A standardized framework guides healthcare professionals through a systematic assessment of a neonate’s health immediately after birth and in the following days. This structured approach typically covers areas such as vital signs (heart rate, respiratory rate, temperature), physical measurements (weight, length, head circumference), and a detailed examination of various body systems (cardiovascular, respiratory, neurological, etc.). A practical example would be a checklist ensuring consistent evaluation of reflexes, skin condition, and musculoskeletal structure. These frameworks can exist in various formats, including paper forms, electronic health record integrations, and mobile applications.
Standardized evaluations offer several crucial advantages. They promote thoroughness, reducing the risk of overlooking critical health indicators. Consistent data collection facilitates early identification of potential problems, enabling timely interventions. Documentation provided by these structured assessments aids communication among healthcare providers, contributing to a coordinated approach to neonatal care. Historically, such frameworks have evolved alongside advancements in medical knowledge and technology, reflecting a growing understanding of neonatal physiology and the development of more sophisticated diagnostic tools.
The following sections delve deeper into specific elements of neonatal assessment, exploring the rationale behind each component and highlighting best practices for accurate and effective examinations. Subsequent topics address common variations, documentation procedures, and the integration of this critical process into the broader context of postpartum care.
Tips for Effective Neonatal Assessments
Optimizing the assessment process enhances the quality of care provided to newborns. These practical tips offer guidance for conducting thorough and efficient examinations.
Tip 1: Ensure a Warm and Stable Environment: Maintaining a neutral thermal environment minimizes stress on the neonate and promotes accurate physiological measurements. A pre-warmed examination area and radiant warmer are essential.
Tip 2: Prioritize Observation: Before initiating hands-on examination, observe the infant’s posture, spontaneous movements, and respiratory patterns. This can offer valuable insights into neurological and respiratory function.
Tip 3: Systematic Approach: Following a consistent head-to-toe approach ensures all body systems are thoroughly evaluated and minimizes the risk of overlooking crucial details.
Tip 4: Gentle Handling: Neonates require delicate handling. Smooth, deliberate movements minimize discomfort and promote cooperation during the examination.
Tip 5: Auscultation Technique: Proper stethoscope placement and minimizing ambient noise are crucial for accurate assessment of heart and lung sounds.
Tip 6: Documentation Best Practices: Clear, concise, and accurate documentation is essential. Utilize standardized terminology and record all findings promptly.
Tip 7: Parental Involvement: Engage parents in the examination process. Explaining findings and addressing concerns promotes parental understanding and strengthens the patient-family relationship.
Tip 8: Continuing Education: Regular review of current guidelines and best practices ensures ongoing competency and promotes high-quality neonatal care.
Adherence to these recommendations contributes to early identification of potential health concerns and facilitates timely interventions, optimizing neonatal outcomes.
In conclusion, a systematic and comprehensive approach to neonatal assessment forms a cornerstone of effective newborn care.
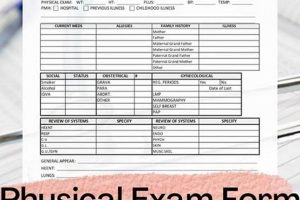
1. Standardized Format
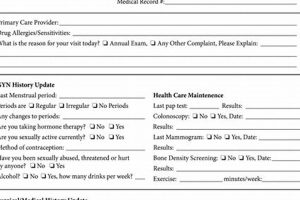
Standardized formats are fundamental to newborn physical exam templates, ensuring consistency and completeness in neonatal assessments. This structured approach facilitates thorough data collection, reduces the likelihood of overlooked details, and promotes effective communication among healthcare professionals. A standardized format provides a framework for capturing essential information about the newborn’s health status, enabling timely identification of potential concerns and facilitating appropriate interventions.
- Consistent Data Collection
Standardization ensures consistent data collection across all newborns, regardless of the examiner. This uniformity facilitates comparison of findings, supports accurate growth tracking, and allows for identification of deviations from established norms. For example, consistent documentation of heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature enables early detection of potential cardiovascular or respiratory issues. This uniformity is crucial for both individual patient care and broader epidemiological studies.
