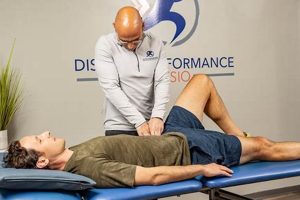
Restoring athletes and active individuals to their peak physical condition is a specialized branch of rehabilitative care. This approach focuses on addressing injuries and functional limitations preventing participation in sports or recreational activities. For example, a tennis player with a rotator cuff injury would undergo targeted exercises and therapies to regain strength, mobility, and sport-specific skills like serving and backhand strokes.
Returning individuals to pre-injury performance levels offers significant physical and psychological benefits. It allows for the resumption of valued activities, promoting physical health, mental well-being, and social engagement. Historically, this type of rehabilitation has evolved from basic injury management to sophisticated programs encompassing advanced techniques like biomechanical analysis, functional movement assessments, and sport-specific training. This evolution has been driven by a greater understanding of human biomechanics and the demands of specific activities.
The following sections will explore the key components of this rehabilitative process, including assessment, treatment modalities, and return-to-play protocols. It will also discuss the role of various healthcare professionals involved in delivering this care.
Tips for Optimizing Athletic Recovery
Maximizing recovery and preventing re-injury requires a proactive and informed approach. The following tips offer valuable guidance for individuals seeking to regain peak performance.
Tip 1: Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting a qualified healthcare practitioner is crucial for accurate diagnosis and a personalized rehabilitation plan. This ensures appropriate treatment strategies are implemented.
Tip 2: Adhere to Prescribed Protocols: Following prescribed exercises, rest periods, and activity modifications is essential for optimal healing and minimizing setbacks. Consistency is key to successful rehabilitation.
Tip 3: Prioritize Proper Warm-up and Cool-down: Preparing the body for activity and allowing for gradual recovery afterward reduces the risk of injury and promotes efficient muscle function.
Tip 4: Focus on Gradual Progression: Increasing activity intensity and duration incrementally allows the body to adapt and rebuild strength safely. Avoid pushing beyond comfortable limits.
Tip 5: Incorporate Sport-Specific Training: Integrating movements and drills relevant to the individual’s sport or activity facilitates a safe and effective return to participation.
Tip 6: Listen to Your Body: Paying attention to pain signals and respecting physical limitations is paramount. Pushing through pain can exacerbate injuries and hinder recovery.
Tip 7: Maintain Overall Health: Proper nutrition, hydration, and adequate sleep are essential for supporting the body’s healing processes and maximizing recovery potential.
By following these guidelines, individuals can optimize their recovery journey, reduce the risk of re-injury, and regain their desired level of activity. This proactive approach empowers individuals to take control of their rehabilitation and achieve optimal outcomes.
This information provides practical advice for maximizing recovery. The concluding section will summarize the key takeaways and emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach to restoring optimal physical function.
1. Sports-Specific Rehabilitation
Sports-specific rehabilitation represents a crucial component of restoring athletes to their pre-injury performance levels. It acknowledges that different sports and activities place unique demands on the body. A baseball pitcher, for example, requires significantly different shoulder mobility and strength compared to a marathon runner. Therefore, rehabilitation programs must be tailored to address the specific biomechanical and physiological requirements of each sport. This targeted approach enhances recovery outcomes and facilitates a safer return to play.
The connection between sports-specific rehabilitation and achieving optimal athletic conditioning is fundamental. Generic rehabilitation programs may address basic strength and mobility deficits, but they often fall short in preparing individuals for the complex movements and high stresses encountered in competitive environments. A volleyball player, for instance, requires explosive jumping and landing abilities, while a swimmer needs exceptional upper body endurance and flexibility. Sports-specific exercises, such as plyometrics for the volleyball player and interval training in the pool for the swimmer, bridge the gap between general rehabilitation and sport-specific readiness. This focused training not only restores physical function but also rebuilds confidence and reduces the risk of re-injury upon returning to competitive play.
In summary, sports-specific rehabilitation is integral to achieving optimal physical conditioning for athletic endeavors. By addressing the unique biomechanical and physiological demands of individual sports, these programs provide a tailored pathway back to competition. This specialized approach fosters a more efficient and effective return to play, minimizing re-injury risk and maximizing performance potential. Furthermore, incorporating sport-specific exercises and drills helps athletes regain confidence and psychological readiness, crucial elements for successful reintegration into competitive environments.
