
A bowling ball designed for “blackout” conditions, where minimal lane lighting is used, necessitates careful consideration of physical principles. These balls typically feature a reactive coverstock formulated to provide optimal grip on... Read more »

These three fundamental scientific disciplines explore the natural world at different levels of organization, from the subatomic particles studied in quantum physics to the complex ecosystems examined in ecology. For example, chemical... Read more »
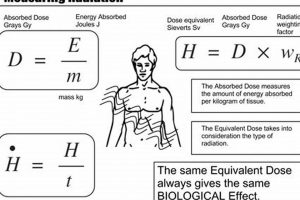
The study of matter and energy, including their interactions and behavior, forms the foundation for medical imaging techniques that use various forms of electromagnetic radiation or other energy sources to visualize internal... Read more »

A dedicated facility for the intertwined disciplines of physics and nanotechnology typically houses advanced laboratories and equipment. These spaces accommodate research into areas such as quantum phenomena, materials science at the atomic... Read more »

This advanced undergraduate course typically delves into a specialized area of physics, such as nuclear physics, particle physics, condensed matter physics, or astrophysics. The specific subject matter covered often varies by institution... Read more »

This course typically represents an introductory calculus-based electricity and magnetism course, often found within a university’s physics curriculum. It usually covers fundamental concepts such as electric fields, magnetic fields, electromagnetic induction, circuits,... Read more »

A compilation of formulas relevant to a typical second-semester, calculus-based physics course often designated as “Physics 212” provides students with a quick reference for key concepts. Such a resource typically covers topics... Read more »

A calculus-based introductory study of electricity, magnetism, optics, and modern physics typically follows an initial course covering mechanics and thermodynamics. Such studies often incorporate laboratory exercises designed to provide practical experience with... Read more »
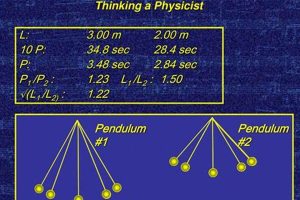
This introductory calculus-based course typically covers fundamental principles of mechanics, including motion, forces, energy, momentum, and rotational dynamics. Example topics often include kinematics, Newton’s laws, work and energy, conservation laws, and oscillations.... Read more »
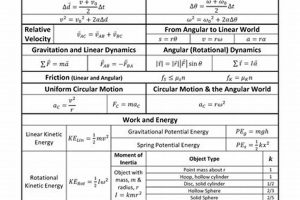
Introductory collegiate physics courses typically cover fundamental concepts in mechanics, electricity, magnetism, optics, and sometimes thermodynamics. These courses often serve as a foundation for further study in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics... Read more »