- Reduced Errors and Omissions
A structured format minimizes the risk of errors and omissions during the examination process. By providing a checklist of essential elements, it ensures that all key areas are assessed. This reduces the likelihood of overlooking critical findings, such as subtle signs of congenital anomalies or neurological abnormalities. A standardized template prompts examiners to evaluate specific reflexes, auscultate heart and lung sounds, and assess skin condition, reducing variability and improving diagnostic accuracy.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
Standardized formats promote clear communication among healthcare providers involved in the newborn’s care. Using a common framework ensures that all team members understand and interpret findings consistently. This shared understanding facilitates efficient collaboration, enabling coordinated decision-making and timely interventions. A standardized template facilitates seamless transfer of information between clinicians, specialists, and other healthcare professionals, optimizing continuity of care.
- Data Analysis and Research
Standardized data collection simplifies analysis and supports clinical research. Consistent data formats allow for aggregation and comparison across large populations, facilitating the identification of trends and risk factors. This aggregated data can inform evidence-based practice guidelines, contribute to the development of new diagnostic tools, and ultimately improve neonatal outcomes. Standardized templates facilitate data entry into electronic health records and research databases, enabling large-scale studies and advancements in neonatal care.
The benefits of a standardized format extend beyond individual patient care. Consistent data collection, reduced errors, enhanced communication, and facilitated research contribute to improvements in neonatal health outcomes across populations. The implementation of standardized newborn physical exam templates is crucial for ensuring high-quality, evidence-based care for all newborns.
2. Head-to-toe Assessment
The head-to-toe assessment represents a systematic approach within the newborn physical exam template, ensuring comprehensive evaluation of the neonate’s condition. This organized method provides a structured framework, minimizing the risk of overlooking crucial details and facilitating early identification of potential concerns. A thorough head-to-toe assessment provides a baseline for ongoing monitoring and informs appropriate interventions.
- Neurological Evaluation
Beginning with the head, the neurological examination assesses cranial nerve function, reflexes (such as sucking, rooting, and grasping), and muscle tone. Observation of spontaneous movements and posture provides insights into neurological integrity. For instance, assessing the Moro reflex involves observing the infant’s response to a simulated falling sensation. This component of the head-to-toe assessment helps identify potential neurological abnormalities early, enabling prompt intervention and management.
- Cardio-Respiratory Examination
Moving down the body, the cardio-respiratory examination focuses on heart and lung function. Auscultation of heart sounds helps identify potential murmurs or arrhythmias. Respiratory rate, rhythm, and effort are assessed, and lung sounds are evaluated for signs of distress or abnormalities. For example, observing retractions or nasal flaring could indicate respiratory distress. These findings within the head-to-toe assessment inform decisions regarding respiratory support and further diagnostic testing.
- Abdominal Assessment
The abdominal assessment involves palpation of the abdomen to assess organ size and identify any masses or abnormalities. Bowel sounds are auscultated, and the umbilical cord is examined for signs of infection or other complications. For example, a distended abdomen might warrant further investigation. This part of the head-to-toe evaluation helps detect gastrointestinal issues or congenital anomalies requiring immediate attention.
- Extremity and Skin Examination
The examination of extremities involves assessing range of motion, evaluating for any deformities or asymmetry, and checking for proper hip alignment. Skin examination assesses color, texture, and the presence of any birthmarks or rashes. For instance, examining the creases on the palms can provide clues about certain genetic conditions. This final stage of the head-to-toe assessment contributes to the overall picture of the newborn’s health and can identify potential musculoskeletal or dermatological concerns.
The head-to-toe assessment, a cornerstone of the newborn physical exam template, ensures a comprehensive and systematic evaluation of the neonate. This structured approach, combined with thorough documentation, provides a crucial foundation for individualized care planning and ongoing monitoring of the newborn’s health and development. By addressing each component meticulously, healthcare professionals can effectively identify potential concerns and initiate appropriate interventions to ensure optimal outcomes.
3. Vital Signs Monitoring
Vital signs monitoring forms an integral component of the newborn physical exam template, providing crucial physiological data that informs immediate care decisions and ongoing assessment of neonatal well-being. Accurate measurement and interpretation of vital signs are essential for detecting potential abnormalities and initiating timely interventions.