2. Functional Movement Restoration
Functional movement restoration is a cornerstone of rehabilitative care aimed at returning individuals to optimal physical condition for sports and activities. It emphasizes restoring the body’s ability to perform fundamental movements efficiently and without pain. This approach recognizes that limitations in foundational movement patterns can hinder performance and increase injury risk, even in the absence of acute pain.
- Core Stability and Control
A stable core is essential for efficient force transfer and coordinated movement. Weakness or instability in the core musculature can lead to compensatory movement patterns, increasing the risk of injury in the extremities. Restoring core strength and control is paramount for athletes in sports like golf or tennis, where rotational power and stability are critical.
- Balance and Proprioception
Balance and proprioceptionthe body’s awareness of its position in spaceare crucial for dynamic activities. Injuries can disrupt these systems, leading to instability and an increased risk of falls or re-injury. Rehabilitation programs incorporate exercises that challenge balance and proprioception, such as single-leg stances and unstable surface training, which are particularly relevant for sports like skiing or basketball.
- Flexibility and Range of Motion
Restrictions in flexibility and range of motion can limit performance and predispose individuals to injury. Tight muscles can alter biomechanics, leading to compensatory movements and increased stress on joints. Restoring optimal flexibility through targeted stretching and mobility exercises is essential for athletes in sports like gymnastics or swimming, which demand extensive range of motion.
- Neuromuscular Control and Coordination
Efficient movement requires precise coordination between the nervous system and the musculoskeletal system. Injury can disrupt this neuromuscular control, leading to inefficient movement patterns and decreased performance. Rehabilitation incorporates exercises that retrain neuromuscular pathways, improving movement quality and efficiency. This is crucial for activities requiring precise movements, like playing a musical instrument or throwing a javelin.
By addressing these fundamental movement components, rehabilitation programs ensure individuals develop a solid foundation for sport-specific training and a safe return to activity. Restoring functional movement not only enhances performance but also mitigates the risk of future injuries. This comprehensive approach, incorporating core stability, balance, flexibility, and neuromuscular control, ultimately enables individuals to achieve optimal physical readiness for their chosen sport or activity.
3. Injury Prevention Strategies
Injury prevention strategies are integral to achieving and maintaining optimal physical readiness for sports and recreational activities. They represent a proactive approach to mitigating risk and ensuring long-term participation. Integrating these strategies into rehabilitation programs and training regimens is essential for minimizing the likelihood of setbacks and promoting sustained athletic performance.
- Movement Screening and Assessment
Identifying potential movement deficiencies and biomechanical imbalances through comprehensive screening and assessment is crucial. These assessments can reveal underlying weaknesses or limitations that may predispose individuals to specific injuries. For example, a runner with excessive pronation may be at increased risk of developing plantar fasciitis or knee pain. Addressing these issues through corrective exercises and targeted interventions helps mitigate risk.
- Neuromuscular Training and Proprioception Enhancement
Neuromuscular training focuses on enhancing the communication between the nervous system and the musculoskeletal system. This includes exercises that improve proprioceptionthe body’s awareness of its position in spaceand reaction time. Plyometric drills and agility training, for example, challenge balance and coordination, promoting neuromuscular efficiency and reducing the risk of ankle sprains or ACL tears in sports like soccer or basketball.
- Flexibility and Mobility Optimization
Maintaining optimal flexibility and range of motion is essential for injury prevention. Restrictions in flexibility can alter biomechanics and increase stress on joints and surrounding tissues. Incorporating regular stretching and mobility exercises, such as yoga or dynamic warm-ups, can address these limitations. This is particularly important for athletes in sports like gymnastics or dance, where extreme ranges of motion are required.
- Strength and Conditioning Programs
Developing adequate strength and conditioning is fundamental to injury prevention. Strong muscles provide stability and support to joints, reducing their susceptibility to injury. Tailored strength and conditioning programs address sport-specific demands, ensuring athletes possess the necessary physical attributes to withstand the stresses of their chosen activity. A weightlifter, for instance, requires significantly different strength and power characteristics compared to a cyclist, and their training programs should reflect these differences.
