-specific guidelines may offer further clarification regarding site limitations.
Question 5: What if a preferred observation site does not offer a formal observation program?
Directly contacting the clinic or facility and inquiring about observation opportunities, even in the absence of a formal program, can be productive. Expressing genuine interest and highlighting the educational value of observation may lead to potential opportunities. Maintaining professional communication and adhering to any established protocols within the facility are essential.
Question 6: What if a documented observation hour form is lost or damaged?
Maintaining meticulous records and retaining copies of completed observation hours forms is crucial. In case of loss or damage, contacting the supervising therapist or the observation site directly may be necessary to obtain supporting documentation or recreate the lost record. Early and proactive communication is recommended to mitigate potential complications.
Thorough understanding of these frequently asked questions ensures accurate documentation and maximizes the value of observation experiences within the physical therapy field. This detailed record-keeping serves as demonstrable evidence of commitment and preparation for professional practice.
For further information, consult program-specific guidelines or contact relevant academic institutions or professional organizations.
Conclusion
Documentation of physical therapy observation hours represents a critical step toward entry into the profession. This rigorous process, encompassing accurate record-keeping, supervisor verification, specified timeframes, detailed clinical setting descriptions, diverse patient interaction types, observed treatment procedures, and strict adherence to established guidelines, ensures the documented experience meets professional standards. This comprehensive approach underscores the importance of practical experience in cultivating competent and ethical practitioners. Understanding and adhering to these requirements ensures the observation hours form serves as a valid and reliable record of practical experience, benefiting both aspiring therapists and the integrity of the profession.
The physical therapy observation hours form, therefore, serves not merely as a documentation requirement but as a crucial bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical application. Meticulous completion of this form reflects a commitment to professional standards and a dedication to patient-centered care. This dedication to thorough documentation ultimately contributes to the advancement of the physical therapy profession and the delivery of high-quality patient care.