- Heart Rate
Heart rate assessment in newborns involves auscultation using a stethoscope or electronic monitoring. Normal heart rate ranges typically fall between 110 and 160 beats per minute. Variations outside this range may indicate underlying cardiac conditions, respiratory distress, or other systemic issues. Accurate heart rate documentation within the newborn physical exam template allows for trending over time and contributes to comprehensive cardiovascular assessment.
- Respiratory Rate
Respiratory rate is assessed by observing chest movements or utilizing specialized monitoring equipment. Normal respiratory rates in newborns typically range between 30 and 60 breaths per minute. Rates outside this range, coupled with signs like retractions or nasal flaring, could indicate respiratory distress, requiring prompt intervention. Careful documentation of respiratory rate within the template facilitates early identification of respiratory compromise.
- Temperature
Temperature measurement is crucial for assessing thermoregulation in newborns. Normal axillary temperature typically ranges between 36.5C and 37.5C (97.7F and 99.5F). Fluctuations outside this range can indicate infection, environmental stress, or metabolic disturbances. Accurate temperature documentation within the newborn physical exam template contributes to identifying and managing thermoregulatory instability.
- Blood Pressure
While not routinely measured in all newborns, blood pressure assessment provides valuable information about cardiovascular function. Normal blood pressure values vary with gestational age and weight. Hypotension may indicate hypovolemia or cardiac dysfunction. Documentation of blood pressure, when indicated, contributes to a complete cardiovascular assessment within the newborn physical exam template.
Systematic monitoring and documentation of these vital signs within the newborn physical exam template provide critical insights into the physiological status of the neonate. These measurements, combined with other components of the examination, contribute to a comprehensive assessment, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding immediate care and ongoing management. Deviations from normal ranges often warrant further investigation and may prompt interventions to stabilize the newborn’s condition and optimize outcomes.
4. Physical Measurements
Physical measurements constitute a fundamental component of the newborn physical exam template, providing quantifiable data that reflects growth, development, and overall well-being. These objective measurements offer crucial insights into the neonate’s physical status, aiding in the identification of potential deviations from established norms and informing appropriate interventions.
- Weight
Weight assessment provides a baseline measure of the newborn’s size and is crucial for monitoring growth trajectory. Recorded in grams or kilograms, birth weight is compared against gestational age standards to assess appropriateness. Low birth weight may indicate intrauterine growth restriction or prematurity, while macrosomia (high birth weight) can be associated with maternal diabetes. Serial weight measurements documented within the newborn physical exam template enable tracking of postnatal weight gain and identification of potential feeding difficulties or other underlying health issues.
- Length
Length measurement, typically recorded in centimeters, provides an additional indicator of growth and is used in conjunction with weight to assess proportionality. Disproportionate length and weight measurements can signal underlying skeletal dysplasias or other growth abnormalities. Accurate length documentation within the template contributes to a comprehensive assessment of physical development and facilitates early identification of potential concerns.
- Head Circumference
Head circumference measurement, taken around the largest part of the head, reflects brain growth and development. Measured in centimeters, head circumference is compared against gestational age norms to assess appropriateness. Microcephaly (small head circumference) can be associated with congenital infections or genetic syndromes, while macrocephaly (large head circumference) may indicate hydrocephalus or other conditions. Serial head circumference measurements documented in the newborn physical exam template provide valuable data for monitoring brain growth and detecting potential abnormalities.
- Chest Circumference
While less routinely performed, chest circumference measurement can provide additional information about thoracic development and proportionality. Measured at the nipple line, chest circumference is typically smaller than head circumference in newborns. Significant discrepancies between these measurements may warrant further investigation for potential thoracic abnormalities. Documentation of chest circumference within the newborn physical exam template, when indicated, contributes to a comprehensive assessment of physical proportions.
These physical measurements, recorded within the structured framework of the newborn physical exam template, offer valuable objective data for assessing neonatal growth, development, and overall well-being. These measurements provide a baseline for ongoing monitoring, facilitate early identification of potential deviations from normal ranges, and contribute to informed decision-making regarding appropriate interventions and follow-up care. The integration of these measurements into the template ensures comprehensive assessment and promotes optimal neonatal outcomes.