By incorporating these injury prevention strategies into rehabilitation and training protocols, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of injury and promote long-term athletic participation. This proactive approach not only safeguards physical well-being but also optimizes performance by ensuring consistent training and minimizing disruptions due to injury. Ultimately, integrating injury prevention strategies is essential for achieving and maintaining optimal physical readiness for any sport or activity.
4. Performance Enhancement Techniques
Performance enhancement techniques represent a crucial aspect of achieving optimal physical readiness for athletic endeavors. Within the context of rehabilitative care, these techniques go beyond simply restoring pre-injury function; they aim to elevate performance beyond baseline levels. This focus on exceeding previous capabilities distinguishes performance enhancement from injury rehabilitation alone and highlights its importance in maximizing athletic potential.
- Biomechanical Analysis and Optimization
Analyzing movement patterns identifies areas for improvement in efficiency and power output. High-speed cameras and motion capture technology provide detailed insights into an athlete’s biomechanics. For a swimmer, this might reveal inefficiencies in stroke technique that limit propulsion. Corrective exercises and drills targeting these specific areas can lead to significant performance gains, such as increased speed and reduced energy expenditure.
- Strength and Power Development
Targeted strength and conditioning programs are essential for enhancing athletic performance. Plyometric exercises, Olympic lifts, and resistance training tailored to specific sports enhance power output and explosive strength. A basketball player, for example, benefits from increased vertical jump height and quicker lateral movements, enabling improved rebounding and defensive agility.
- Speed and Agility Training
Enhancing speed and agility is crucial for many sports. Cone drills, ladder exercises, and sprint training improve acceleration, deceleration, and change-of-direction abilities. A tennis player, for instance, requires rapid changes in direction to cover the court effectively. Enhanced agility enables quicker responses and improved court coverage.
- Sport-Specific Skill Development
Performance enhancement also involves refining sport-specific skills. For a golfer, this might involve analyzing swing mechanics and implementing drills to improve accuracy and distance. Repetitive practice of sport-specific movements, combined with feedback from coaches and therapists, leads to enhanced skill execution and improved overall performance.
Integrating these performance enhancement techniques into rehabilitation programs bridges the gap between restoring function and maximizing athletic potential. By addressing biomechanics, strength, speed, agility, and sport-specific skills, athletes can achieve optimal physical readiness and surpass pre-injury performance levels. This comprehensive approach ensures individuals not only return to their sport but excel in it, reaching new heights of athletic achievement.
5. Personalized Treatment Plans
Personalized treatment plans are fundamental to achieving optimal outcomes in restoring individuals to their desired level of activity. Recognizing that each individual presents with unique circumstances, including injury specifics, physical condition, training history, and personal goals, necessitates a tailored approach. Generic, one-size-fits-all programs often fall short in addressing these individual needs, highlighting the importance of personalized plans in maximizing recovery and performance.
- Individualized Assessment and Goal Setting
Thorough assessments encompassing medical history, physical examination, and performance testing provide a foundation for personalized plans. Clearly defined, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals, specific to the individual’s needs and aspirations, guide the rehabilitation process. For a recreational runner recovering from a knee injury, the goal might be to return to running a 5k race within three months, while a professional basketball player may aim to regain full court agility and jumping ability within six weeks. These individualized goals shape the treatment approach and provide motivation throughout the recovery journey.
- Tailored Exercise Prescription and Progression
Exercise programs are designed based on individual needs, addressing specific impairments and progressively challenging the individual as they recover. A swimmer with a shoulder impingement requires different exercises and progression compared to a cyclist with a hamstring strain. Tailoring exercises to the specific injury, sport, and individual’s physical capacity ensures optimal recovery and minimizes re-injury risk. Progression is carefully monitored and adjusted based on individual responses, ensuring a safe and effective return to activity.
- Integration of Modalities and Interventions
Personalized plans often incorporate various therapeutic modalities and interventions, such as manual therapy, electrotherapy, or dry needling, as needed. The selection and application of these modalities are based on individual responses and specific requirements. An athlete with chronic back pain may benefit from manual therapy and dry needling to address muscle tightness and trigger points, while an individual with acute ankle swelling may require electrotherapy to reduce inflammation. Integrating these modalities enhances the effectiveness of the overall treatment plan.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
Regular reassessments and ongoing communication between the individual and the healthcare team are essential. Monitoring progress and making adjustments to the plan as needed ensure it remains aligned with the individual’s evolving needs. If an athlete experiences unexpected pain or plateaus in their progress, the plan is modified accordingly to address these challenges. This dynamic approach optimizes outcomes and facilitates a smoother recovery process.