5. Reflex Evaluation
Reflex evaluation constitutes a critical component of the newborn physical exam template, providing valuable insights into the integrity of the neonatal neurological system. Assessing these involuntary responses offers a window into the development and function of the central nervous system, enabling early identification of potential neurological impairments or developmental delays. A systematic evaluation of primitive reflexes is essential for comprehensive neonatal assessment.
- Moro Reflex
The Moro reflex, elicited by a sudden change in head position, involves symmetric abduction and extension of the arms followed by adduction and flexion. Absence or asymmetry of this reflex can indicate brachial plexus injury, clavicular fracture, or other neurological deficits. Its presence and symmetry are crucial indicators of normal neurological development within the newborn physical exam template.
- Rooting Reflex
The rooting reflex, triggered by stroking the cheek, involves the newborn turning its head towards the stimulus and opening its mouth in preparation for feeding. This reflex plays a vital role in breastfeeding success. Its absence or weakness may indicate neurological impairment and can inform feeding interventions documented within the newborn physical exam template.
- Sucking Reflex
The sucking reflex, elicited by placing a finger or nipple in the newborn’s mouth, involves rhythmic sucking motions. This reflex, essential for feeding, is assessed for strength and coordination. Difficulties with sucking can indicate neurological issues or prematurity, impacting nutritional intake. Its evaluation is crucial for informing feeding strategies within the newborn physical exam template.
- Grasp Reflex
The grasp reflex, triggered by placing a finger in the newborn’s palm, involves flexion of the fingers and grasping of the finger. Absence or asymmetry of this reflex may suggest neurological dysfunction. Its presence and strength are indicators of normal neurological development, documented within the newborn physical exam template.
Systematic evaluation of these and other primitive reflexes within the newborn physical exam template provides critical information about the integrity of the neonatal neurological system. Documentation of reflex responses contributes to early identification of potential neurological impairments, facilitates appropriate referrals for further evaluation, and informs individualized care planning to optimize developmental outcomes.
6. Anomaly Screening
Anomaly screening represents a critical component of the newborn physical exam template, focusing on the early detection of structural or functional abnormalities. Systematic screening during the immediate postnatal period allows for prompt identification of congenital conditions, facilitating timely intervention and management to mitigate potential long-term consequences. This proactive approach is essential for optimizing neonatal outcomes and ensuring appropriate follow-up care.
- Cardiac Anomalies
Cardiac anomaly screening involves auscultation of the heart, assessing for murmurs, abnormal heart sounds, or irregular rhythms. Detection of potential cardiac defects, such as ventricular septal defects or patent ductus arteriosus, necessitates further investigation through echocardiography and consultation with pediatric cardiology. Early identification within the newborn physical exam template facilitates prompt management and minimizes potential complications.
- Craniofacial Anomalies
Craniofacial anomaly screening includes careful examination of the head, face, and neck, assessing for dysmorphic features, such as cleft lip or palate, micrognathia (small jaw), or unusual ear positioning. Early recognition of these anomalies within the newborn physical exam template allows for timely referral to specialists, such as craniofacial surgeons or geneticists, for comprehensive evaluation and management.
- Musculoskeletal Anomalies
Musculoskeletal anomaly screening focuses on evaluating limb symmetry, range of motion, and joint stability. Assessment for abnormalities, such as hip dysplasia or clubfoot, requires specialized examination techniques, such as the Ortolani and Barlow maneuvers for hip instability. Early detection within the newborn physical exam template facilitates prompt referral to orthopedic specialists for intervention and management.
- Abdominal Anomalies
Abdominal anomaly screening involves palpation of the abdomen, assessing for organomegaly (enlarged organs), masses, or other abnormalities. Detection of potential issues, such as abdominal wall defects or intestinal malrotation, requires further investigation through imaging studies and consultation with pediatric surgeons. Incorporation of this screening within the newborn physical exam template allows for timely diagnosis and intervention.
Thorough anomaly screening within the newborn physical exam template provides a crucial safety net for early detection of congenital conditions. Systematic evaluation and documentation of findings facilitate timely referral to specialists, ensuring appropriate management and minimizing potential long-term morbidity. This proactive approach to anomaly detection significantly contributes to optimizing neonatal health outcomes and ensuring comprehensive care for newborns with identified conditions.