Personalized treatment plans, encompassing individualized assessment, tailored exercises, integrated modalities, and continuous monitoring, are crucial for achieving optimal outcomes in restoring individuals to their desired activity levels. This individualized approach acknowledges the unique nature of each individual’s circumstances and optimizes the rehabilitation process for maximal effectiveness. By addressing specific needs and goals, personalized plans empower individuals to regain their pre-injury function and return to their chosen activities with confidence and reduced risk of re-injury.
6. Evidence-Based Methodologies
Evidence-based methodologies are crucial for effective rehabilitation and achieving optimal physical readiness for sports and activities. This approach prioritizes treatments and interventions supported by rigorous scientific research and clinical trials, ensuring optimal outcomes and minimizing risks. Utilizing evidence-based practices enhances the credibility and effectiveness of rehabilitation programs, fostering trust and confidence in the recovery process.
- Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses synthesize data from multiple studies to provide comprehensive insights into the effectiveness of specific interventions. For example, a systematic review of studies on ACL reconstruction rehabilitation might reveal the most effective protocols for restoring knee stability and function. This evidence-based approach ensures rehabilitation programs incorporate the most effective techniques, optimizing recovery time and outcomes.
- Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
RCTs are considered the gold standard for evaluating treatment effectiveness. They involve randomly assigning participants to different treatment groups, allowing for comparison and minimizing bias. For instance, an RCT comparing two different types of exercise for shoulder impingement can determine which approach yields superior results in terms of pain relief and functional improvement. RCTs provide strong evidence to support treatment decisions.
- Clinical Practice Guidelines (CPGs)
CPGs offer evidence-based recommendations for managing specific conditions or injuries. Developed by expert panels, CPGs synthesize research findings and provide practical guidance for healthcare professionals. CPGs on concussion management, for example, outline best practices for assessment, treatment, and return-to-play decisions. Adhering to CPGs ensures consistent, high-quality care.
- Outcome Measures and Data Analysis
Utilizing standardized outcome measures allows for objective assessment of progress and treatment effectiveness. Tools like the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire or the Lower Extremity Functional Scale (LEFS) provide quantifiable data on functional limitations and improvements. Tracking these measures throughout the rehabilitation process provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of interventions and allows for adjustments as needed.
Integrating these evidence-based methodologies into rehabilitation programs ensures interventions are supported by scientific rigor and clinical data. This approach optimizes recovery outcomes, minimizes risks, and enhances the overall effectiveness of restoring individuals to their desired activity levels. By prioritizing treatments supported by evidence, rehabilitation professionals provide the highest standard of care, fostering confidence and maximizing the potential for successful outcomes in achieving “game shape.” This commitment to evidence-based practice underscores the importance of staying abreast of the latest research and incorporating best practices into rehabilitation protocols.
7. Collaborative Care Approach
A collaborative care approach is essential for achieving optimal outcomes in game shape physical therapy. This approach recognizes that restoring an athlete or active individual to peak performance often requires the expertise of multiple healthcare professionals working together. Physicians, physical therapists, athletic trainers, strength and conditioning coaches, nutritionists, and sports psychologists each bring unique perspectives and skills to the rehabilitation process. Effective communication and coordinated efforts among these professionals are crucial for maximizing recovery and ensuring a safe return to activity. For example, a football player recovering from an ACL tear might require the coordinated efforts of an orthopedic surgeon, physical therapist, athletic trainer, and strength coach. The surgeon addresses the surgical repair, the physical therapist guides the initial rehabilitation, the athletic trainer manages on-field training modifications, and the strength coach oversees the return to sport-specific conditioning.
The practical significance of a collaborative care approach lies in its ability to address the multifaceted nature of athletic rehabilitation. By integrating the expertise of various disciplines, this approach provides a comprehensive and holistic perspective on the individual’s needs. For instance, a collaborative team can address not only the physical aspects of an injury but also the psychological and nutritional factors influencing recovery. A gymnast recovering from a wrist fracture might benefit from a collaborative approach involving a physician to manage the fracture, a physical therapist to restore range of motion and strength, and a sports psychologist to address potential anxiety related to returning to competition. This integrated approach ensures all aspects of the athlete’s well-being are considered and addressed, optimizing the recovery process and facilitating a successful return to sport.