7. Documentation Guidelines
Documentation guidelines play a crucial role in the effective utilization of a newborn physical exam template. Comprehensive and accurate documentation ensures that the examination findings are clearly communicated, facilitates continuity of care, and provides a valuable record for future reference. Adherence to established documentation guidelines contributes significantly to the quality and safety of neonatal care. For instance, precise documentation of a heart murmur, including its location, intensity, and timing, allows for consistent assessment by other healthcare providers and facilitates appropriate follow-up.
Specific documentation guidelines often accompany newborn physical exam templates, outlining the required elements and preferred terminology. These guidelines typically address the recording of vital signs, physical measurements, detailed findings from the head-to-toe assessment, and any identified anomalies. Standardized terminology ensures clarity and minimizes ambiguity in interpretation. For example, documenting the presence of a “sacral dimple” with precise location and measurements provides valuable information for assessing potential spinal dysraphism. Furthermore, clear documentation of parental concerns and communicated information contributes to a comprehensive patient record. This thorough approach fosters collaboration among healthcare providers and strengthens patient-family communication.
Effective documentation practices associated with the newborn physical exam template contribute to improved communication, enhanced patient safety, and informed decision-making. Challenges can include time constraints and variations in clinical practice. However, prioritizing accurate and comprehensive documentation, utilizing standardized terminology, and adhering to established guidelines ultimately optimize the value of the newborn physical exam and enhance the quality of neonatal care. This meticulous approach to documentation contributes to a comprehensive record of the newborn’s health, facilitating early identification of potential concerns and ensuring appropriate follow-up care. Ultimately, adherence to documentation guidelines strengthens the effectiveness of the newborn physical exam template as a tool for promoting optimal neonatal outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the utilization and interpretation of newborn physical exam templates.
Question 1: What is the primary purpose of a newborn physical exam template?
Standardized templates ensure comprehensive and systematic assessment of neonatal health, facilitating early identification of potential concerns and guiding appropriate interventions.
Question 2: Who typically utilizes these templates?
Healthcare professionals, including physicians, nurses, and midwives, utilize these templates during the initial assessment and ongoing monitoring of newborns.
Question 3: How do these templates contribute to patient safety?
Standardized assessments minimize the risk of overlooking critical findings, promoting early detection of potential complications and enabling timely interventions. Consistent documentation supports clear communication among healthcare providers.
Question 4: Are these templates universally standardized?
While core elements remain consistent, some variations may exist based on institutional policies, specific clinical settings, or regional guidelines. However, adherence to core principles of comprehensive neonatal assessment remains paramount.
Question 5: How are these templates adapted for premature infants?
Templates often incorporate specific considerations for premature infants, addressing unique physiological characteristics and potential complications associated with prematurity. Gestational age adjustments and specialized assessments for respiratory function and neurological development are often integrated.
Question 6: How does documentation within the template contribute to continuity of care?
Thorough documentation facilitates seamless communication among healthcare providers, ensuring consistent management and follow-up. Detailed records support informed decision-making throughout the newborn’s care trajectory.
Understanding the purpose, utilization, and benefits of newborn physical exam templates contributes to optimized neonatal assessment and improved patient outcomes.
The subsequent section provides further detail on specific components of the newborn physical exam.
Conclusion
Standardized newborn physical exam templates provide a crucial framework for comprehensive neonatal assessment, enabling healthcare professionals to systematically evaluate vital signs, physical characteristics, and neurological responses. These structured evaluations facilitate early identification of potential health concerns, ranging from minor anomalies to critical congenital conditions. Thorough documentation within these templates promotes effective communication among healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care and informed decision-making. From initial assessment to ongoing monitoring, adherence to standardized procedures contributes significantly to optimized neonatal outcomes.
The ongoing refinement and widespread implementation of standardized newborn physical exam templates represent a continued commitment to enhancing neonatal care. These structured approaches offer a valuable tool for promoting early detection, timely intervention, and ultimately, improved health outcomes for newborns. Continued emphasis on standardized assessment and meticulous documentation reinforces the dedication to providing comprehensive and high-quality care for this vulnerable population.