In summary, a collaborative care approach is paramount for maximizing outcomes in restoring athletes and active individuals to peak performance. The coordinated efforts of multiple healthcare professionals, working together with open communication and shared goals, ensure a comprehensive and individualized approach. This integrated perspective addresses the complex interplay of physical, psychological, and nutritional factors influencing athletic recovery and fosters a safe, efficient, and effective return to sport. Addressing potential challenges, such as communication barriers or differing treatment philosophies, is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of this collaborative approach. Effective teamwork and a shared commitment to the individual’s well-being are foundational to successful collaborative care and achieving optimal outcomes in game shape physical therapy.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the specialized field of restoring athletes and active individuals to peak physical condition.
Question 1: What distinguishes this specialized rehabilitation from traditional physical therapy?
This specialized approach emphasizes restoring function within the context of sport-specific demands. It goes beyond addressing basic strength and mobility deficits to incorporate sport-specific movements, drills, and performance enhancement techniques. Traditional physical therapy, while valuable for general musculoskeletal issues, may not fully address the unique biomechanical and physiological demands of athletic activity.
Question 2: How long does it typically take to regain pre-injury performance levels?
Recovery timelines vary significantly depending on the nature and severity of the injury, the individual’s healing capacity, and the specific demands of their sport or activity. A minor muscle strain might resolve within a few weeks, while a complex ligament injury could require several months of rehabilitation. Adherence to prescribed protocols and consistent effort are crucial for optimizing recovery time.
Question 3: What role does nutrition play in athletic recovery?
Proper nutrition is essential for tissue repair, inflammation management, and overall recovery. Adequate protein intake supports muscle rebuilding, while antioxidants and anti-inflammatory nutrients aid in healing. A balanced diet, tailored to the individual’s energy expenditure and specific needs, optimizes recovery outcomes.
Question 4: How can individuals minimize the risk of re-injury?
Addressing underlying biomechanical imbalances, adhering to proper training techniques, and incorporating injury prevention strategies are crucial for mitigating re-injury risk. Movement screening, neuromuscular training, flexibility optimization, and appropriate strength and conditioning programs play significant roles in reducing the likelihood of future injuries.
Question 5: When is it safe to return to sports or activity after an injury?
Return-to-play decisions are made in consultation with healthcare professionals and are based on objective criteria, such as restored strength, range of motion, and functional capacity. A gradual return to activity, with progressive increases in intensity and duration, minimizes re-injury risk and ensures a safe transition back to full participation. Rushing the return-to-play process can have detrimental consequences.
Question 6: What are the key elements of a successful rehabilitation program?
Successful programs incorporate a comprehensive approach, addressing not only the physical aspects of injury but also the psychological and social factors influencing recovery. Individualized treatment plans, evidence-based methodologies, collaborative care, and a focus on patient education and empowerment are essential components of successful rehabilitation.
Understanding these aspects of restoring athletic function can empower individuals to make informed decisions and actively participate in their recovery journey.
The next section provides concluding remarks on achieving and maintaining peak physical condition for optimal athletic performance.
Conclusion
Restoring athletes and active individuals to peak physical condition requires a comprehensive and individualized approach. This specialized field of rehabilitation encompasses various aspects, including diagnosis, treatment, and performance optimization. Key elements discussed include the importance of sports-specific rehabilitation, functional movement restoration, injury prevention strategies, performance enhancement techniques, personalized treatment plans, evidence-based methodologies, and a collaborative care approach. These components work synergistically to address the complex interplay of physical, psychological, and social factors influencing athletic recovery.
Achieving and maintaining optimal physical readiness for sports and recreational pursuits necessitates a commitment to proactive care, evidence-based practices, and ongoing collaboration among healthcare professionals. This dedication to comprehensive and individualized rehabilitation empowers individuals to not only recover from injuries but also to reach new heights of athletic performance. The future of this field lies in continued advancements in diagnostics, treatment modalities, and performance optimization techniques, promising even more effective and efficient strategies for restoring individuals to peak physical condition and maximizing athletic potential. Investing in these advancements is crucial for fostering a healthier and more active society, empowering individuals to pursue their chosen activities with confidence and reduced risk of injury.